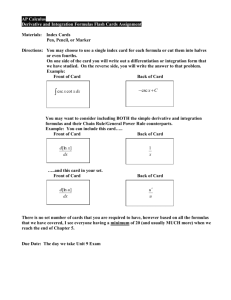
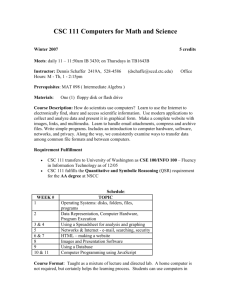
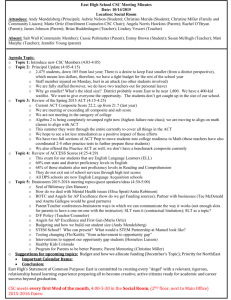
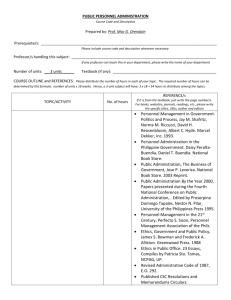
chain rule
advertisement

Find y´´ y csc x y csc x cot x y (csc x)( csc 2 x) (cot x)( csc x cot x) y csc3 x csc x cot 2 x) y csc3 x csc x cot 2 x y csc x(csc2 x cot 2 x) y csc x(csc2 x csc2 x 1) y csc(2csc2 x 1) y 2csc3 x csc x State Standard – 5.0 Students know the Chain Rule and its proof and applications to the calculation of the derivative of a variety of composite functions. Objective – To be able to use the Chain Rule to solve applications. We now have a pretty good list of “shortcuts” to find derivatives of simple functions. Of course, many of the functions that we will encounter are not so simple. What is needed is a way to combine derivative rules to evaluate more complicated functions. Consider a simple composite function: y 6 x 10 y 2 3x 5 If u 3x 5 then y 2u y 6 x 10 y 2u dy dy 2 6 du dx 6 23 dy dy du dx du dx u 3x 5 du 3 dx The Chain Rule: If f and g are both differentiable and F f g is the composite function defined by F ( x) f ( g ( x)) then F is differentiable and F ' is given by the product F ( x) f ( g ( x)) g ( x) In Leibniz notation, if y f u and u g x are both differentiable functions, then dy dy du dx du dx one more: y 9x 6x 1 2 y 3 x 1 y u 2 u 3x 1 2 If u 3x 1 then y u 2 y 9x2 6x 1 du dy dy 18 x 6 3 2u dx du dx dy 2 3 x 1 du dy 6x 2 du This pattern is called the chain rule. 18x 6 6 x 2 3 dy dy du dx du dx The Power Rule and Chain Rule: If n is any real number and u g ( x) is differentiable, then dy n n 1 du (u ) nu dx dx Also, d n n 1 g ( x) n g ( x) g '( x) dx Example 1 dy Find of dx y u y (4 3x) 9 u 4 3x 9 du 3 dx dy 8 9u du dy du du dx 9u ( 3) 8 27u 8 dy 8 27(4 3x) dx Example 2 dy Find of dx y (5x x ) y u 3 7 dy 6 7u du 4 7 u 5x x 3 4 du 15 x 2 4 x3 dx dy du 2 3 6 7u (15 x 4 x ) du dx dy 3 4 6 2 3 7(5 x x ) (15 x 4 x ) dx Example 3 dy Find of dx yu 3 dy 3u 2 du y (3x 7 x 5) 4 3 u 3x 7 x 5 du 12 x 3 7 dx 4 dy du 3 2 3u (12 x 7) du dx dy 4 2 3 3(3x 7 x 5) (12 x 7) dx Example 4 dy Find of dx y x 1 2 y u u 1 u x 1 2 2 dy 1 12 1 u du 2 2 u du 2x dx dy du 2/ x 1 2x du dx 2 u 2/ x 2 1 dy dx x x 1 2 Example 5 dy Find of dx y u 3 dy 4 3u du y 1 x 5 3 u x 5 du 1 dx dy du 3u 4 1 du dx 3u 4 dy 3 4 dx ( x 5) Worksheet