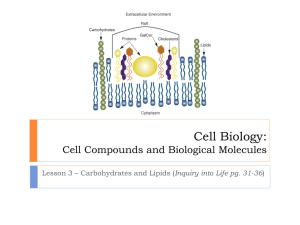
Carbohydrates and Lipids
advertisement
Organic = contains carbon ALL living things contain carbon So ALL living things are organic means “large molecule.” are made from thousands or even hundreds of thousands of smaller molecules. are formed by polymerization, the process in which large compounds are built by joining smaller ones together. Smaller units, called monomers, join together to form polymers, which are large compound formed from combinations of many monomers. Polymer=Marcomolecule Large molecules that contain carbon and are found in living things Four groups of organic compounds found in living things are 1)carbohydrates 2)lipids, 3)nucleic acids, and 4)proteins. are made up of carbon, hydrogen, and oxygen atoms Its monomers are called monosaccharides (one sugar) usually in a ratio of 1:2:1 (1 carbon, 2 hydrogen, 1 oxygen). Are used as main source of energy. Most end in –ose. Plants and some animals also use carbohydrates for structural purposes. There are three types of carbohydrates: 1) Monosaccharide 2) Disaccharides 3) Polysaccharides Single or simple sugar molecules are also called monosaccharides. (Ex. Glucose, galatose, fructose) Formula- C6H12O6 Two monosaccharides combined to form disaccharides (ex. Sucrose, Lactose, Maltose) Formula – C12H22O11 Large macromolecules formed from many monosaccharides are known as polysaccharides or complex sugars(Ex. Glycogen, Cellulose) Here are some examples of carbohydrates! Commonly known as fats, oils, and waxes. Its monomers are fatty acids and glycerol. Lipids are made of carbon and hydrogen atoms. Lipids can be used to store energy. Lipids are not soluble in water. Some lipids are important parts of biological membranes and waterproof coverings. Three Types of Lipids Phospholipids Triglycerides Waxes Three Types of Lipids Phospholipids- two fatty acids joined to one glycerol Three Types of Lipids Continued….. Triglycerides- three fatty acids joined to one glycerol Three Types of Lipids Continued……. • Waxes – many fatty acids joined to many glycerols Two Types of Fats Saturated and Unsaturated If each carbon atom in a lipid’s fatty acid chain is joined to another carbon by a single bond, the lipid is said to be saturated (contains the maximum possible number of hydrogen atoms) Solid at room temp Bad for you Examples: Butter, Lard, Shortening Two types of Fats Continued……. If at least one carbon-carbon double bond is on a fatty acid chain, the chain is unsaturated. Are liquid at room temp. Examples: peanut oil, corn oil, soybean oil Good for you Two Types of Fats Cont………. If there is more than one double bonded carbon, the chain is polyunsaturated. Stupid good for you!!!!