Update on the NIST Smart Grid Standardization Efforts
advertisement

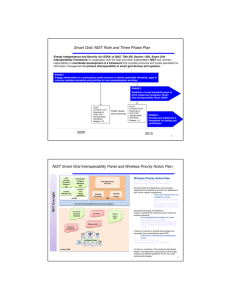
Update on the NIST Smart Grid Standardization Efforts Nada Golmie National Institute of Standards and Technology November 16, 2009 The NIST Role Energy Independence and Security Act (EISA) of 2007 Title XIII, Section 1305. Smart Grid Interoperability Framework In cooperation with the DoE and other stakeholders, NIST has “primary responsibility to coordinate development of a framework that includes protocols and model standards for information management to achieve interoperability of smart grid devices and systems…” Outline • Smart Grid Interoperability Panel • NIST Framework and Roadmap for Smart Grid Interoperability Standards – Priority Action Plan for IP – PAP#1 – Priority Action Plan for Wireless Communications – PAP#2 – Application communication requirements 3 NIST Three Phase Plan PHASE 1 Engage stakeholders in a participatory public process to identify applicable standards, gaps in currently available standards and priorities for new standardization activities PHASE 2 Public review and comments (Draft) Framework and Roadmap for Smart Grid Interoperability Standards ( Release 1.0) Establish a formal standards panel to drive longer-term progress. (Final) Framework and Roadmap for Smart Grid Interoperability Standards ( Release 1.0) PHASE 3 Develop and implement a framework for testing and certification 2010 March 2009 November 4 Smart Grid Interoperability Panel (SGIP) Vision • • • • • • Public-private partnership to support NIST EISA responsibility Open, transparent body Representation from all smart grid stakeholder groups Open to any materially interested stakeholder organizations Not dominated by any one group SGIP does not directly develop or write standards – Stakeholders participate in the ongoing coordination, acceleration and harmonization of standards development. – Reviews use cases, identifies requirements, coordinates conformance testing, and proposes action plans for achieving these goals. 5 NIST Oversight SGIP Structure Smart Grid Identified Standards Stakeholder Category Members (22) SGIP Standing Committee Members (2) One Organization, One Vote Use Cases At large Members (3) Ex Officio (non-voting) Members SGIPGB Priority Action Plans Requirement s Standing Committees Working Groups SGIP Smart Grid Interoperability Panel and Governing Board Standards Descriptio ns Conceptual Model Products (IKB) 6 SGIP Stakeholder Categories 1 Appliance and consumer electronics providers 12 Power equipment manufacturers and vendors 2 Commercial and Industrial equipment manufacturers and automation vendors 13 Professional societies, users groups, trade associations and industry consortia 3 Consumers – Residential, Commercial and Industrial 14 R&D organizations and academia 4 Electric transportation industry Stakeholders 15 Relevant Federal Government Agencies 5 Electric utility companies – Investor Owned Utilities (IOU) and Publicly Owned Utilities 16 Renewable Power Producers 6 Electric utility companies - Municipal (MUNI) 17 Retail Service Providers 7 Electric utility companies - Rural Electric Association (REA) 18 Standard and specification development organizations (SDOs) 8 Electricity and financial market traders (includes aggregators) 19 State and local regulators 20 Testing and Certification Vendors 21 Transmission operators and Independent System Operators 22 Venture Capital 9 Independent power producers 10 Information and communication technologies (ICT) Infrastructure and Service Providers 11 Information technology (IT) application developers and integrators 7 7 SGIP: Governing Board Vision • • • Maintains a broad perspective of the NIST Interoperability Framework and supports NIST Provides guidance and tools that make it an impartial and practical resource for SG stakeholders Members representing a broad community based on breadth of experience and involvement – Each stakeholder category has a position on Governing Board – Additional at-large and ex-officio members – Nominating committee process in steady state • Consensus is a core value – All legitimate views and proposals are considered – Voting mechanisms to be defined 8 First Phase Initial Output: NIST Framework and Roadmap for Smart Grid Interoperability Standards, Release 1.0 • A conceptual reference model to facilitate design of an architecture for the Smart Grid overall and for each of its networked domains; • An initial set of standards; • Priorities for additional standards necessary to resolve important gaps and to assure the interoperability, reliability, and security of Smart Grid components; and • Action plans for responding to short-term and longterm needs for standards, including recommended timetables and identification of necessary collaborative relationships with standards development organizations (SDOs) with expertise in Smart Grid domains or technology areas Smart Grid Priority Action Plans Target Date Smart meter upgradeability standard completed Common specification for price and product definition early 2010 Common scheduling mechanism for energy transactions year-end 2009 Common information model for distribution grid management year-end 2010 Standard demand response signals January 2010 Standard for energy use information January 2010 2010 IEC 61850 Objects / DNP3 Mapping Smart Grid Priority Action Plans (continued) Target Date Time synchronization Transmission and distribution power systems models mapping mid-2010 year-end 2010 Guidelines for use of IP protocol suite in the mid-year 2010 Smart Grid Guidelines for use of wireless mid-year 2010 communications in the Smart Grid Electric storage interconnection guidelines mid-2010 Interoperability standards to support plug-in December electric vehicles 2010 Standard meter data profiles year-end 2010 Harmonize Power Line Carrier Standards Just added for Appliance Communications in the Home Level of urgency • The $3.4 billion in U.S. Smart Grid Investment Grants, combined with matching $4.7 billion in private funds ($8.1 billion total) will result in deployment, over the next 3-4 years of – 40 million smart meters (about 1/4 of the total meter base in the U.S.) – 850 phasor measurement units covering 100% of the grid – 200,000 smart transformers – 700 automated substations – 1 million in-home displays – 170,000 smart thermostats – 175,000 other load control devices. • There is only a very small window of opportunity to specify the standards that will be used in these deployments since they will be completed within 3-4 years. 12 Smart Grid cyber security strategy • Cyber Security Coordination Task Group (CSCTG) to develop a set of recommended cyber security requirements http://collaborate.nist.gov/twikisggrid/bin/view/SmartGrid/CyberSecurityCTG • Draft NIST Interagency Report (NISTIR) 7628, Smart Grid Cyber Security Strategy and Requirements – Comments must be received on or before December 1, 2009 – How to provide comments: http://edocket.access.gpo.gov/2009/E9-24430.htm – Final document planned for publication in March 2010. 13 Issue: Role of Internet Protocol(s) in the Smart Grid • The Smart Grid will use a variety of different networking environments across different smart grid domains and sub-domains • Given its predominance and ubiquity, the Internet technology (IP) is a key networking technology to consider in the context of the Smart Grid • A number of challenges remain to be addressed due to the requirements imposed by many Smart Grid environments and applications: – What suite of IP protocols are applicable for specific Smart Grid applications? – What suite of IP protocols should be used for network control? management? security? – Are there any gaps with existing protocols? – Should new protocols/extensions be developed? IP PAP#1: Guidelines for the use of IP protocol suite in the Smart Grid • Develop Smart Grid application communication requirements and devise a taxonomy for applications with similar network requirements – Draft matrix under development and available for review http://collaborate.nist.gov/twikisggrid/pub/SmartGrid/PAP02Wireless/app_matrix_pap.xls • Identify a Core Protocol Suite for IP-based Smart Grid – IETF drafts and reports submitted for considerations http://collaborate.nist.gov/twiki-sggrid/bin/view/SmartGrid/PAP01InternetProfile • Develop Application-Specific Protocol Requirements – Identify additional protocols or protocol enhancements beyond the core suite required by a specific class of applications – Develop guidelines for IP-based Smart Grid networks • Perform Gap Analysis – Identify new protocol or protocol enhancement standardization activities required to fully support the Smart Grid Vision 15 Issue: Use of wireless communications in the Smart Grid • There are a number of advantages for using wireless communications including: – – – – – Untethered access to information Mobility Interoperability Reduced cost and complexity Availability of technologies with different characteristics to choose from • A number of challenges remain to be addressed: – How to choose among technologies with different characteristics? – How do we know which technology to use for what Smart Grid application? – Are there any implications for using a certain wireless technology in a certain environment? – Are there any deployment? Interference issues? Wireless PAP#2 Guidelines for the use of wireless communications in the Smart Grid • Develop Smart Grid application communication requirements and devise a taxonomy for applications with similar network requirements – Draft under development and available for review http://collaborate.nist.gov/twikisggrid/pub/SmartGrid/PAP02Wireless/app_matrix_pap.xls • • Develop terminology and definitions Create an attribute list and performance metrics for wireless standards – • • http://collaborate.nist.gov/twikisggrid/pub/SmartGrid/PAP02Wireless/NIST_PAP2-_Wireless_CharacteristicsIEEE802-v_02.xls Create an inventory of wireless technologies and standards that are identified by each SDO – • Draft developed and available for review Feedback is expected by December 6, 2009. Conduct an evaluation of the wireless technologies based on the application requirements Perform a gap analysis and developing guidelines for the use of wireless technologies. 17 Approach for developing application communication requirements • Develop a set of characteristics to capture the application communication – – – – • List a representative set of Smart Grid applications – – • • • How much data is being exchanged? How often is the data being exchanged? How much delay can data delivery incur? Who are the recipients of the data? Identify different applications or applications with different characteristics Applications belonging to a different Smart Grid domain are not necessarily different from this stand point Place characteristics and application types on a two dimensional matrix where columns represent the characteristics and rows represent application types Devise a taxonomy for applications with similar network requirements Fill out matrix entries 18 Progress to date on developing application communication requirements • • • • Reviewed many Smart Grid use cases, reports, white papers Reviewed FCC NOI filings on the implementation of Smart Grid technology – http://www.fcc.gov/Daily_Releases/Daily_Business/2009/db09 04/DA-09-2017A1.txt Developed a draft in cooperation with utility groups, Open SG, SG stakeholders, interested parties Posted draft for review on twiki and on PAP mailing lists – http://collaborate.nist.gov/twikisggrid/pub/SmartGrid/PAP02Wireless/app_matrix_pap.xls 19 Seeking input on the application communication requirements 1. Related to the application characteristics – or columns in the matrix: • Do you have any comments on the columns capturing the characteristics? Are there any missing columns? 2. Related to the application types – or rows in the matrix: • Are the rows representative of the Smart Grid space and domains? Are there any missing applications? 3. Related to the quantitative requirements – or matrix entries: • Do you have any numbers, aware of any numbers, reports that contain numbers? 20 What’s next First SGIP meeting held at the Grid-Interop Conference, November 16-19, 2009 in Denver, Colorado – SGIP charter ratification – SGIP governing board (electronic) elections and results – Priority action plan workshop Sources • NIST Smart Grid web site http://www.nist.gov/smartgrid/ • NIST Smart Grid Twiki http://collaborate.nist.gov/twikisggrid/bin/view/SmartGrid/WebHome • IP Priority Action Plan http://collaborate.nist.gov/twikisggrid/bin/view/SmartGrid/PAP01InternetProfile • Wireless Priority Action Plan http://collaborate.nist.gov/twikisggrid/bin/view/SmartGrid/PAP02Wireless 22