Mineral Notes

Chapter 5
1. Inorganic
2. Occurs naturally
3. Crystalline solid
4. Consistent chemical composition Gypsum
Fluorite
Salt?
Sugar?
Ice?
Charcoal?
Rock?
Scientists have identified 3,000 minerals
Of those minerals, there are 20 common
rock-forming minerals
All minerals are divided into 2 main groups: Silicate and Nonsilicate Minerals
Silicates
Nonsilicates
Must have Silicon and Oxygen
Usually has additional elements like Ca, Na, K,
Fe, or Mg
96% of Earth’s crust
Quartz and feldspar make up more than 50% of the crust
Do not contain silicon and oxygen
Make up 4% of Earth’s crust
There are 6 major classes
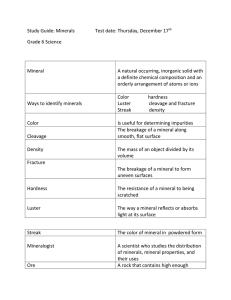
Mineralogists identify minerals based on a number of specific physical properties:
Color
Streak
Luster
Cleavage and Fracture
Hardness
Crystal Shape
Density
Easy to observe
Unreliable
Trace amounts of elements can change color
Weathering can change color
The same mineral can come in different colors.
Rubies are cut from corundum with traces of Chromium (Cr)
Sapphires are cut from corundum with traces of Cobalt (Co)
Color of the mineral in the powder form
More reliable than color
Use a
streak plate
Minerals that are harder than the streak plate will leave no streak because it is too hard to rub off on the plate
Light reflected from the mineral’s surface
Metallic luster
Nonmetallic luster
: waxy, pearly, glassy, dull/earthy, or vitrious/brilliant
Cleavage
is the tendency of a mineral to split along specific planes of weakness to form smooth, flat surfaces
Cleavage in three directions. Example: CALCITE
Fracture
is when the mineral does not split along cleavage planes
Fracture can be irregular, fibrous, or conchoidal
A measure of the ability of a mineral to resist scratching
Hardness relates to the strength of bonds between the minerals atoms (Ex:
Diamond vs.
Graphite)
To determine an unknown mineral’s hardness, you need to scratch it against a mineral of known hardness
TETRAGONAL, ORTHORHOMBIC,
HEXAGONAL, TRICLINIC, MONOCLINIC,
ISOMETRIC
Ratio of mass to volume of a substance
Density = mass/volume
Most minerals have a density between 2 and 3 g/cc
Lead
Density = 11.35 g/cc
Galena
Density = 7.6 g/cc
Fluorescence – ability to glow under UV light
Double Refraction – light is bent to produce a double image
Magnetism
Radioactivity