Adenosine Triphosphate
advertisement

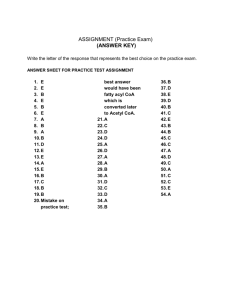
1. ATP (Adenosine Triphosphate): Energy storing molecule in cells composed of an adenosine, a sugar and 3 phosphate groups. 2. ADP (Adenosine Diphosphate): molecule formed from the breaking off a phosphate group for ATP: results in the release of energy. 3. Photosynthesis: process of trapping energy from sunlight with chlorophyll and use this energy to convert CO2 and water into simple sugars. 4. Light-dependent reactions: first phase of photosynthesis where light energy is converted into chemical energy in the form of ATP. 5. Light-independent reactions (Calvin Cycle): a series of reactions during the 2nd phase of photosynthesis in which simple sugars (glucose) and ATP 6. Pigment: molecules that absorb sunlight 7. Chlorophyll: light-absorbing pigment in plants that is required for photosynthesis: absorbs most wavelengths of light except green. 8. Electron Transport Chain: a series of proteins found in a membrane in which electrons are transported and when passed from one molecule to the next energy is released. 9. NADP+: carries electrons 10. Photolysis: reaction in the thylakoid membranes during light-dependent reactions where two molecules of water are split to form oxygen, hydrogen ions and electrons. 11. Cellular Respiration: chemical process where mitochondria break down food molecules to produce ATP 12. Anaerobic: does not require oxygen 13. Aerobic: reactions requiring oxygen 14. Glycolysis: in cellular respiration, series of anaerobic chemical reactions in the cytoplasm that breaks down glucose into pyruvic acid; forms a net profit of two ATP molecules. 15. Krebs Cycle: in cellular respiration, series of chemical reactions that breaks down glucose to produce ATP; energies the electron carriers that pass the electrons to the electron transport chain. 16. Lactic Acid Fermentation: anaerobic chemical reactions in which pyruvic acid uses NADH to form lactic acid and NAD+, which is then used in glycolysis; supplies energy when oxygen for aerobic respiration is scarce. 17. Alcoholic Fermentation: anaerobic process in which cells convert pyruvic acid into carbon dioxide and ethyl alcohol 1. ____________________ (Adenosine Triphosphate): Energy storing molecule in cells composed of an adenosine, a sugar and 3 phosphate groups. 2. _____________________ (Adenosine Diphosphate): molecule formed from the breaking off a phosphate group for ATP: results in the release of energy. 3. ______________________: process of trapping energy from sunlight with chlorophyll and use this energy to convert CO2 and water into simple sugars. 4. ________________________________: first phase of photosynthesis where light energy is converted into chemical energy in the form of ATP. 5. ________________________________ (Calvin Cycle): a series of reactions during the 2nd phase of photosynthesis in which simple sugars (glucose) and ATP 6. ____________________: molecules that absorb sunlight 7. ____________________: light-absorbing pigment in plants that is required for photosynthesis: absorbs most wavelengths of light except green. 8. ____________________: a series of proteins found in a membrane in which electrons are transported and when passed from one molecule to the next energy is released. 9. ____________________: carries electrons 10. ___________________: reaction in the thylakoid membranes during light-dependent reactions where two molecules of water are split to form oxygen, hydrogen ions and electrons. 11. ___________________: chemical process where mitochondria break down food molecules to produce ATP 12. ___________________: does not require energy 13. ___________________: reactions requiring oxygen 14. ___________________: in cellular respiration, series of anaerobic chemical reactions in the cytoplasm that breaks down glucose into pyruvic acid; forms a net profit of two ATP molecules. 15. ___________________: in cellular respiration, series of chemical reactions that breaks down glucose to produce ATP; energies the electron carriers that pass the electrons to the electron transport chain. 16. _______________________________: anaerobic chemical reactions in which pyruvic acid uses NADH to form lactic acid and NAD+, which is then used in glycolysis; supplies energy when oxygen for aerobic respiration is scarce. 17. _______________________________: anaerobic process in which cells convert pyruvic acid into carbon dioxide and ethyl alcohol