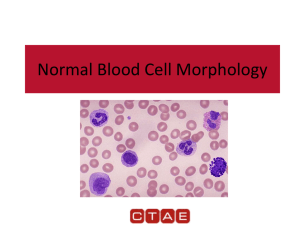
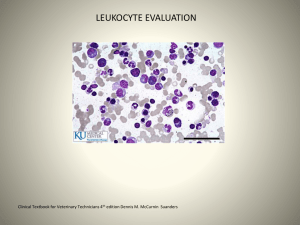
blood cells and plasma.
advertisement

Blood Overview of Blood Blood is a fluid connective tissue. Its total volume is about 5 liters. It has many functions. Blood is made of two parts: blood cells and plasma. Main Functions Transport of nutrients and oxygen to cells. Transport of wastes and carbon dioxide away from cells. Delivery of hormones and other regulatory substances to and from cells and tissues. Maintenance of homeostasis. Transport of humoral agent and cells of the immune system. Blood is made of two parts: blood cells and plasma. Plasma Its main component is water. plasma proteins (albumin, globulins, fibrinogen) A variety of solutes ,including dissolved gases (oxygen, carbon dioxide) , electrolytes (Na, Mg ,Ca), nutrients (glucose, lipids) , regulatory substances (hormones, enzymes) and waste materials (drugs,urea). What do blood cells include? Erythrocytes neutrophils granulocytes eosinophils Leukocytes basophils agranulocytes lymphocytes monocytes Platelets Erythrocytes Anucleate, biconcave disks. Quite flexible. Packed with protein hemoglobin. Main function is O2 and co2 transporting Few reticulocytes. Leukocytes-granulocytes Possess two types of granules: specific granules and azurophilic granules. Granulocytes have nuclei with two or more lobes. Include the neutrophils, eosinophils, and basophils. Neutrophils make up 60-70% of blood leukocytes Spherical, with a nucleus consisting of two to five lobes. cytoplasm is lightly eosinophilic contain specific granules(including bactericidal enzymes) and azurophilic granules The active phagocytes of bacteria and other foreign agents. Eosinophils make up 1-4% of blood leukocytes Nuclei are bilobed. Large and highly refractile acidophilic specific granules. Associated with allergic reactions, parasitic infections. Eosinophils Specific granules: major basic protein (MBP), eosinophil cationic protein(ECP), eosinophil peroxidase(EPO) and eosinophil-derived neurotoxin (EDN); ----destruct parasites. histaminase, arylsulfatase, collagenase. ----attenuate allergic reactions. Azurophilic granules: acid hydrolases. ----attenuate allergic reactions. Basophils Nucleus is divided into irregular lobes. Basophilic specific granules fill the cytoplasm.Specific granules contain heparan sulfate, histamine, and slowreacting substance of allergic reactions. Participate in allergic reactions , anticoagulation. Leukocytes-agranulocytes Do not have specific granules, but contain azurophilic granules. The nucleus is round or indented. Includes lymphocytes and monocytes. Lymphocytes make up 20-40% of blood leukocytes The spherical cell has a densely stained nucleus and a thin rim of blue-gray cytoplasm. T cells differentiate and mature in the thymus;B cells develop in bone marrow. main immune cells. Monocytes make up make up 3-10% of blood leukocytes The largest cells of the leukocytes. The nucleus is oval, horseshoe or kidney shaped and is eccentrically placed. The cytoplasm is basophilic Precursors of the cells of the mononuclear phagocytotic system. Platelets(thrombocytes) Nonnucleated, cytoplasmic fragments derived from megakaryocytes. Promote blood clotting and help repair gaps in the walls of blood vessels. Summary What is plasma? What do blood cells include? What is the characteristics of each kind of blood cells? Homework Review the characteristics of blood cells.