EOC Review- Physical
advertisement

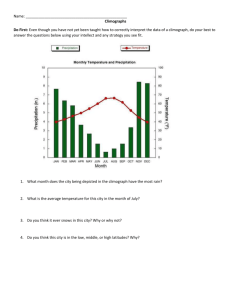
EOC Tutorials Round 1 Physical Sciences CLASSROOM MANIPULATIVE Geography Term Review Vocab Diamond Plate Tectonic Animations Guess the Tectonic Activity! Oceanic-Oceanic Convergent Oceanic-Oceanic Divergent Transform Continental-Continental Convergent Continental-Continental Divergent Oceanic-Continental Convergent CLASSROOM MANIPULATIVE Landform Stations 1. Explain the difference b/w weathering & erosion. Weathering breaks down rocks on Earth’s surface into smaller pieces Erosion wears away Earth’s surface (wind, glaciers, moving water), and then carries materials away 2. Explain the difference b/w physical & chemical weathering; give example. Physical- breaks rock into smaller pieces Water freezes in crack, ice splits rock 2. Explain the difference b/w physical & chemical weathering; give example. Chemical- Δs the actual chemical make-up of the rock Water + CO2 destruction of limestone 7. How can glaciers cause erosion? Slowly move downhill p.u. soil/rocks destroy forests, carve uvalleys, alter river course, wear down mtns. 10. How does water cause erosion? Fast-moving water cuts into land, wears away soil/rock creates sediment which grinds away other rocks Waves erode cliffs, beaches, etc. Earth’s Revolution • As it rotates, Earth revolves around the sun (365 days) • Tilt + revolution = seasons –Δs in length of days and temp. –Reversed for N & S hemispheres Equinoxes & Solstices • Equinox: Spring and Fall –Equal days and nights • Solstice: Summer and Winter –Longer day or shorter day Equinoxes & Solstices • Spring equinox March 21rays hit Equator directly…equal day/night • Summer solstice June 22rays hit Tropic of Cancer…longest day (US) Equinoxes & Solstices • Fall equinox Sept. 23- rays hit Equator directly…equal day/night • Winter solstice December 22- rays hit Tropic of Capricorn…shortest day (US) Equinoxes & Solstices • So if it is summer in Houston, what season is it in Australia? • If we are wearing long sleeves and jackets, what are they wearing in China? The Poles • For 6 months one pole is pointed toward sun constant sunlight • Other is pointed away little to no sunlight “lands of the midnight sun” El Nino • http://www.teachersdo main.org/resource/es s05.sci.ess.watcyc.es elnino/ Landforms Landforms affect climates of places @ the same latitude Bodies of water moderate temps. b/c they take a long time to change temp. Gulf of MX is warm water keeps Houston warmer Continentality– absence of lg. body of water means more drastic weather changes Nebraska can have hot summers and receive snow in the winters (4 seasons instead of 2 ) Rainshadow effect Cool air releases moisture on windward side of mountain; then hot, dry air moves to leeward side creating deserts These are BIOMES! Aquatic Desert Tundra Forests What is a biome? http://www.ucmp.berkeley.edu/glossary/gloss5/biome/ Grasslands How is EARTH made, and how does it make life possible? LITHOSPHERE Greek: Rocky Sphere Why does the SKY swirl and how does it make life possible? ATMOSPHERE Greek: Vapor Sphere Where does the RAIN come from how does it make life possible? HYDROSPHERE Greek: Water Sphere What is life and how do its systems sustain themselves? BIOSPHERE Greek: LIFE Sphere CLASSROOM MANIPULATIVE Climate Stations Climographs CLASSROOM MANIPULATIVE Climograph Matching Let’s see what we know… The Middle East consists of mountains, upland plateaus and valleys. These physical features are the result of: A erosion B tectonic forces C deposition D weathering Let’s see what we know… Because of its location along the "Ring of Fire," Japan is particularly susceptible to which of the following hazards? F earthquakes and volcanoes G floodings and droughts H monsoons and floodings J earthquakes and tornados The Pacific Islands in the Ring of Fire are affected by all of the following except — A volcanoes B earthquakes C tsunamis D tornadoes Let’s see what we know… The Middle East consists of mountains, upland plateaus and valleys. These physical features are the result of: A erosion B tectonic forces C deposition D weathering Let’s see what we know… Which of the following is NOT a landform caused by climate patterns of South America? F Andes Mountains G Atacama Desert H Amazon Rainforest J Argentine Pampas As a river reaches its mouth, it is often affected by incoming tides, resulting in a landform called a _______? A source B atoll C delta D current Let’s see what we know… Because of its location along the "Ring of Fire," Japan is particularly susceptible to which of the following hazards? F earthquakes and volcanoes G floodings and droughts H monsoons and floodings J earthquakes and tornados The Pacific Islands in the Ring of Fire are affected by all of the following except — A volcanoes B earthquakes C tsunamis D tornadoes Let’s see what we know… Which of the following is NOT a landform caused by climate patterns of South America? F Andes Mountains G Atacama Desert H Amazon Rainforest J Argentine Pampas As a river reaches its mouth, it is often affected by incoming tides, resulting in a landform called a _______? A source B atoll C delta D current Let’s see what we know… Which of the following is MOST directly responsible for the different seasons on Earth? A rotation B revolution C solstices D position in planetary system When does the Northern Hemisphere have the warmest climate? F when it is tilted most directly towards the sun G when it faces the sun for twelve hours a day H when it is warmest in the southern hemisphere J when it is tilted away from the sun Let’s see what we know… Which of the following is MOST directly responsible for the different seasons on Earth? A rotation B revolution C solstices D position in planetary system When does the Northern Hemisphere have the warmest climate? F when it is tilted most directly towards the sun G when it faces the sun for twelve hours a day H when it is warmest in the southern hemisphere J when it is tilted away from the sun Let’s see what we know… How does an El Niño affect Texas? A increased rainfall B less rainfall C more tornadoes D fewer tornadoes Let’s see what we know… Japan sits along a subduction zone which makes it a hotbed of volcanic and tectonic activity. What can these activities create in an ocean environment? F monsoons G tsunamis H El Ninas J typhoons Because the island regions of Southeast Asia were formed by tectonic forces, all of the following are hazards that they face except — F tsunamis G volcanoes H hurricanes J earthquakes Let’s see what we know… Which of the following can be directly correlated to temperature? A Longitude B latitude C elevation D latitude and elevation Which of the following statements is TRUE concerning the climates of the U.S. and Canada? F The U.S. has more varied climate zones than Canada. G Canada has more varied climate zones than the U.S. H Both the U.S. and Canada have tropical wet climate zones. J Neither the U.S. or Canada has tropical wet climate zones. Let’s see what we know… Which of the following can be directly correlated to temperature? A Longitude B latitude C elevation D latitude and elevation Which of the following statements is TRUE concerning the climates of the U.S. and Canada? F The U.S. has more varied climate zones than Canada. G Canada has more varied climate zones than the U.S. H Both the U.S. and Canada have tropical wet climate zones. J Neither the U.S. or Canada has tropical wet climate zones. Let’s see what we know… Where would a warm rainforest biome be located? F highlands G tropical latitudes H middle latitudes J high latitudes In which of the following would an Alaskan black bear thrive? A equatorial highlands B tropical latitudes C middle latitudes D high latitudes Let’s see what we know… Where would a warm rainforest biome be located? F highlands G tropical latitudes H middle latitudes J high latitudes In which of the following would an Alaskan black bear thrive? A equatorial highlands B tropical latitudes C middle latitudes D high latitudes Let’s see what we know… An earthquake takes place in which sphere? A atmosphere B lithosphere C biosphere D hydrosphere Hurricanes result from a combination of forces from which two spheres? A atmosphere and hydrosphere B lithosphere and biosphere C biosphere and hydrosphere D hydrosphere and lithosphere Let’s see what we know… An earthquake takes place in which sphere? A atmosphere B lithosphere C biosphere D hydrosphere Hurricanes result from a combination of forces from which two spheres? A atmosphere and hydrosphere B lithosphere and biosphere C biosphere and hydrosphere D hydrosphere and lithosphere