Spinal Cord and Spinal Nerves
advertisement
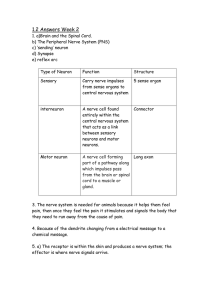
Spinal Cord and Spinal Nerves Major association,reflex and communication center Conduction route to and from the brain Structure of the Spinal Cord About 18 inches long Extends from the foramen magnum to the level of the 1st-2nd lumbar vertebrae Very well protected by the vertebral column, meninges, CSF, vertebral ligaments Gives rise to 31 pairs of spinal nerves MENINGES Pia mater sub-arachnoid space Arachnoid sub-dural space Dura mater Meningitis External Anatomy Cervical enlargement Lumbar enlargement Conus medullaris Filum terminale - extension of pia mater that anchors to coccyx Cauda equina Internal Anatomy Central canal containing CSF Anterior median fissure Posterior median sulcus Gray matter inner portion in the shape of a butterfly Anterior, posterior, and lateral gray horns White matter - 6 columns that contain ascending and descending fiber tracts These white tracts are paired and decussate Ascending tracts - Sensory tracts Descending tracts - Motor tracts Spinal Nerves Numbered and named according to the region of cord from which they emerge Designated by LETTER and NUMBER Coverings - endoneurium, perineurium, epineurium All are mixed nerves Arise from 2 roots Roots Dorsal root - is a sensory root contains sensory nerve fibers carrying impulses toward the CNS into the cord sensory cell bodies are located in the dorsal root ganglion Ventral root - is a motor root contains motor axons carrying impulses AWAY from the cord to the periphery motor neuron cell bodies are located in the gray matter of the cord Spinal Plexuses Cervical plexus - phrenic nerve Brachial plexus - axillary, radial, ulnar Lumbar plexus - femoral nerve Sacral plexus - sciatic nerve tibial nerve and common peroneal Reflexes Rapid, involuntary, automatic responses to stimuli Reflex Arc Receptor - distal end of a sensory neuron dendrite Afferent sensory neuron Integrating center - an association neuron or the spinal cord itself Effector neuron Effector - muscle or a gland Types of Reflexes Stretch reflex – patellar reflex Tendon reflex – produces relaxation in antagonist muscles Withdrawal reflex – touch hot object Crossed extensor - causes opposite motion on other side of body













![[Look for Links]](http://s2.studylib.net/store/data/010278761_1-67d2a1f48bd4ca974e00ec152449c3d2-300x300.png)
