Week 1 - Algonquin College

Week 3
Introduction to Project
Management
1
Planning Projects
“Planning is laying out the project groundwork to ensure your goals are met“
2
Purpose of Planning Process
It answers:
How are we going to SOLVE the problem
What RESOURCES are required
How much effort it requires
What are the DUE DATES
3
Project Plans
◦ Are Not a Microsoft Project File
◦ They are documents that:
Define SCHEDULE
Define RESOURCES needed
Project DELIVERABLES/MILESTONES
4
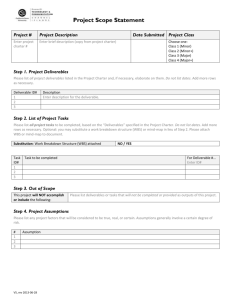
Project Deliverables
◦ Are measurable outcomes or specific items that must be PRODUCED to fulfill the outcomes of the project.
◦ All deliverables must be described in enough detail so that they can be differentiated from
related deliverables. For example:
A twin engine plane vs a single engine plane
A daily report vs a weekly report
5
Project PLANNING Processes
Scope Planning
Specifies the IN -SCOPE requirements for the project and facilitates the creation of the WBS
Preparing a Work Breakdown
Structure ( WBS )
Specifies the breakdown of the project into tasks and sub tasks
Communication Planning
Communication strategy with all project stakeholders
6
Project Planning Processes Cont.
Project SCHEDULE Development
Specifies the entire schedule of the activities detailing the sequence of execution
RESOURCE Planning
Specifies WHO will do the work
Any special equipment or skills required
“Project Schedule Development” & “Resource Planning” are items which have to be inputted into “MS Project 2010”
RISK Planning
Charts the risks,
CONTINGENCY plans: having an alternative course of action planned once a risk surfaces
MITIGATION strategies: minimizing risks once
they arise; a form of “ damage control ”
7
DEVELOPING SMART
GOALS
8
Articulating Project Objectives
S pecific (get into the details).
M easurable (use qualitative language so you know when you are finished).
A cceptable (Achievable) (to stakeholders).
R ealistic (Relevant) (in terms of achievement).
T ime bound (Time frame) (deadlines not durations)
9
SMART GOALS Video
http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=YmOS
3dj9h0s
10
AFTER THE GOALS ARE DRAFTED,
ASK YOURSELF:
Is this goal specific ?
Are the results easily measurable ?
Realistic ?
Does my goal include a completion DATE ?
◦ If the answer is NO to any of these questions, you have more work to do!!
11
SMART Goals Example
GOAL = Write A Long Essay
◦ Specific: I will write my 15 page final paper for my
Business class.
◦ Measurable: I will report my progress in terms of pages completed per week.
◦ Acceptable (Achievable): By completing 2 pages a day for 8 days, I will be able to finish my paper.
◦ Realistic (Relevant): I cannot write a lot at a time, so I am spreading it out over time.
◦ Time Bound (Time Frame): I will finish this paper in 8 days.
12
POORLY WRITTEN GOALS
Use words like….
◦ Try, could, should, possibly, hope, attempt, probably, might, maybe
These are Not specific enough !
What will you DO?
Poorly written goals
◦ Soon, in a few months, by the end of the year
YOU SHOULD PICK A DATE !
13
PROJECT
REQUIREMENT
PLANNING
14
Project Requirements
Requirements specify what the project deliverable should look like and what it should do.
Divided into 6 basic categories:
Functional
Non-Functional
Technical
Regulatory
Business
User
15
1) Functional Project Requirements
Describe the characteristics of what you want your deliverable to be.
Example:
◦ System shall provide users with the ability to “select” whether or not to produce a hardcopy transaction receipt before completing a transaction .
16
2) Non-Functional Requirements
Describe criteria that can be judged
Describe restrictions to be placed on the deliverable
Example:
◦ All displays shall be in white 14 pt Arial text on black background.
17
3) Technical Requirements
Emerges from functional requirements
May include:
◦ Hardware details
◦ Telecommunication protocols
18
4) REGULATORY Requirements
Can be internal or external
Usually non-negotiable
Example:
◦ All ATMs shall connect to
“standard utility power sources
within their civic jurisdiction”, and be supplied with uninterruptible power source approved by “said company”.
19
5) Business Requirements
Always from a management perspective
States “business rationale” for the project
Example:
◦ By providing superior service to our retail customers, ABC Bank’s
ATM network will allow us to increase associated service fee revenue by 10% annually on an ongoing basis, using a baseline of December 2011.
20
6) User Requirements
What users need to do with the system or product
Example:
◦ The system shall complete a standard withdrawal from a personal account, from login to cash, in less than two minutes for a first time user.
21
WORK BREAKDOWN
STRUCTURE (WBS)
22
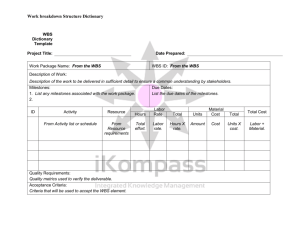
Define WBS
PMI describes WBS as “a deliverable oriented hierarchical decomposition of the
work to be executed by the project team to accomplish the project objectives and create required deliverables .”
In our words:
◦ A structured method for defining the work of the project
23
Sample WBS
WBS does not show the sequence
When creating, start with the goal and then break
it down into smaller and smaller
DELIVERABLES ( MILESTONES )
Activity
Activity
Activity
Deliverable 1) Deliverables
◦ define what you are going to do
◦ Are Nouns Deliverable
Goal
Deliverable
Deliverable
Activity
Activity
Activity
2) Activities
◦ define how you are going to accomplish it
◦ Activities are Verbs
24
WBS DIAGRAM 3
25
WBS DIAGRAM 2
26
WBS DIAGRAM 1
27
Benefits of WBS
Identifies all work necessary to meet the scope of the project
Clarifies responsibilities
Forces detailed planning and documentation
Provides structure for measuring success
IDENTIFIES MILESTONES
28
Milestones
Identifiable point that represents a requirement or completion of an important set of activities
Why use milestones?
◦ Helps identify progress
◦ Helps define “ dependencies”
◦ Provides visibility of major deliverable dates
29
Milestones vs Tasks
Milestones are what management &/or clients really want to hear about
Milestones are the large outcome of many little tasks.
◦ Not necessarily have a DATE
Tasks are activities that need to be completed in order to make the milestone happen.
30
WBS
Comes from
◦ Past projects
◦ Templates and documents of procedures
◦ System tutorials
◦ Brainstorming
◦ Subject Matter Expert (SME)
31
WBS does not show the sequence
When creating, start with the goal and then break it down into smaller and smaller
DELIVERABLES
( MILESTONES )
1) Deliverables
(
Milestones
)
◦ define what you are going to do
◦ Are Nouns
2) Activities
◦ define how you are going to accomplish it
◦ Activities are Verbs
32
WEEK 3 HYBRID
Read Chapter 2
Complete ALL activities required while reading Chapter 2
Complete the Matching questions for Chapter 2
Complete the Multiple Choice questions for Chapter 2
Please note, you must complete Matching and Multiple
Choice questions in an EXCEL document. Please name the excel file: Chapter2_[yrLastName]
Name “Matching” workSHEET “ worksheet M Chap2”
Name the “Multiple Choice” workSHEET :
“ worksheet MC Chap 2”
Provide the answers in the order as they are presented in the book.
33