The Urinary system
advertisement

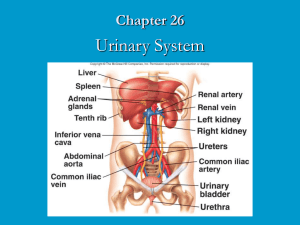
THE URINARY SYSTEM By; Aarynn M, Lauren Br, and Becky D Functions • To remove certain salts and nitrogenous wastes • Maintain normal concentrations of water and electrolytes • Regulation of pH • The volume of bodily fluids • Along control of red blood cell production and blood pressure management Organs in the urinary system • Kidneys • Tubular ureters • The urinary bladder • Tubular urethra The kidneys • Structure • Laterally convex • Medially concave • Hilum- ureter passes through • Renal pelvis- at the superior end of ureter • Pelvis divides twice • 1. major calyces • 2. minor calyes Kidney function • Help maintain homeostasis • Balance ph • Secrete hormones (aka renin & erythropoietin) Renal blood vessels aka •Renal artery hilum interlobar arteries arcuate arteries interlobar arteries afferent arterioles renal vein inferior vena cava nephrons • Contain renal corpuscles and renal tubules • Corpuscle is made of glomerulus • Glomerular capsules surround glomerulus and receives fluid from glomerulus filters • proximal convoluted tubule becomes descending limb of nephron loop which in turn becomes ascending limb of nephron loop and turns into the distal convoluted tubule. Urine • Glomar filtration- plasma being filtered to create urine • Nephrons have two capillary networks • 1.filters fluid • 2.tubular reabsorption and tubular secretion • Reabsorption moves fluid back into the blood • Secretion moves substances from peritubular capillary into the renal tubular. • Waste and excess products leave the body • These wastes = urine Urine (2) • Urine is roughly 95% water • Composed of water and waste the kidneys must eliminate • The other 5% of urine is usually urea and uric acid • Urea- the byproduct of amino acid catabolism (is reabsorbed by filtration) • Uric acid- product of metabolizing nucleic acids (requires active transport • http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=oCQ-5iwTQvM Urine excretion • Made with in nephrons • Passes through renal palpitate • Goes to renal pelvis then ureters and urinary bladder • Exists the body through the urethra Diseases • Chronic Kidney Disease • Causes • Diabetes • High Blood Pressure • Treatments • Medicines to lower blood pressure • Control blood glucose • Dialysis • Kidney Transplantation Diseases • Polycystic Kidney Disease • Autosomal dominant PKD • Starts at the ages of 30-40 • Autosomal recessive PKD • Begins in the womb or months following birth • Causes • Genetic Disorder • Symptoms • Enlarged kidneys • Headaches, urincary tract infections, blood in urine , pain in the back and lower sides • Treatments • There is no treatment for PKD Work cited • http://en.wikibooks.org/wiki/Human_Physiology/The_Urinary_Syste m • http://www.studyblue.com/notes/note/n/practical-2/deck/6343870 • http://anatomyforme.blogspot.com/2008/05/pathways-of-fluidflow-through-kidney.html • http://www.ivyrose.co.uk/HumanBody/Urinary/Urinary_System_Nephron_Diagram .php