Evidenced Based Practice 2010 - Department of Communication
advertisement

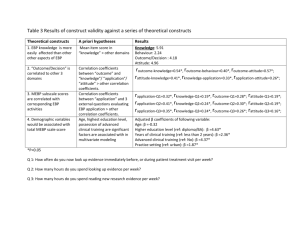
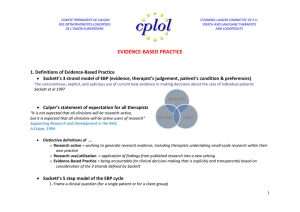
Evidence Based Practice In School Settings By Perry Flynn Consultant to NC DPI in SLP What IDEIA says: “ The Special Education and related services in the IEP must be based on peer-reviewed research to the extent practicable” What is EBP? • The goal of EBP is the integration of: (a) clinical expertise, (b) best current evidence, and (c) client values to provide high-quality services reflecting the interests, values, needs, and choices of the individuals we serve. Factors that influence Clinical Decisions Clinical Expertise EBP Research Evidence Patient Preferences Steps in the Process 1.Framing the Clinical Question 2.Finding the Evidence 3.Assessing the Evidence 4.Making the Decision PICO Step 1 Population, What population are you investigating? Intervention, What types of intervention are being considered? Comparison, What other interventions might be considered? Outcome, What are the desired outcomes? A 7 Step EBP DecisionMaking Process (adapted from Porzsolt et al. (2003)) • 1 • 2 • 3 • • • • 4 5 6 7 Create a clinical question Find studies that relate to the question Determine the level of evidence that the study represents and assess the quality of the study Assess the child/parent factors Assess clinician/agency factors Integrate the evidence Evaluate the decision Finding the Evidence, Step 2 1.Systematic reviews 2.Individual studies http://www.asha.org/members/ebp/ compendium/ Cochrane Collaboration Campbell Collaboration What Works Clearinghouse (US Department of Education) Psychological Database for Brain Impairment Treatment Efficacy National Electronic Library for Health (National Health Service of the UK) Evidence-based Communication Assessment and Intervention (EBCAI) Journal Assessing the Evidence, Step 3 Level Ia Ib IIa IIb III IV Description Well-designed meta-analysis of >1 randomized controlled trial Well-designed randomized controlled study Well-designed controlled study without randomization Well-designed quasiexperimental study Well-designed nonexperimental studies, i.e., correlational and case studies Expert committee report, consensus conference, clinical experience of respected authorities Meta-analysis A specialized form of systematic review in which the results from several studies are summarized using a statistical technique to yield a single weighted estimate of their findings Making the Decision, Step 4 Clinical Expertise EBP Research Evidence Patient Preference Evidence Maps http://www.ncepmaps.org/ Autism Spectrum Disorders Parkinson's Disease Traumatic Brain Injury (Adults) Traumatic Brain Injury (Children Where to find Everything from ASHA on EBP? http://www.asha.org/Members/ebp/intro/ References • Ehren, B., Fey, M., Gilliam, R., SLP’s Start Your Engines: Evidence –Based Practise in Schools, ASHA Schools Conference, Indianapolis, July 8, 2005 • Evidence Based Practice Tool Available, ASHA Leader, June 13, 2006 • Perspectives on Language Learning and Education, Volume 13, number1 March 2006 • Porzsolt, f., Ohletz, A., Gardner, D., Ruatti, H., Meier, H., Schotz-Gorton, N., & Schrott, L. (2003) Evedence-based decision making: The 6 step approach. American College of Physicians Journal Club, 139 (3), 1-6. • Scottish Intercollegiate Guidelines Network. (2004). SGN 50 A guideline developer’s handbook. Received November 27,2005 fromhttp://wwwisign.ac.uk/guidelines/fulltext/ 50/section6.html • Straus, S.E., Richardson, W.S. Glasziou, P., & Hayes R.B. (2005) Evidence-based medicine: How to practice and teach EBM. New York: Elsevier