Industrialization
advertisement

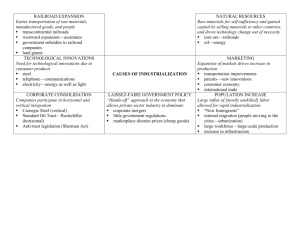
Industrialization 1865-1901 Events of the Indian Wars Sand Creek Massacre • 1864: The Army persuaded a group of Cheyenne to stop raiding farms and return to their Colorado reservation. • Then army troops attacked, killing about 150 people, and burned the camp. • Congress condemned the actions but did not punish the commander. Battle of the Little Bighorn • The Sioux responded to government relocation by joining other tribes near the Little Bighorn River. • Led by Sitting Bull, they slaughtered General Armstrong Custer’s smaller U.S. force. Wounded Knee Massacre • Army troops captured Sitting Bull’s followers and took them to a camp at Wounded Knee Creek. • Fighting began, and the soldiers slaughtered 300 Native American men, women, and children. • The massacre shocked Americans and broke Native American resistance. Immigration: Why the United States? Promise of a better life European immigrants came to America because of rising population. Chinese and Japanese immigrants came to America because of transcontinental railroad in the West. Where did immigrants travel from? China and Japan Europe 1870-1920- Italian, Irish, German Transcontinental Railroad Pacific Railway Act of 1862 – U.S. Government hired Union Pacific and Central Pacific Railway Company to extend railways across the United States. Central Pacific – Started in Sacramento, CA Union Pacific – Started in Omaha, NE The 2 railroad companies met in Promontory, Utah to drive the “Golden Spike” on May 10, 1869 Promontory, Utah May 10, 1869 Who did the Railroad Impact? Native Americans (called it the Iron Horse) Helped Westward expansion Solve problems of over population Hurt the farmers economically because of the higher costs for farmers They made deals with wealthy businessmen (became corrupt) Became crucial to the U.S. economy Mass transportation of goods Dealing With Corruption Interstate Commerce Act of 1887 – put in place for Govt. to supervise railroad activities Led to more financial problems Railroads were forced out of business Led to the Panic of 1893: caused by railroad overbuilding and shaky railroad financing which set off a series of bank failures. U.S. goes through a serious depression This caused the Large Firms to start buying up the railways, which paved the way for Big Businesses Essential Questions 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. Why did many immigrants come to the U.S.? Explain the events of the Panic of 1893. Discuss 3 groups of people that were directly impacted by the railroads. Describe the Pacific Railway Act. What were the two companies trying to construct? From where did each company start? Describe the Interstate Commerce Act. What did this cause large firms to do? Why? Industrialization Factors Unskilled and semi-skilled labor in abundance New, talented entrepreneurs Oil Wealth Inventions New technology that allows mass production Bessemer Process Railroads Changes in business strategy Vertical Integration & Horizontal Consolidation Social Darwinism The Power of Steel Bessemer Process: made it easier and cheaper to produce steel Contributed most to the growth of American industry Improved railroad industry and led to development of skyscrapers Railroads: after the Civil War, many consolidated, or merged together standard gauge – all the same size tracks Steel rails would replace iron rails New signals prevented accidents Twin tracks allowed for simultaneous opposite direction travel A Problem With Time Different times in different places caused problems Towns set time according to the sun 1883, the govt. established a system of standard time: Divided the country into four time zones Railroads increased western settlement Stimulated urban growth and growth of other industries Led to increased urbanization: mass movement to the cities Communications Telegraph invented by Samuel Morse (1844) Replaced the Pony Express Grew along with railroads Telephone invented by Alexander Graham Bell (1876) By 1880’s over 300,000 telephones were used in business Would be early 1900’s before homes had them (too expensive) Essential Questions #2 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. Define Bessemer Process, laissez-faire, Social Darwinsim, John D. Rockefeller, Andrew Carnegie, Cornelius Vanderbilt Describe 4 effects that steel had on railroads. Who invented the telegraph? Explain its significance. Who invented the telephone? Explain its impact on businesses and homes. Why did railroads have a problem with time? What did they do to solve this problem? Define urbanization. How did the railroads impact urbanization? Explain. Other Inventions Other inventions affected other industries Refrigerated car = meatpacking industry Pullman Car (sleeping, dining, and passenger railroad cars) Westinghouse Air Brake = safer trains Increased passenger safety/comfort Allowed faster and longer trains Edison light bulb (1879) = electrical transformers changed the lay out of cities other inventions of the mid-1800s to 1900 elevator, typewriter, and electric streetcars Pullman Cars A Pullman porter A “Company Town”: Pullman, IL Mass Marketing Newspapers were cheap to produce (penny press) Advertising increased because it reached more people Brand names and packaging labels promoted goods Occurred in magazines, newspapers, and on billboards Special catalogs were distributed to rural areas Department stores gave people choice from a variety of items Offered credit, free delivery, and a marked fixed price Items could be bought in bulk and inexpensive items tempted customers to buy things they didn’t really need. Rise of Big Business Many became wealthy because of American industry Business leaders supported laissez-faire capitalism No government intervention in the economy Ideas of good work ethic, individualism and self-reliance Led to belief economy would prosper best under competition allowed in a free market/enterprise Entrepreneurs believed govt regulation would reduce individuals’ prosperity and self-reliance Critics countered with proposals of socialism and communism: Believed people who own means of production take advantage of workers Called for everyone in community to own property and means of production The Corporations After Civil War, business expanded and consolidated Formed corporations – Industries found sources of capital to help them expand- 1) Banks 2) Selling stock to the people Corporations sought ways to get ahead of competitors Some formed trusts: group of companies merge their stock together to a common board of trustees Trusts limit overproduction by reducing competition which leads to monopolies: gain control of the market for a product. Social Darwinism Many business leader supported Social Darwinism: applied “survival of the fittest” to business Believed free market would determine who would produce goods and services Also supported Laissez-faire economics Small businesses can not compete Would often be bought out by larger businesses– This is how trusts and monopolies would develop Eventually, a “trust buster” is needed Essential Questions #3 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. Define Trusts and Monopolies. How can they have a negative impact on economics? Explain the concept of Social Darwinism. What is laissez-faire economics? Explain the concepts of socialism and communism. List and Explain 3 key developments in mass marketing. List 4 key inventions that we discussed today, and explain their impact on the world. Explain how small businesses were effected by the concept of Social Darwinism. Industrial Giants Andrew Carnegie: invested money in steel Pioneered a new way of organization – Vertical integration: provided the materials and services required in his enterprise All were separate industries each critical in making steel John D. Rockefeller: formed the Standard Oil Company Believed competition was wasteful and destructive Andrew Carnegie Standard Oil Co. Rockefeller pioneered a form of organization called horizontal integration: purchased other industries that all made the same type of product… in this instance oil companies Allowed him to control production and prices of oil Eventually he would turn to vertical integration as well By expanding vertically and horizontally, Standard Oil gained a monopoly on the oil industry Vanderbilt, Westinghouse and Pullman All railroad giants Gospel of Wealth Philanthropy: donate money for a cause. Carnegie believed in the Gospel of Wealth: rich had right to earn wealth and the responsibility to spend it properly. Many were philanthropists: not afraid to throw their money around Not everyone shared in his philosophy Many took advantage of their wealth J.P. Morgan: made his money in the banking industry Responsible for creation of General Electric “The Protectors of Our Industries” Regulating the Trusts Sherman Anti-Trust Act: allows the government to investigate and pursue trusts, companies and organizations suspected of corruption. First attempt to limit trusts Purpose is to protect competition and secure a competitive free-market Serves as the basis for anti-trust legislation today Named after Senator John Sherman of Ohio The Changing American Labor Force The Reorganization of Work Frederick W. Taylor The Principles of Scientific Management (1911) The Reorganization of Work The Assembly Line Vertical and Horizontal Integration Standard Oil Co. Regulating the Trusts 1877 Munn. v. IL 1886 Wabash, St. Louis & Pacific Railroad Company v. IL 1890 Sherman Antitrust Act in “restraint of trade” “rule of reason” loophole 1895 US v. E. C. Knight Co. “On Wealth” $ The Anglo-Saxon race Andrew Carnegie is superior. $ “Gospel of Wealth” (1901). $ Inequality is inevitable and good. $ Wealthy should act as “trustees” for their “poorer brethren.” Cornelius [“Commodore”] Vanderbilt Can’t I do what I want with my money? William Vanderbilt $ The public be damned! $ What do I care about the law? H’aint I got the power? New Financial Businessman The Broker: J. Pierpont Morgan New Business Culture: “The American Dream?” Protestant (Puritan) “Work Ethic” Horatio Alger [100+ novels] Is the idea of the “self-made man” a MYTH?? The Protectors of Our Industries The Changing American Labor Force Child Labor Child Labor Management vs. Labor “Tools” of Management “scabs” Pinkertons lockout blacklisting yellow-dog contracts “Tools” of Labor Collective Bargaining informational picketing organized strikes A Striker Confronts a SCAB! Knights of Labor Terence V. Powderly An injury to one is the concern of all! ù Goals of the Knights of Labor Eight-hour workday. ù Workers’ cooperatives. ù Worker-owned factories. ù Abolition of child and prison labor. ù Increased circulation of greenbacks. ù Equal pay for men and women. ù Safety codes in the workplace. ù Prohibition of contract foreign labor. ù Abolition of the National Bank. Labor Unrest: 1870-1900 The Great Railroad Strike of 1877 Haymarket Riot (1886) McCormick Harvesting Machine Co. Haymarket Martyrs The American Federation of Labor: 1886 Samuel Gompers How the AF of L Would Help the Workers ù Catered to the skilled worker. ù Represented workers in matters of national legislation. ù Maintained a national strike fund. ù Evangelized the cause of unionism. ù Prevented disputes among the many craft unions. ù Mediated disputes between management and labor. ù Pushed for closed shops. Homestead Steel Strike (1892) Homestead Steel Works The Amalgamated Association of Iron & Steel Workers A “Company Town”: Pullman, IL Pullman Cars A Pullman porter The Pullman Strike of 1894 The Pullman Strike of 1894 Government by injunction! The Socialists Eugene V. Debs International Workers of the World (“Wobblies”) “Big Bill” Haywood of the IWW Violence was justified to overthrow capitalism. IWW Mother Jones: “The Miner’s Angel” Mary Harris. Organizer for the United Mine Workers. Founded the Social Democratic Party in 1898. One of the founding members of the I. W. W. in 1905. The “Formula” unions + violence + strikes + socialists + immigrants = anarchists Labor Union Membership The Rise & Decline of Organized Labor Discussion Questions What were the cost and benefits of the industrial transformation of the Post- Civil War era? Was the growing class division of the time a threat to American democracy? Why or why not?