Chap 12 - Iowa State University
advertisement
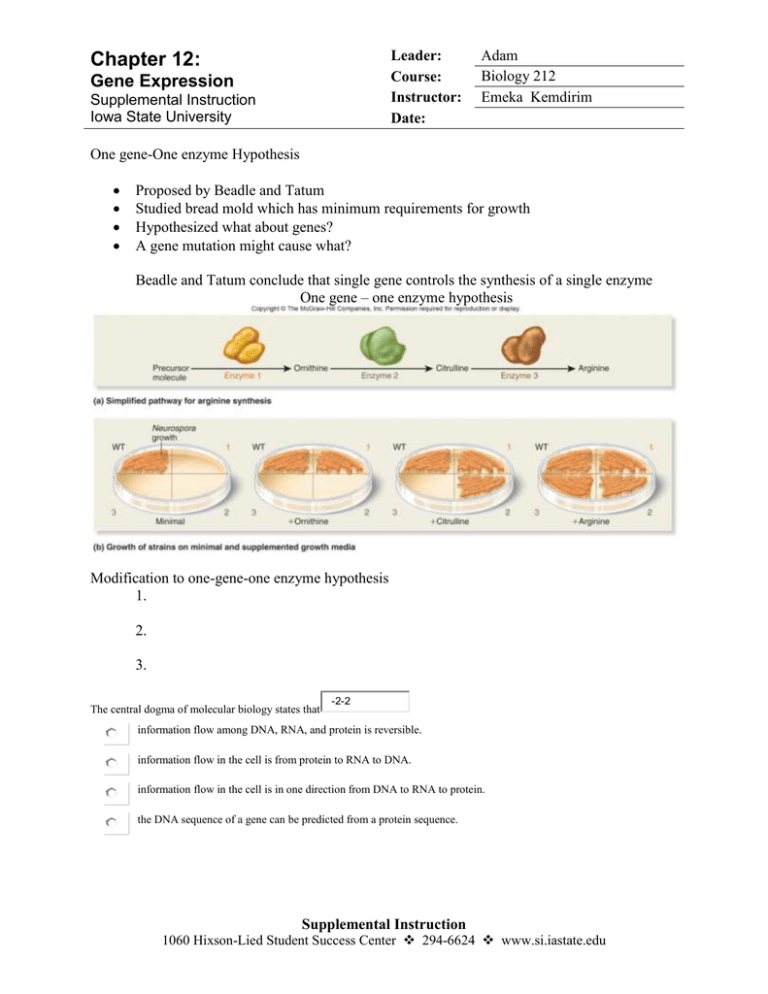
Leader: Course: Instructor: Date: Chapter 12: Gene Expression Supplemental Instruction Iowa State University Adam Biology 212 Emeka Kemdirim One gene-One enzyme Hypothesis Proposed by Beadle and Tatum Studied bread mold which has minimum requirements for growth Hypothesized what about genes? A gene mutation might cause what? Beadle and Tatum conclude that single gene controls the synthesis of a single enzyme One gene – one enzyme hypothesis Modification to one-gene-one enzyme hypothesis 1. 2. 3. The central dogma of molecular biology states that -2-2 information flow among DNA, RNA, and protein is reversible. information flow in the cell is from protein to RNA to DNA. information flow in the cell is in one direction from DNA to RNA to protein. the DNA sequence of a gene can be predicted from a protein sequence. Supplemental Instruction 1060 Hixson-Lied Student Success Center 294-6624 www.si.iastate.edu I. Transcription -produces an RNA copy of a gene DNA is transcribed into what? Transcription starts at site on DNA called ______ and ends at a site called _______? Three steps: 1. Initiation2. Elongation3. Termination Three forms of RNA polymerase 1. RNA polymerase II2. RNA polymerase I and III Transcription produces ________ that have to be further modified to get specific mRNA. Some segments are spliced out by what is called a spliceosome, segements that are sliced out are called what? Those left in the mRNA are called what? Pre-mRNA is further modified how? II. Transcription Process of synthesizing specific ________ at the ribosome The 3 nucleotide sequence on mRNA are called _______ and the three sequence of complementary nucleotides on tRNA are called ________. The start codon to begin the coding sequence codes for __________. Codons that stop translation are called what? Three stages, can you guess what they are called? 1. Which of the following best represents the central dogma of gene expression? 1. During transcription, DNA codes for polypeptides. 2. During transcription, DNA codes for mRNA, which codes for polypeptides during translation. 3. During translation, DNA codes for mRNA, which codes for polypeptides during transcription. 4. none of the above 2. Transcription of a gene begins at a site on DNA called _____ and ends at a site on DNA known as _____ . 1. an initiation codon, the termination codon 2. a promoter, the termination codon 3. an initiation codon, the terminator 4. a promoter, the terminator 5. an initiator, the terminator 3. The functional product of a structural gene is 4. 5. 6. 7. 8. 9. 1. tRNA. 2. mRNA. 3. rRNA. 4. a polypeptide. 5. a, b, and c. During eukaryotic RNA processing, the translated sequences that are not removed are called 1. exons. 2. introns. 3. promoters. 4. codons. 5. ribozymes. The is the site where the translation process takes place. 1. mitochondria 2. nucleus 3. ribosome 4. lysosome 5. ribozyme The region of the tRNA that is complementary to a codon in mRNA is 1. the acceptor stem. 2. the codon. 3. the peptidyl site. 4. the anticodon. 5. the adaptor loop. During the initiation step of translation, the first codon, , will enter the and associate with the initiator tRNA. 1. UAG, A site 2. AUG, A site 3. UAG, P site 4. AUG, P site 5. AUG, E site The movement of the polypeptide from the tRNA in the P site to the tRNA in the A site is referred to as 1. peptide bonding. 2. aminoacyl binding. 3. translation. 4. peptidyl transfer reaction. 5. elongation. The synthesis of a polypeptide occurs during which stage of translation? 1. initiation 2. elongation 3. termination 4. splicing