sentencing - LegalStudiesYr12LSC
advertisement

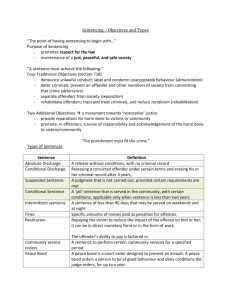
(POST – TRIAL) The Act states that the sentencing judge is obliged to consider the following when sentencing: Maximum penalty Current sentencing practices Nature and gravity of the offence Offenders culpability and responsibility Impact of the offence on the victim Injury loss or damage resulting from the offence Whether offender pleaded guilty – stage Offenders compliance during directions hearings Offenders previous character, previous convictions, significant contributions to the community Aggravating or mitigating factors Sentencing Discounts – less severe sentence due to guilty plea. (The act requires the court to state the amount of discount given for a plea of guilt where the sentence is of a custodial nature over 10 penalty units or an aggregate fine over 20 penalty units) Sentence Indicators –magistrate or judge (after reviewing summaries and materials before a case) advises the defendant of the likely sentence. An indication can only be given on the application of accused and may only be given once – unless the prosecution otherwise consents. If the indicator is given the accused pleads guilty the court may not impose a more severe sentence. 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. What is the aim of the sentence indicator and sentence discounts? How is this beneficial for the defendant and the legal system? What is the aim of a victim impact statement? What kind of things are included in a victim impact statement? What is the significance of the Sentencing (Further Amendment) Act 2005 (Vic)? Protection Punishment (Retribution) Sentencing Act 1991 (Vic) Section 5(1) Denunciation Deterrence (General and Specific) Rehabilitation Deferred sentence Aged between 17 to 25 Up to 6 months Opportunity for young offenders to address criminal behaviour Return for sentencing – court takes behaviour during deferred period into account Conviction or without conviction Long term serious consequences – employment opportunity Nature of the offence Character and past history Impact on offenders economic or social well being employment prospects Dismissal Guilty – without recording conviction Discharge Record conviction and discharge Record a conviction and adjourn for a period of up to 5 years and attach conditions (e.g. drug alcohol program etc) Levels (1 to 12) Each penalty unit $110.12 This enables enables the government to increase the value of penalty units without changing all the acts If unable to pay fine – imprisonment or community work (one day – for each penalty unit)(one hour of community work for each 0.2 penalty units) Undergo treatment to stop behaviour and undergo treatment or take part in education, vocational or personal development programs Guilty of an offence punishable by imprisonment or fine of more than 5 penalty units Court must receive a pre sentence report Offender must agree to comply Conditions apply to CBO (Page 377 to 378) Three requirements of CBO 1. Supervision – monitored regularly – community correction officer 2. A program (treatment and assessment) 3. Community service (40 to 120 hours) at least 12 hours in 7 day period In custody for no longer then 3 years Offenders aged between 15 and 20 years repeat offenders CSP (Client Service Plan) – participation in a range of activities Report to youth justice unit for up to 10 hours a week 10 to 18 – youth supervision order up to 12 months If a term of imprisonment is given of no more than 2 years in Magistrates court or 3 years in Supreme or County court whole or part can be suspended. During the time of the suspension if offender commits another offence- the original sentence will be restored together with a further sanction for a second offence. What is the significance of the Sentencing (suspended sentences) Act 2006 (Vic)? Second most severe punishment after imprisonment Aimed at offenders who have recieved shorter prison term Pre-sentence report, prison not more than 12 months, order served by way of ICO to the community Stringent conditions see page 381 Expressed as levels 1 to 9 (1 for life and 9 for 6 months) Parole – release after minimum served (conditions can be attached to parole) Concurrent and cumulative sentences Drug treatment orders Home detention scheme Hospital security orders and restricted involuntary treatment orders Indefinite sentences see page 387 to 389 Question 38 Read and summarise pages 394 to 405 Answer practice exam- Questions 1, 2, 3 page 404 (relevant to SAC)