PowerPoint 簡報
advertisement
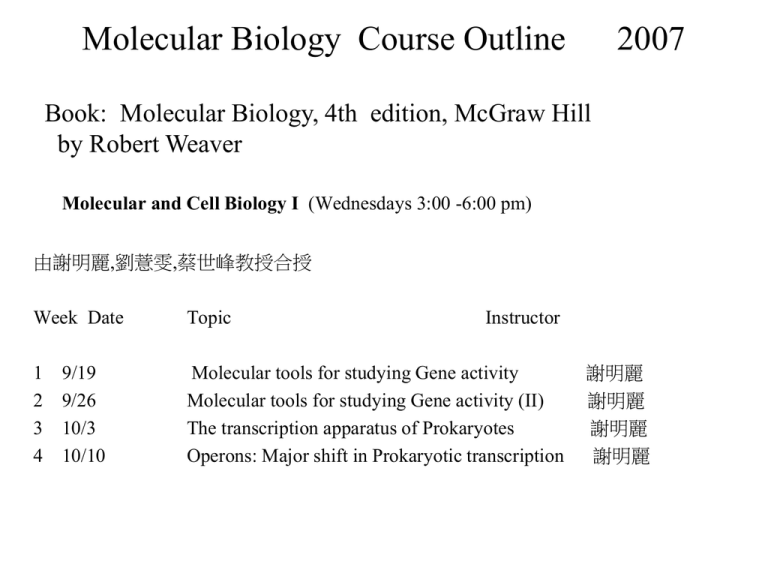
Molecular Biology Course Outline 2007 Book: Molecular Biology, 4th edition, McGraw Hill by Robert Weaver Molecular and Cell Biology I (Wednesdays 3:00 -6:00 pm) 由謝明麗,劉薏雯,蔡世峰教授合授 Week Date Topic Instructor 1 9/19 2 9/26 3 10/3 4 10/10 Molecular tools for studying Gene activity Molecular tools for studying Gene activity (II) The transcription apparatus of Prokaryotes Operons: Major shift in Prokaryotic transcription 謝明麗 謝明麗 謝明麗 謝明麗 • • • • • • • • • • • • • 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 10/17 10/24 10/31 11/7 11/14 11/21 11/28 12/5 12/12 12/19 12/26 1/2 1/9 Eukaryotic RNA polymerases and their promoters General transcription factors in Eukaryotes Transcription activators in Eukaryotes Message RNA processing: Splicing Message RNA processing: Capping and polyadenylation Mid-term The Human Genome Project and the HapMap Project Genomic technology, microarray, and proteomics Cancer genomics, microbial genomics, and pharmacogenomics Model organisms and systems biology 特別演講 特別演講 Overview 劉薏雯 劉薏雯 劉薏雯 劉薏雯 劉薏雯 劉薏雯 蔡世峰 蔡世峰 蔡世峰 喻秋華 Molecular Tools for Studying Genes and Gene Activity Molecular Separation Gel Electrophoresis • Gel electrophoresis is used to separate different species of: – Nucleic acid – Protein 5-5 DNA Gel Electrophoresis • Melted agarose is poured into a form equipped with removable comb • Comb “teeth” form slots in the solidified agarose • DNA samples are placed in the slots • An electric current is run through the gel at a neutral pH 5-6 DNA Separation by Agarose Gel Electrophoresis • DNA is negatively charged due to phosphates in its backbone and moves to anode, the positive pole – Small DNA pieces have little frictional drag so move rapidly – Large DNAs have more frictional drag so their mobility is slower – Result distributes DNA according to size • Largest near the top • Smallest near the bottom • DNA is stained with fluorescent dye 5-7 DNA Size Estimation • Comparison with standards permits size estimation • Mobility of fragments are plotted v. log of molecular weight (or number of base pairs) • Electrophoresis of unknown DNA in parallel with standard fragments permits size estimation • Same principles apply to RNA separation 5-8 Electrophoresis of Large DNA • Special techniques are required for DNA fragments larger than about 1 kilobases • Instead of constant current, alternate long pulses of current in forward direction with shorter pulses in either opposite or sideways direction • Technique is called pulsed-field gel electrophoresis (PFGE) 5-9 Protein Gel Electrophoresis • Separation of proteins is done using a gel made of polyacrylamide (polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis = PAGE) – Treat proteins to denature subunits with detergent such as SDS • SDS coats polypeptides with negative charges so all move to anode • Masks natural charges of protein subunits so all move relative to mass not charge – As with DNA smaller proteins move faster toward the anode 5-10 Summary • DNAs, RNAs, and proteins of various masses can be separated by gel electrophoresis • Most common gel used in nucleic acid electrophoresis is agarose • Polyacrylamide is usually used in protein electrophoresis • SDS-PAGE is used to separate polypeptides according to their masses 5-12 Two-Dimensional Gel Electrophoresis Ion-Exchange Chromatography • Uses a resin to separate substrances according to their charges • DEAE-Sephadex chromotography uses an ionexchange resin that contains positively charged diethylaminorthyl (DEAE) group. • These positive charges attract negatively charged substances, including proteins. • Phosphocellular is commonly used negatively charged resin. Gel Filtration Chromatography • Uses columns filled with porous resins that let in smaller substances, but exclude larger ones. • The smaller substances are slowed in their journey through the column, but larger substances travel relatively rapidly through the column. Tracers Detection Labeled tracers (e.g. 3H, 14C, 32P, 35S, 125I) Autoradiography using x-ray film phosphorimaging, liquid scintillation counting Non-radioactive tracers (e.g. fluorochrome, hapten) Fluorescence microscope Enzyme-couple chemiluminescence Autoradiography or phosphorimaging Enzyme-couple chromogenic Nucleic Acid hybridization Southern blot DNA : DNA DNA fingerprinting and DNA typing DNA : DNA Colony hybridization DNA : DNA Northern blot RNA : cDNA In situ hybridization (e.g fluorescence in situ hybridization; FISH) Chromosomal DNA : DNA Microarray DNA: DNA cDNA : cDNA Southern blots RFLP (Restriction Fragment Length Polymorphisms) DNA Testing by Allele-Specific Cleavage DNA Testing by Allele-Specific Oligonucleotide hybridization DNA fingerprinting DNA typing Northern blots (measuring gene activity) FISH (Fluorescence in situ Hybridization) Locating genes in chromosomes 22q11.12 Gene chips (Microarray) Gene identification Southern blot FISH Immunoblots (Western Blots) DNA sequencing Restriction mapping Restriction mapping (physical mapping) Identification of a new gene Identification of the transcript mapping the start site and stop site measuring active transcripts Identification of the gene product quantitative and qualitative Immunoblots (Western blots) analysis Identification of the gene function gain of function loss of function Mapping the start site of transcripts S1 mapping Primer extension Run-off transcription S1 mapping the 5’ end Primer extension Run-off transcription Mapping the stop site of transcripts S1 mapping S1 mapping the 3’ end Measuring active transcripts Northern blot In situ Histochemistry stain Nuclear run-on transcription Nuclear Run-on transcription Immunoblots Immunoblots (also called Western blots) use a similar process to Southern blots – Electrophoresis of proteins – Blot the proteins from the gel to a membrane – Detect the protein using antibody or antiserum to the target protein – Labeled secondary antibody is used to bind the first antibody and increase the signal 5-46 Western Blots 5-47 Qualitative analysis of the cis/trans element activity Reporter gene activity Cellulose filter binding assay Gel mobility shift assay DNase footprinting DMS footprinting Reporter gene Gel mobility shift assay DNase footprinting DMS footprinting Gain of function Transgenic clone Reporter gene activity Transgenic clones Loss of function Site-directed mutagenesis Knockout mouse Site-directed mutagenesis By oligonucleotide Making a knockout mouse Finding RNA sequences that interact with other molecules • SELEX (systematic evolution of ligands by exponential enrichment) • RNAs that interact with a target molecule are selected by affinity chromatography, then converted to double-stranded DNAs and amplified by PCR. Fig. 5.39





