Ionic Bonds
advertisement

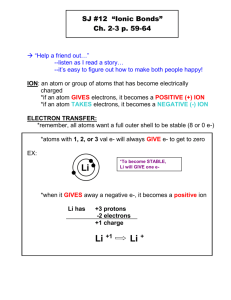
Ionic Bonds For review pages 211-227 Sections 8:1- 8:3 Forming Chemical Bonds The Formation and Nature of Ionic Bonds Names and Formulas for Ionic Compounds Valence Electrons • What are valence electrons – Valence electrons are the outermost electrons that are available for bonding • The number of valence electrons will determine how many bonds the atom can form. • What kind of elements form bonds – Atoms that have unfilled valence shells are considered unstable. Atoms will try to fill their outer shells by bonding with other atoms. How does an atom become a positive ion? When an atom loses an electron it becomes a positive ion called a cation. When a cation loses outermost valence electron(s): • Ionic radius is smaller than the atomic radius. • Achieves a stable octet like_________ Example: Sodium (Na) has 11 + and 11 - charges as a neutral atom. When it loses an electron it has 11 + and 10 - charges or a net charge of +1. When sodium cations look in the mirror they see _________. How does an atom become a negative ion? When an atom gains an electron it becomes a negatively charged ion called an anion. When anions gains an outer most valence electron: • Ionic radius is larger than the atomic radius. • Achieves a stable octet like_________ Example: Chlorine has 17 + and 17 charges. When it gains an electron, it have 17 + and 18 - for a net charge of -1. When a chloride ion looks in the mirror it sees ___ Atomic vs Ionic Radii Cations like Lithium get smaller Anions like Fluoride get bigger How do ions form neutral compounds? Positive and negative ions combine their charges which cancel out to form a neutral compound. Example: Na +1 + Cl -1 becomes NaCl with a zero net charge When do ionic bonds form • Ionic bonds form: – between metals and non-metals. – between oppositely charged atoms (ions). – by the transfer of electrons (exchanging). • One atom (cation) donates electrons to the high electronegativity element (anion) • One atom (anion) take electrons from low ionization energy elements (cations) Ionic compounds form crystals • Ionic bond between ions form crystals that are regular repeating structures called lattices. • In an ionic bond, oppositely charged ions are strongly held together by electrostatic forces. What characteristics do ionic compounds share? • A crystal structure when solid (lattice) • A high melting point -many strong bonds to overcome between the ions • A high boiling point -many strong bonds to overcome between the ions • A tendency to form ions in solution • Are conductors of electricity in solution or when melted • But nonconductors as solids How does electrical conductivity of ionic compounds change when they are melted or dissolved in water? Ionic Compounds tend to conduct electricity because their ions separate in water allowing for the transfer of electrons through the solution. Electrical conductivity is the ability of a material to carry the flow of an electric current (a flow of electrons). How many potassium ions are needed to balance the charge of one sulfide ion? • Potassium has a charge of +1. • Sulfide has a charge of -2. • It takes two potassium ions to neutralize one sulfide ion. K2S = Potassium sulfide Predict the formulas for calcium chloride and potassium phosphate? Answers CaCl2 K3PO4 What are polyatomic ions? + NH4 ammonium -3 PO4 phosphate Because they are composed of two or more different elements covalently bonded. Drawing Ionic Bonds • We can illustrate ionic bonding using Lewis structures. 1 – Draw the Lewis structure for each element. Ex: Na Cl 2 – Draw arrows to show the gain/loss of electrons Lewis Dot Formula continued 3 – Draw ion Lewis diagrams showing the new charge for each ion. Ex: The chemical formula for the compound formed represents the ratio of negative ions to positive ions. Ex: NaCl – for every 1 sodium ion, there is also 1 chlorine ion. Practice Drawing Ionic Bonds Elements Formula Calcium Fluorine Magnesium Bromine Lewis Ion Lewis Diagram Diagram Where do ions come from? • Ions can form in a solution. • Ionic bonds can form between a metal ion and a nonmetal ion or nonmetallic polyatomic ion • Usually from the breaking apart of the ions of a salt formed by an acid-base reaction or a metal and acid reaction. Ionic Compounds Form when reacting with an acid • Hydrogen will bond covalently with a nonmetal such as chlorine to form hydrochloric acid- HCl. • A metal will react with an acid to release hydrogen and form a metallic salt. Zn + 2 HCl ZnCl2 + H2 Okay, so is that all? An acid will also react with a hydroxide compound of a metallic ion and hydroxide (OH) ion to form an ionic compound and water. 3NaOH + H3PO4 Na3PO4 + H2O Sodium hydroxide and phosphoric acid become sodium phosphate and water Okay, so is that all? A nonmetallic ion such as ammonium can also form an ionic compound. NH4OH + HCl NH4Cl + H2O ammonium hydroxide and hydrochloric acid become ammonium chloride and water Ionic Compound Formulas The subscript indicates the number of ions of an element in a molecule of a compound. Na3PO4 Ca3(PO4)2 3 Na ion and 1 PO4 ion 3 Ca ions and 2 PO4 ions Note the parens around the polyatomic ion when a subscript is needed. Naming Ionic Compounds The first name of the ionic compound is the name of the positive ion. The second name is the name of the negative ion. positive ion negative ion For example: Magnesium sulfide Ammonium chloride Potassium oxide Vocabulary • • • • Ion- a charged atom Cation- a positively charged ion (lost electron) Anion- negatively charged ion (gained electron) Ionic bond- forms when electrons are lost or gained between ions • Ions in a crystal are arranged in a lattice.