Sentencing II
advertisement

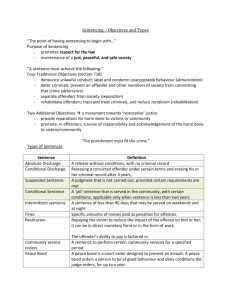
SENTENCING Overview/Review The “PSI” and “Risk Assessment” Sentencing Disparity Sentencing Guidelines Who Dictates Time Served? Review • The penalty ordered by the court after a defendant has been convicted of a crime • Structures • Determinate vs. Indeterminate • Mandatory (mand. minimum, mand prison) • Truth in Sentencing, 3-Strikes, Life W/O Parole • Concurrent vs. Consecutive Sentencing Options • Secure Confinement • Prison/Jail • Split sentences, shock probation • Intermediate Sanctions • Halfway houses, boot camps, electronic monitoring • Community • Probation, Intensive Probation • Fines, Restitution, Community Service • Other “conditions of probation” Considerations at Sentencing • Presentence investigation report (PSI) • Social history • Current employment, family, housing status • Information about current offense(s) • Victim statement, police report, etc. • Criminal history • Sentencing recommendation • Guideline score (offense-based, grids) • Risk assessment • Legal issue—should defendant be allowed to see the PSI? • Uses beyond sentencing Risk Assessment • Actuarial prediction of the risk for reoffending • History: emerged in the 1980s, became common 1n 1990s • Interview and/or review of criminal file • Criminal history factors • Static prediction • Salient factor score • Dynamic • Level of supervision inventory Sentencing Guidelines • Emerged as an alternative to indeterminate sentencing structures in the 1980s • Conservatives and liberals both embrace • Advisory vs. Presumptive • United States v. Booker (2005) • Grids or scales with instructions • Prison/not, length of sentence • Mitigating/aggravating circumstances • Created by “sentencing commissions” • Variation in purpose, structure, how “political” Sentencing Disparity • Legal factors • Prior record • Offense seriousness • Extralegal factors • Gender, race/ethnicity, social class • Demeanor • Family situation • Employment • Some are viewed as “legitimate,” others not… Do Guidelines Reduce Disparity? • Legal factors explain most sentencing differences • Some studies find that, after controlling for legal factors, extra-legal factors still matter (but are weak predictors) • Gender most common • Race (sometimes) • Not much sentencing disparity to reduce • Studies mixed on whether they reduce disparity Sentencing Discretion • Who plays a role in a sentence? • Legislature • Front end / back end • Probation (PSI) • Prosecutor • Judge • Parole board/corrections official/PO • Discretion Hydraulics • “Indirect” sentencing by others Reasons why guidelines may not reduce disparity • Some biases are built into guidelines • Crack Multiplier • Prior Record • Based on “past practices” • Bias from other sources • Discretion shifted to prosecutors • Police create the “pool” of offenders Courtroom Workgroup • Judges, Defense Attorneys, Prosecutors, and Probation Officers share a set of informal norms/rules • “The Going Rate” • Legal Variables • Relationship between victim/offender, mitigating/aggravating circumstances • Prosecutor charging decisions (plea negotiations) • Probation Officer PSI recommendations