Notes: Mendel's Law of Independent Assortment 1/27 p#___ Mendel
advertisement
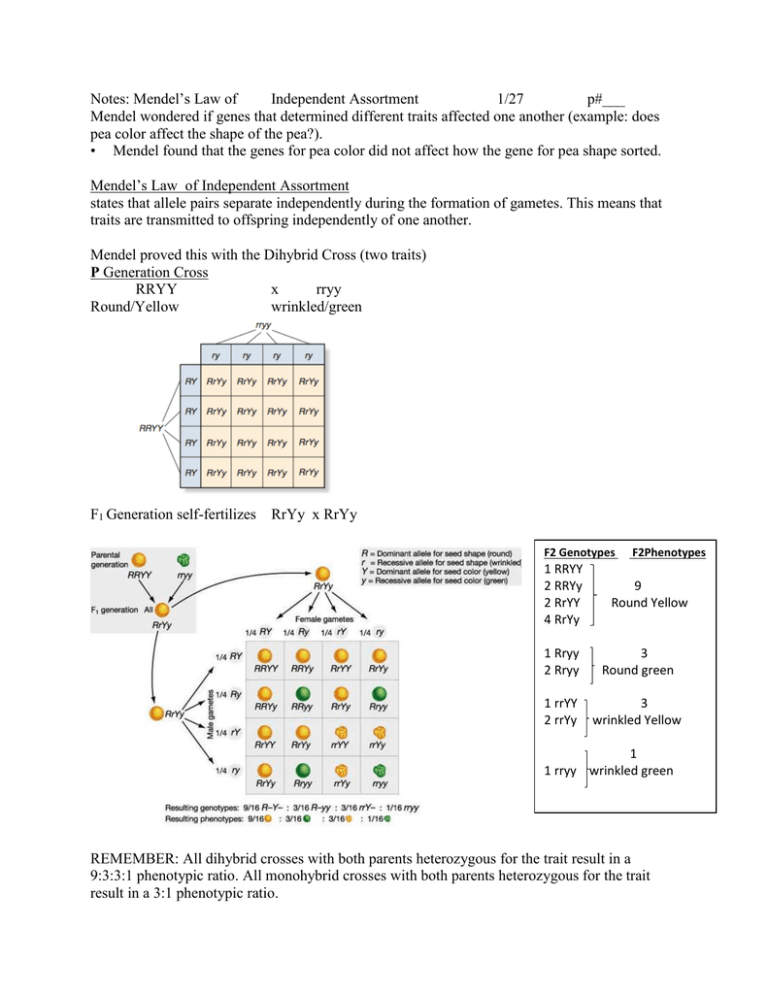
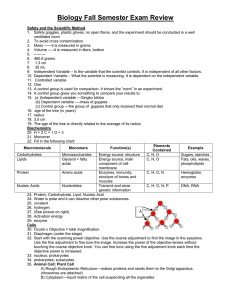
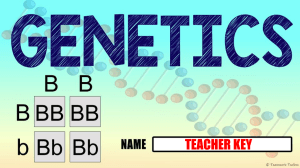
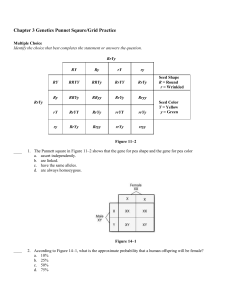
Notes: Mendel’s Law of Independent Assortment 1/27 p#___ Mendel wondered if genes that determined different traits affected one another (example: does pea color affect the shape of the pea?). • Mendel found that the genes for pea color did not affect how the gene for pea shape sorted. Mendel’s Law of Independent Assortment states that allele pairs separate independently during the formation of gametes. This means that traits are transmitted to offspring independently of one another. Mendel proved this with the Dihybrid Cross (two traits) P Generation Cross RRYY x rryy Round/Yellow wrinkled/green F1 Generation self-fertilizes RrYy x RrYy F2 Genotypes 1 RRYY 2 RRYy 2 RrYY 4 RrYy F2Phenotypes 9 Round Yellow 1 Rryy 2 Rryy 3 Round green 1 rrYY 2 rrYy 3 wrinkled Yellow 1 1 rryy wrinkled green REMEMBER: All dihybrid crosses with both parents heterozygous for the trait result in a 9:3:3:1 phenotypic ratio. All monohybrid crosses with both parents heterozygous for the trait result in a 3:1 phenotypic ratio.