The Hydrosphere and Oceans

Units 10 and 11
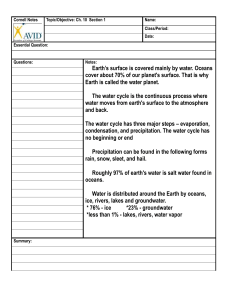
The Water Cycle
1. What is the hydrosphere?
1. The
hydrosphere
contains all water that exists on the earth.
• Water covers 75% of earth’s surface.
• 97% of water is contained in the ocean.
• 2% is ice
• Less than 1% is streams, lakes, rivers, vapor, etc.
2.
What is the water cycle?
2. The water cycle is the continual movement of water from one place or form to another.
• Runs on solar energy
• The same water has been recycled and reused for billions of years
3. What is evaporation?
3
.
Evaporation is the process by which water is converted from its liquid form to its vapor form.
Evaporation from the oceans accounts for
80% of the water delivered as precipitation.
http://techalive.mtu.edu/meec/module01/Evaporation
.html
4. What is condensation?
4.
Process in which water vapors changes to a liquid.
5. What is precipitation?
5.
water falling as rain, snow, sleet and hail.
6. What is runoff?
6. Runoff i s the process of water running off the land surface. Water flows downhill from high places like mountains and hills into streams, then rivers, and finally into the ocean.
7. WHAT IS A
WATER
COLLECTION?
7. When water falls back to earth as precipitation, it may fall back in the oceans, lakes or rivers or it may end up on land.
• “Ground water” -plants and animals use to drink or it may run over the soil and collect in the oceans, lakes or rivers
8. What is groundwater?
8. Groundwater is water that comes from the ground.
Groundwater comes from rain, snow, sleet, and hail that soaks into the ground. The water moves down into the ground because of gravity, passing between particles of soil, sand, gravel, or rock.
http://www.brainpop.com/science/earthsystem/groun dwater/
9. What is a watershed?
9. A watershed is the area of land where all of the water that is under it or drains off of it goes into the same place
Water Cycle and Life
10. How does water move through living things?
10.
• photosynthesis
• respiration
• about 68% of human body weight is water
11. What is photosynthesis?
Water Cycle and Life
•
11.
photosynthesis
– plants use solar energy to make glucose from water and carbon dioxide and release oxygen as waste
12. What is respiration?
Water Cycle and Life
12. organisms use oxygen to break down glucose and release water and carbon dioxide as waste
13. What is transpiration?
Water Cycle and Life
13. Transpiration occurs when plants move water upward from their roots and release the water through pores in their leaves
14. What is running water?
Surface Water
14. Running water flows downhill into rivers and streams
Stream – body of flowing water
Drainage System – collection of streams that drain an area of land
Tributary – small stream that flows into a larger stream
• Most major cities and farmland are along streams
15. What is a divide?
15. Divide – ridge of land that separates drainage systems
• Continental Divide – runs along the Rocky
Mountains rain on east side runs to
Atlantic Ocean or Gulf of
Mexico
• Almost all rain on west side runs to Pacific Ocean
Review: Types of Rocks and Soils
16. What is permeable and impermeable?
16. Permeable – water can flow through.
Impermeable – water can’t flow through
Review: Types of Rocks and Soils
17. What is the water table?
17.
The water table is the underground depth at which point the ground is totally saturated with water.
• Levels depend on how much is going in and out.
Review: Types of Rocks and Soils
18. What is an aquifer?
18. layer of rock or sediment containing groundwater.
Usually trapped between impermeable layers
• Recharge areas allow water into the aquifer
• Used as source of fresh water
Ogallala Aquifer in Midwest – largest in U.S.
Floridian Aquifer – our source of water
19. What is considered standing water?
Standing Water
Standing water is water that collects in low areas
• Lake – body of water that is too deep for sunlight to reach the bottom
• Pond – shallow body of water in which sunlight reaches the bottom
• Reservoirs – artificial lakes made by dams
20. What is considered frozen water ?
Frozen
Water
Glaciers – large masses of ice in motion; snow that doesn’t melt during the summer is crushed to form ice
• Continental Glaciers – form near the poles a) Greenland and Antarctica b) pieces break off to form ice bergs
• Alpine Glaciers – form in valleys in mountains a) flow down like frozen rivers
Quicktime Video: Two Types of
Glaciers
Mt. McKinley: QuickTime video
http://www.brainpop.com/science/earthsystem/glacie rs/
Karts
Sinkholes and Caverns
21. Description of sinkholes and caverns
1. carbonic acid in water dissolves rock
2. stalactite – mineral formation that hangs down from a cavern ceiling (hangs on tight)
3. stalagmite – pillar of minerals that forms on a cavern floor
4. ) sinkhole – hole formed when roof of a limestone cavern collapses
Formation of a cave
. Stalagmite and Stalactite
22. What are the concerns for groundwater?
22.
• Provides drinking water for 53% of U.S.
• Rock and soil are natural filters
• Easily contaminated a) sewage b) fertilizers c) landfills d) chemical spills e) saltwater intrusion