Chapter 1 powerpoint
advertisement

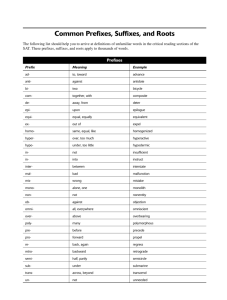
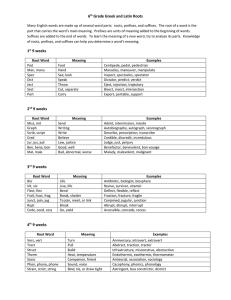
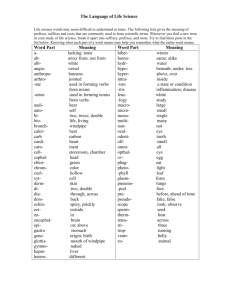
HTHS 1101 Chapter 1 Introduction to Medical language Medical Terminology Basics History The foundations of modern medicine stemmed from ancient Greek and Roman civilizations. Latin was the language of scholars and the language used to disseminate scientific discoveries for centuries. Most medical terms have their roots in Greek or Latin. Sometimes acronyms and eponyms are used as well. Medical Terminology Basics Word Parts Medical terms are comprised of roots, prefixes and suffixes. The root most often describes the body part, or body substance involved. The prefixes and suffixes describe what is happening to that body part or substance. hepatitis pneumonia electrocardiogram Medical Terminology Basics Pronunciation Medical terms can be long and complex The sounds associated with each part of the term are important to learn spelled out in the text phonetically fon-et-ik-al-lee The emphasis placed on the syllables of the word is also important the syllable receiving the emphasis is written in capital letters EM-fah-sis on the SIL-ah-bul Medical Terminology Basics Pronunciation Term: cardiac Divide into syllables: car/di/ac Pronounced as: KAR/dee/ak Term: cardiology Divide into syllables: car/di/o/lo/gy Pronounced as: kar/dee/AW/loh/jee Medical Terminology Basics Word Roots Roots function like nouns in medical language Often refer to body parts, organs or fluids We often add a vowel to make it a combining form gastr = root for stomach gastr/o = combining form meaning stomach Medical terminology roots can be divided into general purpose roots and anatomical roots The roots/combining forms presented in this chapter are especially important General Purpose Roots gen/o hydr/o morph/o myc/o necr/o orth/o path/o phag/o • • • • • • • plas/o py/o scler/o sten/o troph/o xen/o xer/o Anatomical Roots arthr/o cardi/o enter/o gastr/o hepat/o neur/o • hem/o or hemat/o • my/o or muscul/o • angi/o, vas/o or vascul/o • derm/o, dermat/o or cutane/o • pneum/o, pneumon/o or pulmon/o Suffixes Simple -ac -al -ar -ary -eal -ic -tic -ous -ia -ism -ium -y -icle -ole -ule -ula Suffixes Complex -iatrics -iatry -iatrist -ist -logist -logy -algia or dynia -cele -emia -iasis -itis -lysis -malacia -megaly -oid -oma -osis -pathy -penia -ptosis -rrhage -rrhea -rrhexis -spasm Suffixes Complex -centesis -gram -graph -graphy -meter -metry -scope -scopy -desis -ectomy -pexy -plasty -rrhaphy -stomy -tomy Common Prefixes a-, ananti-, contradeante-, preprobrady- tachypostreabadcircum-, peridia- e-, ec-, execto-, exo-, extraen-, endo-, intraepisubinter- Common Prefixes bihemi-, semihyperhypomacromicromono-, uni oligopanpoly-, multicon-, syn-, symdyseu- Plurals Word Building Adding prefixes are easy, you just add them to the beginning of the root or root+suffix. Suffixes are a bit trickier A consonant at the end of a root and the beginning of a suffix would sound weird together, so add an ‘”o” to the root. hyperactive, tachycardia, periumbilical hepatomegaly, nephropexy, retinopathy If the suffix starts with a vowel or the root ends in a vowel, you don’t need to add a vowel antibiotic, scleroderma, orthostatic Making sense of Medical Terms When reading the word: Suffix first Then prefix (if there is one) Then root or roots How to translate: 1. Read the word 2. Say the word out loud 3. Break the word into parts (suffix, root, prefix) 4. Translate the parts 5. Reassemble the pieces into a statement Making sense of Medical Terms Translate bradycardia: 1. Read the word: bradycardia 2. Say the word: bray/dee/KAR/dee/a 3. Break the word into parts: brady/card/ia 4. Translate the parts in order: suffix: -ia means condition prefix: brady- means slow root: card means heart (rate) 5. Definition: condition of slow heart rate