Acid Nomenclature
advertisement

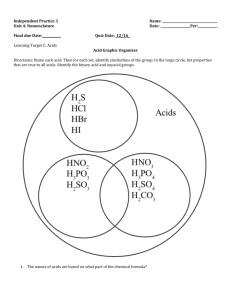
Acid Nomenclature Acid Nomenclature • Traditional inorganic acids contain hydrogen combined with a negative ion. To name these compounds, apply the following rules: A. Binary Acids – an acid that contains TWO elements – a hydrogen and a non-metal ion Naming Binary Acids • 1. Use the prefix hydro• 2. Use the root of the full name of the nonmetallic element • 3. Add the suffix –ic and the word acid Naming Binary Acids Hydro + root of non-metal + -ic and “ACID” • Examples: HCL hydrochloric acid H2Se hydroselenic acid Practice Problems • Name the following acids. – HBr – H2Se – HCl – HI – HF Practice Problems • Write formulas for the following acids: – Hydrofluoric acid – Hydrosulfuric acid – Hydrophosphoric acid – Hydrobromic acid – Hydroiodic acid Naming Ternary Acids B. Ternary Acids – “oxyacids” – acids that contain hydrogen and a polyatomic ion that has oxygen 1. Determine the name of the polyatomic ion (radical). 2. Change the radical’s ending i. -ate changes to –ic ii. -ite changes to -ous Naming Ternary Acids 1. Determine the name of the polyatomic ion (radical). 2. Change the radical’s ending i. -ate changes to –ic ii. -ite changes to –ous 3. Keep any prefixes like hypo- and per4. Add the word acid Radical name -ic (if ion ends in -ate) and ACID Or Radical name -ous (if ion ends in -ite) and ACID Examples HClO4 HClO2 HClO3 HClO Writing Formulas for Oxyacids Hydrogen is always listed FIRST. Look at the name of the acid and find the radical. Remember that the -ic ending came from the -ate ion and the -ous ending came from the -ite ion. Write the formula so the total charge is equal to zero. Examples Sulfuric Acid Sulfurous Acid Nitric Acid