ch07_sec1
advertisement
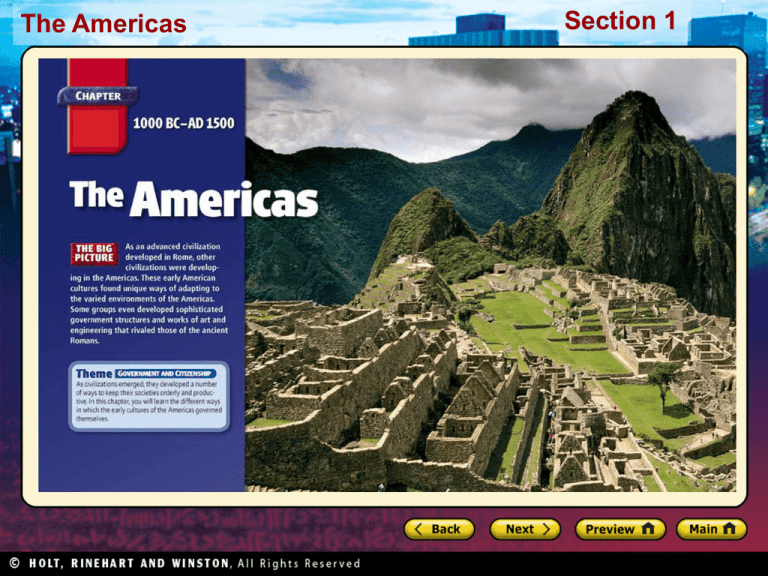
The Americas Section 1 Section 1 The Americas North America Preview • Starting Points Map: Environments of the Americas • Main Idea / Reading Focus • Cultures of the Desert West • The Mound Builders • Other Cultures of North America The Americas Click the icon to play Listen to History audio. Click the icon below to connect to the Interactive Maps. Section 1 Section 1 The Americas North America Main Idea As people settled in North America, they adapted to different types of geography by developing different styles of housing and ways of getting food. Reading Focus • How did cultures adapt to the environment of the Desert West? • How have scientists learned about the mound builders? • How did geography affect the Inuit, the Iroquois, and the Plains Indians? Section 1 The Americas Cultures of the Desert West Most of southwestern U.S. and northern Mexico is desert • Hohokam flourished from 100 BC to AD 1500 • Learned to farm in the desert – Built shallow canals for irrigation – Planted crops in earthen mounds next to canals – Woven mats created dams in canals, directed water to crop mounds Section 1 The Americas Cultures of the Desert West • Hohokam expanded irrigation system • Channeled water into villages – Used wells and other containers for storing water – Created pithouses, dwellings formed by digging shallow holes in the ground and building walls and roofs with mixture of clay and straw called adobe Section 1 The Americas Cultures of the Desert West The Anasazi lived in the Desert West near the Hohokam from about 100 BC to AD 1300. Pueblos Cliff Dwellings • Like Hohokam, Anasazi had pithouses • Another type of Anasazi architecture, cliff dwellings • Also developed the pueblo – Several stories high – Many rooms – Similar to apartments • Pueblos built in shallow caves in walls of rocky canyons • Villages also had underground rooms called kivas • Kivas used as meeting places, for religious ceremonies • To enter, rock staircases carved into rock or ladders • Limited accessibility offered protection from attack Section 1 The Americas Make Generalizations How did cultures of the Desert West adapt their architecture to their environment? Answer(s): used local materials such as clay and built pueblos in caves in high canyons Section 1 The Americas The Mound Builders Hopewell • Lived in eastern woodlands, near Ohio and Mississippi river valleys • Mound builders, 200 BC to AD 500 • Built large stone and earth mounds as burial sites • Size suggests some form of organized labor Burial Mounds • Hopewell buried objects like pottery and metal ornaments • Daggers of obsidian from Rocky Mountains • Shells from Gulf of Mexico • Clues that Hopewell developed extensive trade network • Culture began to decline AD 400, cause not clear Section 1 The Americas The Mound Builders Mississippian • Also lived in eastern woodlands, near Ohio and Mississippi river valleys • Built some of the earliest cities in North America • Cahokia had population up to 20,000 people • Contained more than 100 mounds, with ruler living atop largest in city center Cahokia • Planned city built by an organized labor force • Mathematical and engineering skills evident • Different types of soils in mounds for proper drainage • Artifacts show complex society, differences between common people and those with status Section 1 The Americas Summarize What do the mounds tell us about Hopewell and Mississippian society? Answer(s): Hopewell—extensive trade network; Mississippian—distinct social classes The Americas Section 1 Other Cultures of North America Cultures developed differently according to their environments • Varied geography determined the way these peoples got food • Also how they made their shelter • Environment also played a role in how societies organized The Inuit • Lived in the Arctic regions of North America • Frozen, treeless landscape meant no vegetation for food source • Became skilled hunters and fishers Year-round hunting • Used kayaks to hunt sea mammals, caught fish through holes in ice • Hunted caribou in summer, used skins and furs for warm clothing • Houses were igloos, made from ice blocks The Americas Section 1 Other Cultures of North America The Iroquois • Lived in eastern North America in warmer climate • Relied on materials from the forest • Built dwellings called longhouses from elm bark Hunting and farming • Trapped forest animals for food • Farmed crops such as beans, squash, maize Five different nations • Iroquois included Cayuga, Mohawk, Oneida, Onondaga, Seneca • Shared characteristics, eventually formed government, Iroquois League • Later admitted Tuscarora, but did not grant equal status The Americas Section 1 Plains Indians • Like Iroquois, Plains Indians consisted of different tribes • Not all spoke same language, communication problematic • Developed a form of sign language to communicate when they met • Lived mostly on a treeless grassland Europeans brought change • Plains Indians originally lived along rivers and streams • Introduction of horses by Europeans changed their lives • Followed buffalo herds over long distances • Buffalo center of lives, with buffalo meat as food, skins for clothing and tents, and bones and horns for tools The Americas Section 1 Identify Supporting Details What details show that the Inuit, Iroquois, and Plains Indians lived in different environments? Answer(s): Inuit lived in frozen, treeless landscape, no vegetation; Iroquois lived in forest environment, relied on trees and forest animals, farmed beans, squash, and maize; Plains Indians lived in treeless grassland, farmed along rivers, used horses to hunt buffalo used for food, clothing, tools