General Overview
advertisement

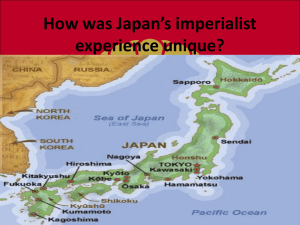
The Rise Of Japan Wealth & Power -Story of Two Cultures on Opposite Paths- China Japan 1800 1840 1868 1900 Tokugawa Era 1600s-1860s -Period of peace • Emphasis on order & conformity rigid class structure, discipline, loyalty, isolation from outsiders • Weak emperor strong shogun Late Tokugawa Era Isolation – not stagnation Economic growth & peace • Dutch Studies • Daimyo's “Alternate Attendance System” Samurai lose importance/wealth in comparison to merchants Late Tokugawa Era Spark… 1850 - recession 1853 - Commodore Perry arrives from U.S. demanding Japan end its isolation & trade with the West Familiar Conditions? 1. 2. Crumbling social structure Foreign pressure ? “Revolutions are about economics.” ? • In comparison to China, what can Japan do differently to be more successful? Result? 1868: “Meiji Restoration” • Shogun overthrown • Emperor restored to power Meiji Restoration 1. 2. Selective borrowing from West Effort at modernization & reform • Industrialization • Constitutional monarchy • Compulsory education & medical advances Meiji Foreign Policy World Power? Imperialism 1. 2. Sino-Japanese War Russo-Japanese War – Japan acquired Korea, Taiwan, & other islands Explain why this period is often referred to as the great divergence. In general, what are the major similarities and differences in responses to the West among: • Ottomans • Egypt • China • Russia • Japan Evaluate the claim that the industrial revolution was a global phenomenon.