Mod 4 Glossary & Practice Exam
advertisement
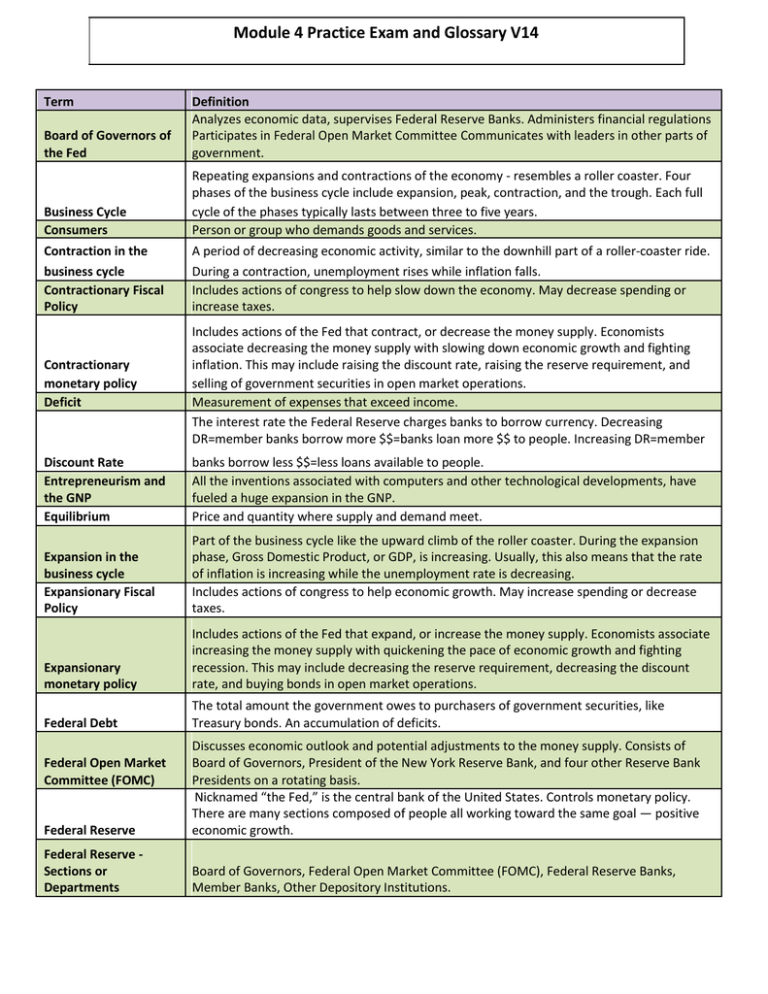
Module 4 Practice Exam and Glossary V14 Term Board of Governors of the Fed Definition Analyzes economic data, supervises Federal Reserve Banks. Administers financial regulations Participates in Federal Open Market Committee Communicates with leaders in other parts of government. Business Cycle Consumers Repeating expansions and contractions of the economy - resembles a roller coaster. Four phases of the business cycle include expansion, peak, contraction, and the trough. Each full cycle of the phases typically lasts between three to five years. Person or group who demands goods and services. Contraction in the A period of decreasing economic activity, similar to the downhill part of a roller-coaster ride. business cycle Contractionary Fiscal Policy During a contraction, unemployment rises while inflation falls. Includes actions of congress to help slow down the economy. May decrease spending or increase taxes. Contractionary monetary policy Deficit Includes actions of the Fed that contract, or decrease the money supply. Economists associate decreasing the money supply with slowing down economic growth and fighting inflation. This may include raising the discount rate, raising the reserve requirement, and selling of government securities in open market operations. Measurement of expenses that exceed income. The interest rate the Federal Reserve charges banks to borrow currency. Decreasing DR=member banks borrow more $$=banks loan more $$ to people. Increasing DR=member Discount Rate Entrepreneurism and the GNP Equilibrium banks borrow less $$=less loans available to people. All the inventions associated with computers and other technological developments, have fueled a huge expansion in the GNP. Price and quantity where supply and demand meet. Expansion in the business cycle Expansionary Fiscal Policy Part of the business cycle like the upward climb of the roller coaster. During the expansion phase, Gross Domestic Product, or GDP, is increasing. Usually, this also means that the rate of inflation is increasing while the unemployment rate is decreasing. Includes actions of congress to help economic growth. May increase spending or decrease taxes. Expansionary monetary policy Includes actions of the Fed that expand, or increase the money supply. Economists associate increasing the money supply with quickening the pace of economic growth and fighting recession. This may include decreasing the reserve requirement, decreasing the discount rate, and buying bonds in open market operations. Federal Debt The total amount the government owes to purchasers of government securities, like Treasury bonds. An accumulation of deficits. Federal Reserve Discusses economic outlook and potential adjustments to the money supply. Consists of Board of Governors, President of the New York Reserve Bank, and four other Reserve Bank Presidents on a rotating basis. Nicknamed “the Fed,” is the central bank of the United States. Controls monetary policy. There are many sections composed of people all working toward the same goal — positive economic growth. Federal Reserve Sections or Departments Board of Governors, Federal Open Market Committee (FOMC), Federal Reserve Banks, Member Banks, Other Depository Institutions. Federal Open Market Committee (FOMC) Federal Reserve Banks Fiscal Policy Gross National Product Inflation rate Member Banks of the Federal Reserve Minimum Wage Monetary Policy Money Supply Natural Monopolies Natural Resources and the GNP Open Market Operations Other Depository Institutions (NOT part of the Fed) Peak in the business cycle Population and the GNP Price Control Price Stability Regulation Regulatory Laws Reserve Requirement Provides service to banks and the U.S. Treasury—“the bankers’ bank”. Supervises bank operations within their region Handles check collection, electronic funds transfer, distribution of currency and coin to banks. Comprised of 12 Federal Reserve Banks, each serving its own region of the United States. Government use of taxing and spending to meet economic goals. The government utilizes fiscal policy to promote the economic goals of full employment, price stability, and economic growth. The sum of the production of goods and the supply of services in a given country. GNP can be effected by population, entrepreneurism, trade, war, and natural resources. The general rise of prices over time. Best measure of price stability. Receive services from regional Federal Reserve Bank, The lowest amount a business can pay for the work of an employee, set by the government. Federal Reserve actions that monitor and control the U.S. money supply to meet economic goals. The tools of monetary policy include: The discount rate, reserve requirement, and open market operations. The Federal Reserve utilizes monetary policy to promote the economic goals of full employment, price stability, and economic growth. The total amount of money available in the national economy. Product produced most efficiently when there is one supplier. Examples: police, sewer systems, highways. The discovery of oil is a classic case of natural resources driving up the GNP of a region such as the Middle-East. Similarly, in rain forests around the world, harvesting trees has had a positive impact on the GNP. The Federal Reserve’s frequent buying and selling of government securities (bonds), considered the most significant of the three tools. Buy bonds= FED gives banks $$ for bonds=banks loan more $$ to people. Sell bonds=FED gets $$ from banks=less loans available to people by bank. Not technically not part of the Federal Reserve System, yet subject to regulations. Includes credit unions, savings and loan associations, commercial banks, and savings banks. Receive services from regional Federal Reserve Bank. The momentary pause at the summit is the peak, where production reaches the highest current level. This is a time when the inflation rate is at it’s highest and unemployment is at the lowest. Population growth can increase both GNP and per capita GNP. Government intervention in markets in which legal restrictions are placed on the prices charged. Little fluctuation in the price level for goods and service. The inflation rate is the best indicator of price stability. Government laws that control businesses. Laws set by a government that control aspects of how a firm conducts business. The percentage of a bank’s deposits that must be kept as currency and coin in the bank. Decreasing RR= banks keep less $$ in vault=banks loan more $$ to people. Increasing RR=banks keep more $$ in vault=less loans available to people. Shortage Lack of product due to demand exceeding supply. Stagflation Subsidies A period of high unemployment and inflation. Financial assistance payments by the government. Surplus Trade and the GNP Trough in the business cycle Unemployment rate Excess product due to supply exceeding demand. Global trading increases GNP. The lowest point of the roller coaster ride and of the business cycle. The trough is the transition from a contraction to an expansion phase and thus the worst point in a period of decline. Reflects the percentage of people over age 16 who are trying but unable to find work. War and the GNP For countries like the U.S. and much of Western Europe, which today supply military arms, war can have a positive effect on the GNP. Module 4 Practice Exam V14 1. Use this image to answer the following question. In the business cycle phase marked A, economists expect A. inflation to be high B. unemployment to be low C. economic growth to slow down D. consumer sales to increase 2. In the diagram above, what will happen if the government sets the price for potatoes at Point B? A. There will be a shortage of potatoes. B. There will be a surplus of potatoes. C. The price of potatoes will rise to meet equilibrium. D. The price of potatoes will fall to meet equilibrium. 3. Natural monopolies are A. food products with a monopoly market B. products that one supplier can produce most efficiently C. products where the government chooses a company to produce it D. markets for items where consumers have considerable price control 4. What role does government regulation serve in business? A. Ensure that markets operate freely B. Increase tax revenues C. Protect consumers and producers D. Restrict competition 5. The part of the Federal Reserve having the greatest impact on our overall economy is the A. Board of Governors B. Member Banks C. Federal Open Market Committee D. Federal Reserve Regional Bank 6. Which actions would the Federal Reserve most likely take to slow inflation? A. Lower discount rate and buy government securities B. Raise reserve requirement and sell government securities C. Raise reserve requirement and lower discount rate D. Buy government securities and raise discount rate 7. This text appears on the economics page of the local newspaper. One of the sentences is incorrect. Which corrected sentence would make the passage accurate? A: Investments and lending have taken a dive while prices have stagnated. B. Unemployment is down as businesses move to reduce costs. C. The Fed considers raising discount rates and reserve requirements in increase monetary circulation. D. The Fed considers lowering discount rates and reserve requirements to decrease monetary circulation. 8. Increasing government spending usually A. increases the unemployment rate B. decreases the unemployment rate C. increases the stagflation rate D. decreases the stagflation rate 9. How could government-sponsored grants for the private development of new technologies result in a lower national debt? A. Funding private American initiatives would decrease dependence on foreign technologies. B. Getting private industry involved in technological development would increase national security. C. Making initial development private saves the government from funding all of the research. D. Successful start-up companies would inspire young people to careers in science and technology. 10. Inflation is on the rise. Which of the following demonstrates how the Federal Reserve would combat inflation? A. Increase taxes and decrease spending B. Decrease the reserve requirement C. Increase the discount rate D. Buy government securities 11. Unemployment is high and inflation is low. Which of the following explains how the US Congress would likely proceed? A. Contractionary fiscal policy B. Expansionary fiscal policy C. Contractionary monetary policy D. Expansionary monetary policy 12. How does the Federal Reserve promote economic growth? A. Increase taxes and decrease spending B. Decrease taxes and increase spending C. Decrease reserve requirement, decrease discount rate, buy government securities D. Increase reserve requirement, increase discount rate, sell government securities 13. You have been studying the recent events in our economy. You observe the Gross Domestic Product and inflation are increasing, while unemployment is decreasing. Based on this info, you can infer that we are experiences a(n): A. Expansion Phase B. Peak Phase C. Contraction Phase D. Trough Phase 14. America is currently experience a time of slow economic growth with high unemployment. Based on that information, draw a conclusion as to which would be the best option for the government to turn the situation around: A. increase taxation and decrease spending B. decrease taxing, while decreasing spending at the same time C. increase taxing, while increase spending at the same time. D. Decrease taxing and increase spending 15. Currently, America is spending less than it is bringing in with taxes. This would be an example of A. Debt B. Shortage C Deficit D Surplus 16. In 2007, the US Economy suffered a real-estate crash leading to a rise in the unemployment rate in the United States. As a member of Congress, what action would you recommend Congress to take to stimulate the economy? a. Decrease the discount rate to encourage banks to borrow more money at a lower interest rate. b. Implement a tax rebate for first time home buyers c. Sell greater shares of securities to businesses and banks to reduce the US money supply d. Increase the Minimum wage within the US to encourage the employment of only qualified workers 17. Using the following graph, the GDP is increasing and the unemployment rate is decreasing. Which action will the Federal Reserve most likely to take to control the inflation rate? a. Reduce spending on the construction of interstate highways b. The Federal Reserve will advise banks to lower interest rates to encourage the stimulation more economic growth c. Increase the interest rates at which banks can borrow money from the Central bank d. Require makes to retain a lower percentage of every deposit 18. Congress needs to control the national debt from reaching 15 trillion dollars. Their tax revenue is estimated at 1.4 trillion dollars and expenses are projected at 1.7 trillion. How can Congress reduce the national deficit? a. Increase the tax rate from 7% to 9% over the next 7 years to reduce the national debt b. Increase the reserve requirement, which will enable banks to hold onto a greater percentage of every deposit. c. Defer the construction of the new Schmidt highway stretching from Chicago, IL to Jacksonville, FL estimated to cost 3 hundred billion dollars for one year. d. Increase spending on military planes knowing it will create new high paying jobs and a new tax stream for the National Government. 19. When would the use of open market transactions result in an increment of the economic activity? A. selling of government securities B. buying of government securities C. Increase of the Federal Reserve D. Increase of the discount rate 20. What fiscal policies should be considered when consumer spending is high, and prices are increasing dramatically? A. increase taxes, lower spending B. increase taxes, increase spending C. lower taxes, lower spending D. lower taxes, increase spending 21. What are the differences between price ceiling and price floor? A. price floor is above the equilibrium while price ceiling is under the equilibrium B. price floor is below the equilibrium while price ceiling is above the equilibrium C. price ceiling produces a decrease in demand and an increase in supply, while price floor produces an increase in demand and a decrease in supply D. price ceiling produces a decrease in demand, while a price floor produces a decrease in supply 22. Deflation is occurring and unemployment is increasing. The economy is likely in which phase of the Business cycle? (4.01) A. Contraction B. Expansion C. A Peak D. A Trough 23. Which is an example of a price control? (4.02) A. A single source for electricity in your community B. Rent Controlled apartment C. Police and fire protection D. Natural resources 24. Unemployment is high and deflation has begun. Gross Domestic Product is decreasing. The Federal Reserve may lower the discount rate at this point in order to… (4.04) A. Slow economic growth B. Increase the money supply because it encourages banks to grant more loans. C. Reduce the amount of money banks keep in their cash reserves D. Reduces the money supply because the banks are more reluctant to approve loans. 25. Unemployment is rising and inflation is decreasing. What could the Federal Reserve do to help in this situation? a. Raise the discount rate and sell government securities b. Raise taxes and cut spending c. Lower the discount rate and reserve requirement d. Decrease taxes and increase spending 26. Use the above image to answer the following question. When the economy is at Point B, the government would most likely a. Use contractionary fiscal policy b. Use contractionary monetary policy c. Use expansionary fiscal policy d. Use expansionary monetary policy 27. In the diagram above, what will happen if the price of gasoline is set at point B? a. The price of gas will fall b. The price of gas will rise c. There will be a shortage of gasoline d. There will be a surplus of gasoline 28. Government assisted housing is received by people living below the poverty line and helps to ensure they have affordable housing. If there was an increase in the number of people living below poverty due to a recession, synthesize the effect this would have on housing. a. There would be a surplus b. There would be a shortage c. Rent control would not be in effect d. The government would have to build more homes. 29. The Federal Reserve is responsible for the economic decisions regarding our monetary policy. What group in the Federal Reserve is responsible for controlling monetary policy? a) Banks b) Board of governors c) Open Market Committee d) President of the United States 30. Following U.S. involvement in Afghanistan in 2001-2010 and the related period of low unemployment and rising prices, the Federal Reserve intervened to increase growth and decrease recession. At what point in the business cycle did the Federal Reserve take action? a. Expansion b. Contraction c. Peak d. Trough 31. In which situation is a price floor more likely to occur? A: Minimum Wage B: Agricultural Products C: Clothing Manufacturers D: Government Housing 32. Which is not an example of a natural monopoly? A: US Currency B: Highway construction C: Computer sales D: Police force 33. Congress is operating a deficit, spending more than they are receiving in taxes. The Federal Reserve is buying government bonds at a rate of $85B a month. At what point are we in the business cycle? A. Point A B. Point B C. Point C D. Point D Module 4 Practice Exam V14 Answer Key 1. C: Point A is during a contractionary period, economic decline continues. 2. A: Setting a price below equilibrium price will create a shortage. More people will want potatoes than what sellers are willing to provide. 3. B: Examples of natural monopolies would be an electric company or water company. It makes more sense to have one set of pipes for water in a city than multiple providers and multiple sets of pipes, etc. This one company can provide water more efficiently than multiple providers. 4. C: Government regulations make sure that consumers are safe – for example, hot dog providers are regulated by the government to make sure that meat is used that is not rotten or from animals such as horses 5. C: The Federal Open Market Committee determines if adjustment of the money supply is needed based on economic outlook. They determine the use of buying and selling of bonds in open market operations, setting the reserve requirement, and setting the discount rate. 6. B: Raising the reserve requirement would mean banks need to hold on to more of their money and cannot loan out funds. By not being able to loan funds, they hope to slow the inflation rate. 7. A: During an economic downturn, lending slows and inflation slows. Therefore, prices will stagnate. 8. B: Increasing government spending puts more money into the economy. As there is more money in government programs, etc., businesses will hire more workers to increase production. 9. C: Making initial development private saves the government from funding ALL of the research, thus saving money to only partially fund research. 10. C: Remember that the Federal Reserve is the monetary policy and their tools are discount rate, reserve requirement and open market operations. The Federal Reserve will want to slow the money down in the economy to help fight inflation. By increase the discount rate which is the interest rate banks are charged to loan out money less businesses and people will be willing to get loans if they have to pay back more money to the bank. 11. B: expansionary fiscal policy. Remember that Congress is in control of fiscal policy. During the trough, Congress will decrease taxes and increase spending to help promote economic growth in the economy. 12. C: To help promote Economic growth the Federal Reserve will decrease reserve requirement to allow more banks to loan out money. They will decrease the discount rate which encourages businesses and people to get loans from the bank. They will buy back government securities. Remember that the Federal Reserve is in control of monetary policy. 13. A: When inflation and GDP increase and unemployment decreases, a country is experience an expansion phase because the economy is growing and expanding. 14. Rationale: D: If a time of economic growth is needed, the government would need to decrease taxing, while increasing spending so that more money is circulating in the economy. 15. D: When a person or country spends less than they are bringing in, it results in extra money, which would be classified as surplus. 16. B Taxing is a tool Congress used under the Fiscal Policy. By offering first time home buyers a tax rebate, it will encourage them to purchase homes versus renting, therefore, increasing bank loans for mortgages, ultimately leading to an increase in the money supply 17. C: The Federal Reserve controls the monetary policy. The 3 tools of the monetary policy include the discount rate, open market operations, and reserve requirement. Since the GDP is rising, we need to control the inflation level by reducing the money supply in the market. By increasing the discount rate, we are discouraging banks to borrow money from the central bank as well as discouraging consumers to take out loans. 18. C: Interstate highways are paid with Federal Tax money. A deficit is the overspending in one fiscal year. By deferring the construction, the National Government will be able to save 3 trillion dollars; therefore, spending equals the amount of revenue generated through taxes. 19. B: As they buy government securities, they take the bond and in turn pay out funds. These funds will enter the economy and hopefully boost economic activity. 20. A: Increasing taxes and lowering spending will slow down (contract) the economy during high inflationary periods. 21. A: A price ceiling means you cannot charge greater than that amount for a good, service, or rent. A Price Floor means that they cannot charge less than that amount, usually set above the equilibrium to protect the producer. 22. (A): During a contraction, the unemployment rate is increasing while the rate of inflation is decreasing. We call a period of falling prices "deflation." See Lesson of 4.01 23. (B): One example of “a price control is when the government sets the price below the equilibrium price. This means that buyers and sellers can exchange a good at prices less than the maximum price, but not greater. The primary goal of such regulation is to keep the price of a good low and thus more affordable for consumers. Rent control laws, for example, dictate how much a landlord can charge for rent in a specific area.” See page 2 of Lesson 4.02 24. (B): “Decreasing the discount rate is expansionary policy because it costs banks less to borrow from the Fed. This action increases the money supply because it encourages banks to grant more loans.” See page 3 of Lesson 4.04 25. C – In this situation, an expansionary measure is the best choice because unemployment is rising. The Federal Reserve uses monetary policy to influence the economy, so you must choose from the tools of monetary policy – the discount rate, the reserve requirement, and the discount rate. The tools of fiscal policy are taxing and spending, so those answers would not apply here. 26. A – Point B represents the peak of the business cycle. At the peak in the business cycle, inflation will be rising, so a contractionary policy will be used here. Because the question asks what the government would do here, you must also choose fiscal, rather than monetary, policy. 27. C – Point B is below the equilibrium, and this price point will result in a shortage of gasoline. 28. B: There would be a shortage in rent control due to the increase in need for housing. 29. C: The Open Market Committee controls monetary policy. 30. B: The action would take place in contraction due to the increase in unemployment and rising recessional effects. 31. B: Price floors usually benefit the seller of a product. The government may intervene when a product on the market sells too low to provide needed income. It is in these situations for which the government may create a price floor. Agricultural products are the best example here as we may see a minimum price set so Farmers may have income to live off of. The problem with any price floor occurs when there is a surplus of product thus farmers have goods that do not sell. 32. C: A natural monopoly is allowed because it is safer and more efficient for the system, business or good to be under government regulation rather than the market. US Currency, Highway construction and the Police force are all managed or provided for by the government. There are many computer sellers in the market and thus would be considered a monopolistic competition. 33. D: When Congress is running a deficit they are spending more than they are bringing in through taxes. When the Federal Reserve is buying bonds they are trying to push currency out to consumers to spend. This means we are in an expansionary period-Point D. **After the recent recession this is exactly where our economy is-expanding.








