11._Voting_in_Congress
advertisement

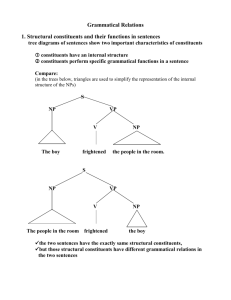
Voting in Congress Learning Objectives • To identify the factors that affect how members of congress vote • To investigate to what extent each factor affects members voting Pressures Political Party Constituents The administration Pressure Groups Colleagues and Staff Personal Beliefs Political Party • Can be the most important factor – ‘party votes’ on contentious issues. • Parties have few punishments/incentives to offer members. • Party labels don’t always mean whole party voting together (regional ideologies). • Internal party groups e.g. Blue Dog Democrats Constituents • Trustee model of representation Pause for Thought Representation • This term can be used in a number of different ways. • Representation can be understood in terms of how legislators represent their constituents. • In this sense there are three different models of representation – the trustee model, the delegate model, the mandate model and the resemblance model. Pause for Thought; Representation Trustee Model Delegate Model Mandate Model Resemblance Model The representative acts as the person who is vested with formal responsibility for the affairs of others. Such representation is based upon the considered judgement of the legislator. The elected representative is ‘trusted’ to make the right judgement. Constituents elect their representatives as delegates for their constituency. Essentially, the representative acts as the voice of those who are (literally) not present. Constituents elect their representatives and consequently provide them with a mandate to carry out certain policies that they have campaigned on. This model focuses on who represents the electorate, and considers how representative legislators are in terms of such factors as gender and race. Constituents • Trustee model of representation • “folks back home”, “locality rule” • Failing to look after/represent constituents can result in electoral defeat • Phone, email, local news, visits, letters from constituents • Regular visits “home” for party/town hall meetings, ‘surgeries’, local TV and radio, interviews with local media, addressing groups, visiting schools, hospitals etc. • Views of constituents = divided (discontented v content = representative?) • (National good + local popularity + electoral benefit) of policies to balance The administration • Members of the executive branch including POTUS, VPOTUS, cabinet members etc. • Legislation initiated by the administration – keen interest so in touch with members/committees to influence votes • Two way street of cooperation • Supporting unpopular legislation/administration can be costly Pressure Groups • • • • • • • • Try to influence members and votes Direct contact with members Attempt to generate public support Phone calls, make visits Provide evidence to committees Organise rallies, demonstrations and petitions Fundraising and campaigning Campaign donations Colleagues and Staff • Huge number of votes – impossible to be an expert on all issues and policies • Reliance on others for help • Colleagues – same party, same philosophy, same views – ‘mentors’, advice, suggestions • Senior staff – chief of staff or legislative director Personal Beliefs • Applicable on certain votes – usually abortion, capital punishment etc. • Generally members personal beliefs are similar to the majority of their constituents especially if a member adopts a trustee or mandate model of representation Pressures Political Party Constituents The administration Pressure Groups Colleagues and Staff Personal Beliefs • To what extent does each factor affect how a Member of Congress votes? • Can you identify a single “deciding factor”? • How do members balance all of these factors? EXAM FOCUS How do members of Congress decide to vote? How do members of Congress decide how to vote? Homework • Reading and Note Taking, Oversight of the Executive Branch, p215-219