Name: Date: ______ Per: ____ Teacher:
advertisement

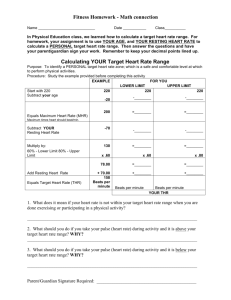
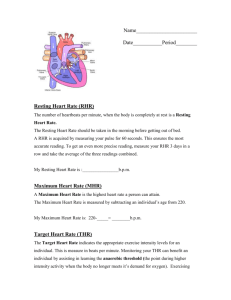
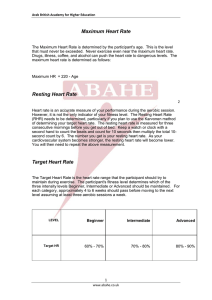
A. Name: _____________________________ Per: ______ Teacher: __________________ Vernon Hills High School Polar Heart Rate Monitors nd 2 Semester 2009 1 Polar Heart Rate Monitors Why Monitor Heart Rate? Heart rate monitors allow you to: o exercise at a constant rate to obtain your maximum health benefits o work out at varying intensity levels o safely monitor your heart rate o Grading: Eliminates subjectivity o Workout: Ensure quality workout based upon current research recommended guidelines o Individual Medical Conditions: Teacher can make changes to your daily requirements should you have a medical condition. Please let your teacher know. Structures and Functions of the Heart When the heart contracts and blood flows to the rest of the body, it does so at a certain pressure. Factors Affecting Heart Functioning: Body position – standing vs. sitting Fitness level – fit people have a lower working and resting heart rate Age – see target range chart below Gender – women typically have 5-7 beats more per minute Mood – relaxed vs. stressed Temperature – higher temp = higher heart rate Stimulants – smoking, caffeine, etc. raise heart rate Depressants – alcohol, prescription drugs, etc. lower heart rate Surgeon’s General’s Report People who are usually inactive can improve their health and well-being by becoming even moderately active on a regular basis Measuring Heart Rate without Monitors For use when monitors aren’t available: Teacher Demonstration with class Cardiovascular Workout Workout that primarily trains your heart and lungs Heart Rate The number of beats of the heart, normally expressed as beats / min or bpm 2 Resting Heart Rate (RHR) This is a person's heart rate at rest. The best time to find out your resting heart rate is in the morning, after a good night's sleep, and before you get out of bed. The heart beats about 50 to 80 beat / minute (bpm) when at rest. Resting heart rate usually rises with age Lower in physically fit people. Olympic athletes may have a resting heart rate in the mid 30’s!!!!!!! Do you know your resting heart rate? Take your resting heart rate three different mornings and enter HR’s in the boxes Maximum Heart Rate (MHR) Your maximum heart rate represents your heart’s highest possible beating rate. Calculated by the following equation: 220-age Calculate your Maximum Heart Rate: 220- ______= ______bpm Training Heart Rate Zones (Tz) – Between 60%-85% o A training heart rate zone is the heart rate zone within which the heart should beat to achieve the desired cardiovascular benefits. The most common way to calculate your training heart rate zone (Tz) is by finding percentages of you maximum heart rate (MHR). See chart below for target heart rate zones. Example: Step 1.) 220-14= 206 (MHR) Step 2.) 60% of 206 = 142 Calculation 206 x 0.6 ~125bpm at 60% effort of Max Calculate your Training Heart Rate for 75% (using your MHR from above) 3 Definitions and key concepts: Aerobic: Exercising at a level of strain in which a person is sweating and is no more than slightly out of breath. This level of exercise can be sustained for long periods of time. Anaerobic: Exercise at a heavy level of strain in which a person faces fatigue quickly. Typically, this exercise intensity can only be sustained for short periods of time TRAINING HEART RATE ZONES EXERCISE ZONES AGE B E A T S P E R M I N U T E 100% 10 15 20 25 30 35 40 45 50 55 60 210 205 200 195 190 185 180 175 170 165 160 VO2 Max (Maximum Effort) – Can’t talk to friend 90% 189 185 180 176 171 167 162 158 153 149 144 Anaerobic (Hardcore Training) – Can’t talk to friend 80% 168 164 160 156 152 148 144 140 136 132 128 Aerobic (Cardio Training / Endurance) – Can hold conversation 70% 147 144 140 137 133 130 126 123 119 116 112 Weight Control (Fitness / Fat Burn) – Can hold conversation 60% 126 123 120 117 114 111 108 105 102 99 96 Moderate (Warm-up / Cool-down) – Easy to hold conversation 50% 105 103 100 98 95 93 90 88 85 83 80 4 Polar Heart Rate Individual Heart Rate Curve Report Use the Individual Heart Rate Curve Report to answer the following questions. The numbers on this page correspond with the circled numbers on the report. 1. These numbers are considered to be “in your training / target zone.” What is the range for each: Low end of training zone (Tz):_________ High end of training zone (Tz):_________ 2. List a few reasons why the graph does not show a reading? ______________________ _____________________ ______________________ _____________________ ______________________ _____________________ 3. What was the average Heart Rate (HR) of this student?__________________________ 4. What activity is graphed on the chart?________________________________________ 5. List a few reasons why the graph does not show a reading? ______________________ _____________________ ______________________ _____________________ 6. What does this graph symbolize? ___________________________________________ ______________________________________________________________________ 7. How long was this student: Above Tz: ____min. _____% In Tz: ____min. _____% Below Tz: ____min. _____% 8. How long did this student workout? ________________________________________ 5 6