Document
advertisement

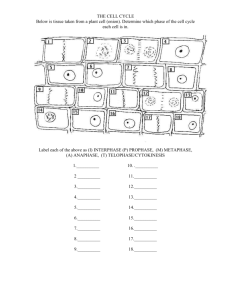
MEIOSIS LINDA HEIDENRICH BIOLOGY ALL ABOUT MEIOSIS Occurs in sex organs (testes and ovaries) Cuts the chromosome number in half Has two stages: Meiosis I and Meiosis II Follows PMAT Entire process preceded by INTERPHASE and succeeded by CYTOKINESIS PROPHASE I Just like mitosis Nuclear envelope disintegrates Chromosomes become visible and pair with homologous chromosomes to form a tetrad Spindle fibers appear METAPHASE I Homologous chromosomes align at the center of the cell http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Meiosis ANAPHASE I Homologous chromosomes move to opposite poles of the cell http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Meiosis TELOPHASE I Nuclear membranes reform Spindle fibers disappear DIFFERENCE: Chromosomes remain visible http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Meiosis MEIOSIS II (MITOSIS) REVIEW: Prophase: Nuclear envelope disappears, spindle fibers form Metaphase: Chromosomes align in the center of the cell Anaphase: Sister chromatids separate to different poles of the cell Telophase: Nuclear envelope reforms, spindle fibers disappear, chromosomes become invisible NONDISJUNCTION Term for what happens when homologous chromosomes or sister chromatids fail to split. Leads to trisomy (extra chromosome) or monosomy (too few chromosomes) http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Nondisjunction http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Down_syndrome