ECS Ch.3 Sec. 2
advertisement

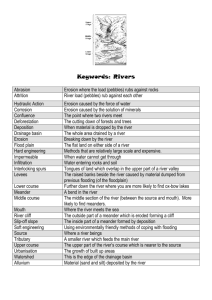
Water Erosion Chapter 3 Section 2 Pages 72-81 Moving water is the major agent of the erosion that has shaped Earth’s land surface. Run-Off: The water that moves over Earth’s surface. More run-off means more erosion. Things that reduce run-off (like plants and roots) reduce erosion. In wet areas, run-off & erosion may be low because there are more plants to protect the soil. Run-Off flow chart: Rills -> Gullies -> Streams -> Rivers Tributary: A stream or river that flows into a larger river. Through erosion, a river creates valleys, waterfalls, flood plains, meanders, and oxbow lakes. Waterfalls: Occur where a river meets an area of hard rock that erodes slowly, while eroding softer rock quickly. This will eventually develop a waterfall. Flood Plain: The flat wide area of land along a river. Meander: A loop-like bend in the course of a river. Oxbow Lake: Is a meander that has been cut off from the river. Deposition creates landforms such as alluvial fans and deltas. It can also add soil to a river’s flood plain. Alluvial Fan: A wide, sloping deposit of sediment formed where a stream leaves a mountain range. Delta: Sediment deposited where a river flows into an ocean or lake. Beaches: Sand carried downstream by the river spreads along the coast to form beaches. Groundwater: Underground water *Groundwater can cause erosion through a process of chemical weathering. Stalactite: A deposit that hangs like an icicle from cave ceiling. Stalagmite: A cone-shaped deposit on cave floor. Karst Topography: A landscape created from sinkholes. These sinkholes were caused by the erosion of underlying Limestone. (Found in Florida and Texas for example.)