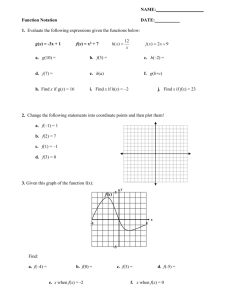
objective 6 - Outbreaks 2015
advertisement

http://outbreaks.globalincidentmap.com/ http://www.who.int/csr/don/en/ http://www.cdc.gov/outbreaks/ OUTBREAKS, EPIDEMICS, & PANDEMICS http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=yToii3-p-NI (the sneeze) CANCER https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=SGaQ0WwZ_0I cancer https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=LEpTTolebqo (cancer) TERMS YOU SHOULD KNOW: OUTBREAK when a disease occurs in more people than expected in a community or region. http://www.who.int/csr/don/en/ / (WHO) http://www.cdc.gov/outbreaks/index.html (CDC) http://www.cdc.gov/CDCTV/RespondOutbreaks/index.html (video) October 2012 - strawberries imported from China were thought to be contaminated with norovirus. More than 11,000 students were sickened throughout eastern German, with 32 requiring hospitalization. About 500 schools were involved in the outbreak of this norovirus, which is the leading cause of stomach flu. Transmission? TERMS YOU SHOULD KNOW: EPIDEMIC Same as an outbreak except the percentage of overall deaths caused by the epidemic of severe acute respiratory syndrome (SARS) in 2003, sickened about 8,098 people and led to about 774 deaths in 29 countries. (Transmission: direct/indirect/possible airborne) disease is higher OR the Washington State Secretary of Health declared a number infected pertussis (whooping cough) epidemic on April 3, dramatically increases from 2012 after a 1,300% increase in cases were reported one year to the next in an epidemic. compared with 2011 . (Transmission: direct/indirect) TERMS YOU SHOULD KNOW: PANDEMIC A pandemic is 1918 Spanish Flu (Virus) DNA mutated into something more virulent. particularly deadly in 20 to 35 year olds. a global First reported case in Kansas disease estimated up to 40% of the world's population outbreak. was infected – killing 20 to 50 million people. (Transmission: direct/indirect) (Rosenburg 2012) REVIEW QUESTIONS What factors may determine if a person who is exposed to a pathogen will actually become ill? Why do outbreaks or epidemics end? Works Cited •"2009 Flu Pandemic." Wikipedia. Wikimedia Foundation, 17 Nov. 2012. Web. 20 Nov. 2012. <http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/2009_flu_pandemic>. •"Chinese Strawberries Sickened Thousands of German Students." Food Safety News. N.p., 9 Oct. 2012. Web. 20 Nov. 2012. <http://www.foodsafetynews.com/2012/10/german-students-got-sick-onchinese-strawberries/>. •"Families Fighting Flu." Families Fighting Flu Resources Comments. N.p., n.d. Web. 20 Nov. 2012. <http://www.familiesfightingflu.org/resources/>. •"FAQ: Methods of Disease Transmission." Mount Sinai Hospital Department of Microbiology, n.d. Web. 17 Nov. 2012. <http://microbiology.mtsinai.on.ca/faq/transmission.shtml>. •"Frozen Strawberries Linked to 11,000 Food Poisoning Norovirus Illnesses in Germany." Food Poisoning Bulletin. N.p., 6 Oct. 2012. Web. 20 Nov. 2012. <http://foodpoisoningbulletin.com/2012/frozen-strawberries-linked-to-11000-food-poisoning-norovirusillnesses-in-germany/>. •Koerner, Brendan. "Whether It's Time to Freak about the Flu." Slate Magazine. N.p., 19 Dec. 2003. Web. 20 Nov. 2012. <http://www.slate.com/articles/news_and_politics/explainer/2003/12/outbreaks_vs_epidemics.html>. •Rosenburg, Jennifer. "1918 Spanish Flu Pandemic." About.com 20th Century History. N.p., 2013. Web. 14 Nov. 2013. <http://history1900s.about.com/od/1910s/p/spanishflu.htm>. •"OUTBREAK: An Infectious Disease Role-playing Activity." Howard Hughes Medical Institute, n.d. Web. 17 Nov. 2012. <http://www.hhmi.org/biointeractive/disease/pdf/outbreak.pdf>.