Egypt Section 2 SG
advertisement

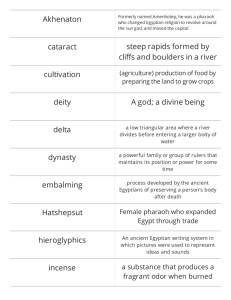
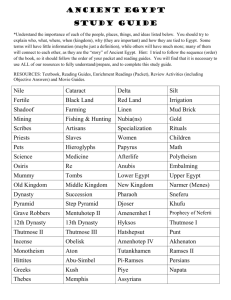
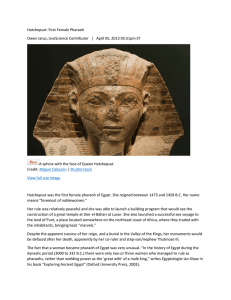
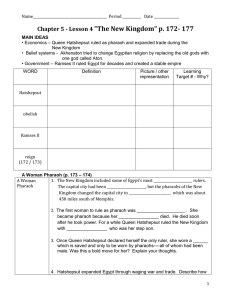
Section 2: Rulers of Egypt Pharaoh Dynasty Absolute Power Regent the title of the kings of Ancient Egypt a series of rulers from the same family or ethnic background complete control over someone or something someone who rules for a child until the child is old enough to rule (Hatshepsut) Key Idea: Pharaohs were known as “god-kings” and had absolute power. Believed to be earthly form of the falcon god, Horus, and later other gods, such as Ra. Believed to bring the yearly floods and harvest Key Idea: The history of Ancient Egypt Is defined by 3 time periods known as kingdoms. Characteristics Old Kingdom Peaceful civilization (2686BC--2125BC) Well-run government Traded with Nubia Middle Kingdom (2055BC--1650BC) New Kingdom (1550BC--1069BC) Restored order and reunited the country Spent money on public works, like irrigation, not war Grew rich Strong princes forced invaders out Wanted to build an empire Large, strong armies Notable Pharaohs King Menes United Upper and Lower Egypt Built city of Memphis (now near Cairo) King Tutankhamen Child king Died around 18 Tomb found in 1922 Hatshepsut Appointed regent for Thutmose III Declared herself Pharaoh (15 years) Created peace and wealth Refused to give up throne Thutmose III Destroyed statues of Hatshepsut Led wars and conquered lands Treated defeated people with mercy Well-educated Had absolute power Made all laws The end of each kingdom is marked by a time of trouble- wars or invasions. End of Kingdom Governors challenged Pharaoh People were divided Dynasty became weak Weak rulers lost control to invaders Civil war made Egypt weak Fell to Alexander the Great of Macedonia Queen Cleopatra was the last Macedonian ruler Egypt became part of the Roman Empire in 31BC