Motion
advertisement

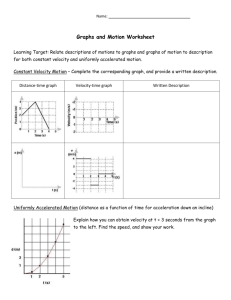
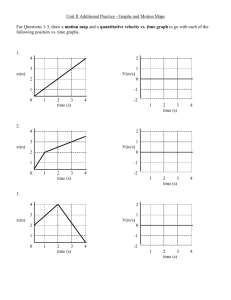
Motion - the process of changing position Describing Position Reference point – the starting point you choose to describe the location, or position, of an object Position – describes an object’s distance and direction from a reference point Displacement – the difference between the starting position and the final position Speed the distance an object moves in a unit of time ◦ ex. 2m/s or 60 km/h Constant Speed ◦ when an object moves the same distance over a given unit of time Changing Speed ◦ when the distance an object covers increases or decreases over a given unit of time Average Speed total distance traveled divided by the total time speed(s) = distance(d)/time(t) Calculating Speed (s = d/t) 1. On a hike you travel 2800 m in 2 h. What is your average speed? 2. A jet airliner flew 4100 km from New York City to San Francisco in 4.25 h. What was its average speed? 3. How long would it take you to bike 20 km at an average speed of 5 km/h? Velocity the speed and the direction of a moving object ◦ ex. 5 m/s to the east Constant Velocity ◦ An object moves with constant speed and its direction does not change Changing Velocity Velocity changes if either the speed or the direction of the object changes Acceleration the measure of the change in velocity during a period of time ◦ Positive Acceleration acceleration is in the same direction as its motion; speeds up ◦ Negative Acceleration (deceleration) acceleration is in the opposite direction of its motion; slows down DESCRIBING MOTION WITH GRAPHS DISTANCE- TIME GRAPHS A graph that shows how distance and time are related. ◦ Time is on the x axis ◦ Distance is on the y-axis shows the distance an object travels from a reference point. This type of graph shows how an object’ s position changes over time DISTANCE- TIME GRAPHS The line on this distance-time graph shows that the bus is traveling at a constant speed DISTANCE- TIME GRAPHS The line on this distance-time graph shows that the object’s speed is changing DISTANCE- TIME GRAPHS Distance-Time graphs can be used to compare the motion of two objects ◦ The slope of Line A is greater than the slope of Line B. The object A traveled faster than the object B SPEED- TIME GRAPHS Shows the speed of an object on the y-axis and time on the x-axis. ◦ It shows how the speed of an object changes during an interval of time. Constant speed Acceleration