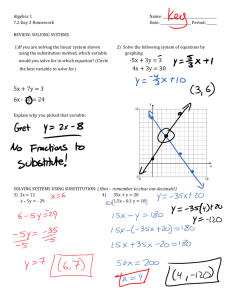
substitution reaction.
advertisement
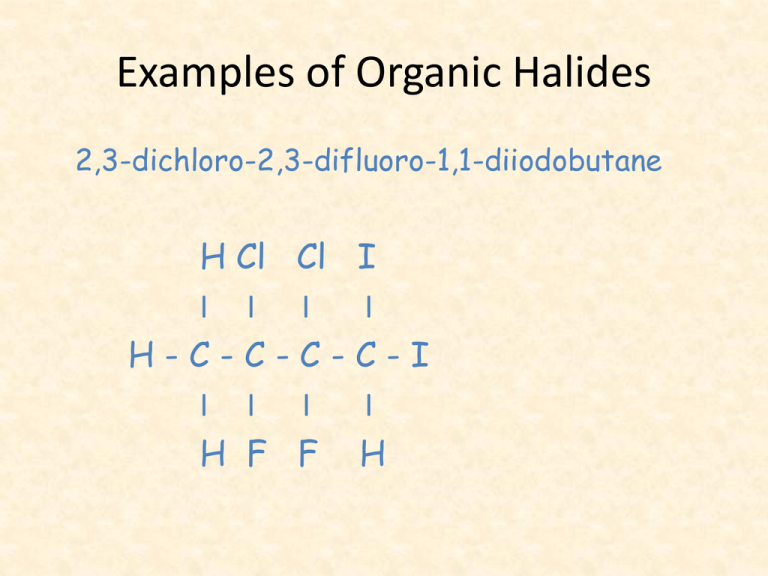
Examples of Organic Halides 2,3-dichloro-2,3-difluoro-1,1-diiodobutane H Cl Cl I I I H-C-C-CI I I H F F I I C-I I H Ozone Depletion • An environmental concern has been raised by this type of reaction, which ends up producing products known as chlorofluorocarbons (CFC’s). • These molecules have been used widely in foam products, as aerosol propellants and refrigerator/air conditioning coolants. • Their use has been banned in the last 10 years or so but they are still present in many older refrigerators and AC units. • Proper disposal of these appliances is essential to prevent further release of CFC’s. • CFC’s react in the atmosphere to destroy ozone molecules. • As a result of this destruction, deadly UV radiation passes through our atmosphere and causes skin cancer. • CFC’s have also been identified as a greenhouse gas and are so contributing to global warming. Answers to Activity 1. 2. 3. 4. bromobenzene chloroethane 3-chlorobut-1-ene 1,4-dichlorobenzene (p-dichlorobenzene) Organic Halide Reactions • Halocarbons are chemically reactive. • They are involved in a number of different reactions such as addition, substitution and elimination. • We will look at elimination reactions after looking at alcohols. Addition Reactions • These occur when a substance is added to double or triple bonds in alkenes or alkynes, since these bonds are reactive. • Addition reactions add a new functional group to a compound. Addition • When water is added, this is called a hydration reaction. This can occur when an alkene and water are heated to 100oC in the presence of a trace amount of a catalyst, such as nickel metal. H - C = C – H + HOH(l) I I H H ethene + water Ni H OH I I H-C-C-H I I H H ethanol Test for Unsaturation • The addition of bromine to the carboncarbon double or triple bonds is often used as a test for unsaturated organic molecules. • Bromine has a brownish-orange colour. • The loss of this colour when bromine is added to an organic compound is a positive test for unsaturation. • Although benzene has double bonds, it is stable and does not give a positive test for unsaturation with bromine. Example-Reaction 1 Pt H-C ≡C-H ethyne + + Br2(l) bromine Br I H-C=C-H I Br 1,2 - dibromoethene The addition of halogens to alkynes results in alkenes or alkanes. Example-Reaction 2 Br Br Br l Pt I I H - C = C - H + Br2(l) H-C-C-H I I I Br Br Br 1,2-dibromoethene + bromine 1,1,2,2 -tetrabromoethane Since addition reactions are very fast, the alkene produced, can undergo a second addition reaction. Substitution Reactions • Under the right conditions alkanes will undergo chemical reactions with halogens, such as chlorine: UV light • Eg: CH4 (g) + Cl2 (g) CH3Cl (g) + HCl (g) chloromethane • Note that in situations such as this, ultraviolet light (UV light) is included as a catalyst. Substitution Reactions • A chemical reaction in which an atom or a group of atoms replace another atom or group of atoms is called a substitution reaction. • In these reactions, the product of the previous reaction is reacted with chlorine again. • We continue this process to end up with products such as chlorinated solvents, paint removers and degreasing agent. Substitution Reactions • This involves the replacement of an atom or group of atoms by another atom or group of atoms. • For example: a halogen substituting hydrogen on an alkane to give a halocarbon: H H I I H-C-C-H I I H H ethane UV + Cl2(g) + chlorine Cl H I I H - C - C - H + HCl(g) I I H H chloroethane Substitution Example 2: This reaction is so slow that it requires both light and a catalyst. Substitution • Example 3: Alcohols may be produced by the substitution of a halogen by hydroxide ions: water & heat CH3CH2Cl (l) + NaOH(s) chloroethane CH3CH2OH (l) + NaCl(aq) ethanol Activity • Section 10.2 Questions 2-5 & 7.