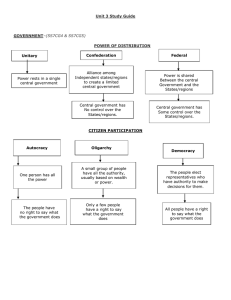
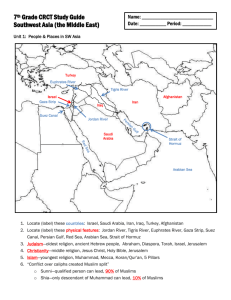
Countries in the Middle East Overview
advertisement

Hartanto, S.I.P, M.A. Lies on peninsula known as Asia Minor Lies on the continent of Europe & Asia Severe earthquakes occur in northern Turkey Anatolia – plateau region rimmed by mountains in central Turkey. Most people live in the northern part of Anatolia, on coastal plains, or in valleys. About 100% are Mulsims Turkish is the official language Istanbul – largest city and only city in world located on 2 continents Once part of the Ottoman Empire, Byzantine Empire, and Roman Empire Woven rugs http://www.travelerswonder.com/turkey/turkeytravel-information.html Dead Sea located between Israel and Jordan Desert in south Mediterranean climate Major agricultural export = citrus fruits Most industrialized country in SW Asia Mining is important to Israel’s economy About 80% of people in Israel are Jewish. The other 20% belong to an Arab people called Palestinians. Most are Muslims but there are a few Christians. West Bank and Gaza Strip – two areas given to the Palestinians Diplomatic Republic Deserts cover the region Water comes from wadis – dry riverbeds filled by rainwater from rare downpours Holds major share of the world’s oil Oil helped improve standard of living. $ helps build schools, hospitals, roads, and airports. Islamic holy city of Mecca (Makkah) is located in Saudi Arabia Islam influences life. Gov’t, business, school, and home schedules are timed to Islam’s five daily prayers and 2 yearly celebrations. Strict rules for women Once known as Persia An oil-rich nation World’s largest producer of pistachios More than ½ are Persians not Arabs or Turks Official language is Farsi, or Persian. Tehran – largest city and capital 98% are Muslim Many refugees from Iraq and Afghanistan have fled to Iran Islamic Republic – gov’t run by religious leaders Landlocked & covered by Hindu Kush mountain range. Khyber Pass – major trade route 20 different ethnic groups. 2 largest are Pashtuns and Tajiks. 70% of people farm and herd sheep & goats Fought Soviet in the 1980s. Then faced poverty, food shortages, and crime so turned to Taliban for leadership. Taliban – group of fighters educated at Islamic schools. Enforced strict laws Men had to grow beards Women had to completely cover themselves in public Women couldn’t hold a job or go to school There are many different types of economic systems in Southwest Asia. Many countries have mixed economies with different levels of government control. Some countries are less developed than others in the region. Southwest Asian countries have thrived on producing exports to other countries. Cash crops have included grain, silk, and cotton. For the last sixty years, the region’s main export has been oil. The region imports much of its food and other essential products. Israel has a mixed economy that is also technologically advanced. The Israeli government and private Israeli companies own and control the economy. Israel does not have many natural resources. Israel has to import grain, oil, military technologies, and many other goods. The country is a producer of high-tech equipment, some crops, and cut diamonds. The service industry accounts for much of Israel’s economy—areas such as insurance, banking, retail, and tourism account for over half of it. Israel relies heavily on U.S. economic and military aid. Saudi Arabia also has a mixed economy. The government largely controls the economy. Saudi Arabia’s main export is oil. The oil industry has made the Saudi royal family quite wealthy. In fact, several members of the royal family are among the wealthiest people in the world. Oil accounts for well over half of the country’s economy. Oil funds the country’s education, defense, transportation, health, and housing. The government of Turkey controls the country’s economy. Turkey’s economy, however, is not entirely a command economy. A large part of the country’s economy is based on farming. The Turkish government has had many disputes with other countries over its use of natural resources, such as the Euphrates River. Clothing and textiles are the country’s major industries. The service industry makes up about half of Turkey’s economy, as it does Israel’s economy. The entrepreneur Aydin Dogan controls the largest oil and gas company in Turkey, as well as two television networks and two newspapers. Such entrepreneurs are new to Turkey. Economic growth has been difficult to achieve for many Middle Eastern countries. War is a major threat to the region’s economies. For example, both war and a large number of immigrants present challenges to the Israeli economy. The Israeli government has taken control of certain economic activities in order to address these problems. The Israeli government controls most activities related to agriculture. In the last century, the Turkish government has played a major role in helping its economy to grow. After World War I, the Turkish government invested large amounts of money in Turkey’s weapons and steel industries. After World War II, many people objected to the Turkish government having so much control over the economy. By the 1980s, the government had begun to allow private businesses more control. Today, entrepreneurs play an important role in Turkey. Some gulf countries invest money to make their economies more diverse. In the last few decades, Saudi Arabia has begun encouraging the development of industries other than oil in order to make its economy stronger. In 1976, the Saudi government created the Saudi Basic Industries Corporation. The Saudi Basic Industries Corporation invests in capital goods. These capital goods have made the country a steady producer of steel, industrial gases, plastics, and petrochemicals. The natural resources of a country can affect economic growth. Most Southwest Asian economies were once based on farming. When oil was discovered, it became the main source of money for many countries in the region. Governments with large oil reserves stopped investing in other parts of their economies. Countries in the Southwest Asia that do not have oil are often poorer than countries that do. The region has many deserts and mountains and few rivers. This physical makeup causes it to be more difficult to produce and transport goods. Countries often spend money made from exporting oil on imports of items that are not available in the region.