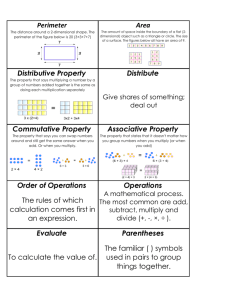
Lesson 13-2
advertisement
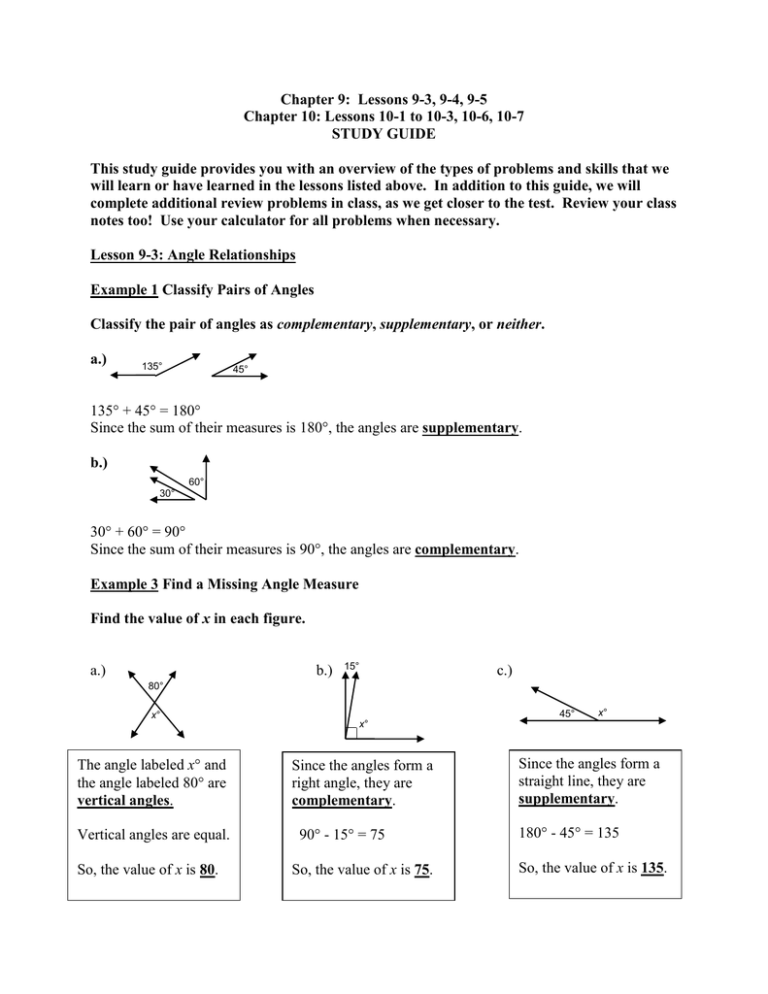
Chapter 9: Lessons 9-3, 9-4, 9-5 Chapter 10: Lessons 10-1 to 10-3, 10-6, 10-7 STUDY GUIDE This study guide provides you with an overview of the types of problems and skills that we will learn or have learned in the lessons listed above. In addition to this guide, we will complete additional review problems in class, as we get closer to the test. Review your class notes too! Use your calculator for all problems when necessary. Lesson 9-3: Angle Relationships Example 1 Classify Pairs of Angles Classify the pair of angles as complementary, supplementary, or neither. a.) 135° 45° 135° + 45° = 180° Since the sum of their measures is 180°, the angles are supplementary. b.) 60° 30° 30° + 60° = 90° Since the sum of their measures is 90°, the angles are complementary. Example 3 Find a Missing Angle Measure Find the value of x in each figure. a.) b.) 15° c.) 80° x° The angle labeled x and the angle labeled 80 are vertical angles. Vertical angles are equal. So, the value of x is 80. 45° x° x° Since the angles form a right angle, they are complementary. 90° - 15° = 75 So, the value of x is 75. Since the angles form a straight line, they are supplementary. 180° - 45° = 135 So, the value of x is 135. they are s Lesson 9-4: Triangles (Classify only) Example 1 Classify a Triangle by Its Angles Classify the triangle as acute, right, or obtuse. 60° 60° 60° All the angles are acute. So, the triangle is an acute triangle. Example 2 Classify a Triangle by Its Angles Classify the triangle as acute, right, or obtuse. 60° 90° 30° The 90° angle is a right angle. So, the triangle is a right triangle. Example 3 Classify a Triangle by Its Sides Classify the triangle as scalene, isosceles, or equilateral. All three sides are congruent. 4 in. So, the triangle is an equilateral triangle. 4 in. 4 in. Lesson 9-5: Quadrilaterals (classify only) Example 1 Classify Quadrilaterals a.) b.) square c.) trapezoid d.) rectangle parallelogram Lesson 10-1: Perimeter Example 1 Perimeter of a Square CARPET The Brown family is having new carpet installed in their family room. The room is a square that measures 18 feet on each side. What is the perimeter of the family room? P = 4(s) P = 4(18) P = 72 feet Perimeter of a square Replace s with 18. Multiply. The perimeter of the room is 72 feet. Example 2 Perimeter of a Rectangle 3m Find the perimeter of the rectangle. 9m P = 2ℓ + 2w P = 2(9) + 2(3) P = 18 + 6 P = 24 meters Write the formula. Replace ℓ with 9 and w with 3. Multiply. Add. The perimeter is 24 meters. 9m 3m Lesson 10-2: Circles and Circumference Example 1 Find the Radius The diameter of a circle is 8 centimeters. Find the radius. d 8 cm r=2 8 Radius of circle r=2 Replace d with 8. r=4 Divide. The radius is 4 centimeters. Example 2 Find the Diameter The radius of a circle is 10 inches. Find the diameter. 10 in. d = 2r d = 2 ∙ 10 d = 20 The diameter is 20 inches. Diameter of circle Replace r with 10. Multiply. Example 3 Find the Circumference Find the circumference of the circle. 4 ft The diameter of the circle is 4 feet. C = d Circumference of circle C = 3.14 ∙ 4 Replace with 3.14 and d with 4. C = 12.56 ft Multiply. The circumference is about 12.56 feet. Example 4 Find the Circumference Estimate the circumference of the circle. The radius of the circle is 7 centimeters. 7 cm C = 2r C = 2 ∙ 3.14 ∙ 7 C = 43.96 cm Circumference of circle Replace with 3.14 and r with 7. Multiply. The circumference is 43.96 centimeters. Lesson 10-3: Parallelograms Example 1 Find Areas of Parallelograms Find the area of the parallelogram. The base is 3 units, and the height is 6 units. A = bh Area of parallelogram A=36 Replace b with 3 and h with 6. 2 A = 18 units Multiply. The area is 18 square units or 18 units2. Example 2 Find Areas of Parallelograms Find the area of the parallelogram. A = bh A = 15 9 A = 135 in2 Area of parallelogram Replace b with 15 and h with 9. Multiply. The area is 135 square inches or 135 in2. Example 3 Real-World Example FLAGS An amusement park is designing a new flag for its entrance. The new flag is in the 3 1 shape of a parallelogram with a base of 84 feet and a height of 52 feet. Find the area of the new flag. A = bh Area of parallelogram 3 1 A = 84 ∙ 52 Replace b with 9 and h with 6. 1 A = 48 8 𝑓𝑡 2 Multiply. 1 𝟏 The area of the new flag is 48 8square feet or 𝟒𝟖 𝟖 𝒇𝒕𝟐 . Lesson 10-6: Volume of Rectangular Prisms Example 1 Find the Volume of a Rectangular Prism Find the volume of the rectangular prism. In the figure, the length is 18 inches, the width is 4 inches, and the height is 6 inches. Use V = ℓwh. V = ℓwh V = 18 4 6 V = 432 in3 Volume of rectangular prism Replace ℓ with 18, w with 4, and h with 6. Multiply. The volume is 432 cubic inches or 432 in3. Example 2 Real-World Example PACKAGING A box used to ship textbooks is a rectangular prism with length 2.75 feet, width 2 feet, and height 1.5 feet. What is the volume of the box? Find the volume. V = ℓwh V = 2.75 2 1.5 V = 8.25 ft3 Volume of rectangular prism Replace ℓ with 2.75, w with 2, and h with 1.5. Multiply. The volume of the box is 8.25 cubic feet or 8.25 ft3 Lesson 10-7 Example 1 Find the Surface Area of a Rectangular Prism Find the surface area of the rectangular prism. Find the area of each face. top and bottom: 2(ℓw) = 2(5 4) or 40 front and back: 2(ℓh) = 2(5 10) or 100 two sides: 2(wh) = 2(4 10) or 80 Add to find the surface area. The surface area is 40 + 100 + 80 or 220 square inches. Example 2 Real-World Example GIFT WRAP Julie needs to wrap a gift for her mother and is trying to determine how much wrapping paper she needs. The box has length 14 inches, width 9 inches, and depth 4 inches. Find the amount of wrapping paper Julie needs to cover the box completely. S = 2ℓw + 2ℓh + 2wh S = 2(14 9) + 2(14 4) + 2(9 4) S = 2(126) + 2(56) + 2(36) S = 252 + 112 + 72 S = 436 Surface area of a prism ℓ = 14, w = 9, h = 4 Simplify within parentheses. Multiply. Add. Julie needs 436 square inches of wrapping paper to cover the box completely.