MALE REPRODUCTIVE SYSTEM - mbbsclub.com

MALE REPRODUCTIVE
SYSTEM
Dr Iram Tassaduq
COMPONENTS
The male reproductive system consists of the testes, genital ducts and accessory sex glands .
The accessory sex glands include the seminal vesicles, prostate, & bulbouretheral glands.
FUNCTIONS
The testes have two functions: they produce the male gametes or spermatozoa, and they produce male sexual hormone, testosterone, which stimulates the accessory male sexual organs and causes the development of the masculine sex characteristics.
TESTIS
The adult testes are paired ovoid organs that lie within the scrotum, located outside the body cavity.
Testes are suspended by the spermatic cords and tethered to the scrotum by scrotal ligaments, the remnants of the gubernaculum.
STRUCTURE OF TESTIS
The testes have an unusually thick connective tissue capsule known as
tunica albuginea.
The inner part of this capsule, the tunica
vasculosa, is a loose connective tissue layer that contains blood vessels.
CAPSULE
Along the posterior surface of testis, the tunica albuginea thickens and project inwards as the medistinum testis.
LOBULES OF TESTES
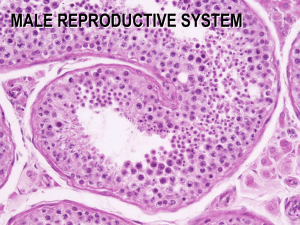
From the mediastinum, delicate fibrous septa radiate towards the tunica albuginea and divide the parenchyma of the testis into about 300 lobules, which communicate peripherally. Each lobule contains 1-4 convoluted seminiferous tubules
SEMINIFEROUS TUBULE
Each seminiferous tubule continues near the mediastinum into a straight tubule, a tubulus rectus. The straight tubules continue into the rete testis.
SEMINIFEROUS TUBULE
CELLS OF SEMINIFEROUS
TUBULE
The seminiferous epithelium is an unusual and complex striated epithelium composed of two basic cell populations:
◦ Sertoli cells (supporting or
Sustentacular cells)
◦ Spermatogenic cells
SEMINIFEROUS EPITHELIUM
1
. Spermatogonia
2. Primary spermatocytes
3. Spermatids
4. Developing spermatozoa
5. Sertoli cell nucleus
6. Myoepithelial cell of tunica propria
7. Interstitial cell of Leydig
7
SEMINIFEROUS EPITHELIUM
The most immature spermatogenic cells, called spermatogonia, rest on the basal lamina.
The most mature cells, called spermatids, are attached to the apical portion of the Sertoli cell, where they border the lumen of the tubule.
SPERMATOGENIC CELLS
These cells regularly replicate and differentiate into mature sperm.
These cells are derived from primordial germ
cells originating in the yolk sac.
Spermatogenic cells are organized in poorly defined layers of progressive development between adjacent Sertoli cells.
SERTOLI CELLS
are far less numerous than the spermatogenic cells and are evenly distributed between them. Their shape is highly irregular
SERTOLI CELLS
Also known as supporting, or
sustentacular cells.
These cells do not replicate after puberty.
Sertoli cells are
columnar cells with extensive apical and lateral processes.
FUNCTIONS
Support, protection and nutritional regulation of spermatozoa
Phagocytosis
Secretion
Production of AMH
Formation of blood testes barrier
LEYDIG CELLS
Leydig cells (interstitial
cells) are large polygonal eosinophilic cells that contain lipid droplets.
Lipofuscin pigment is also frequently present in these cells as well as distinctive, rod shaped cytoplasmic crystals, the
crystals of Reinke.
•
TUNICA (LAMINA)
PROPRIA
Also called peritubular tissue.
• This is a multilayered connective tissue that lacks typical fibroblasts.
•
In man, it consists of 3 to 5 layers of myoid
cells (peritubular contractile cells) and collagen fibrils, external to the basal lamina of the seminiferous epithelium.
BLOOD-TESTIS BARRIER
Adluminal compartment
The blood testis barrie r
Basal compartment
Interstitial compartment
DIAGRAM OF THE
TUBULAR
ARCHITECTURE
Spermatids
Primary spermatocyte
Intercellular bridge
Junctional complex
Spermatogonium
Basement membrane
Leydig cell
Blood vessel
DEVELOPMENT OF
TESTIS
The testes develop on the posterior wall of the abdomen and later descend into the scrotum.
Testis are derived from 3 sources:
Intermediate mesoderm
Mesodermal epithelium
Primodial germ cells