Chapter 10
advertisement

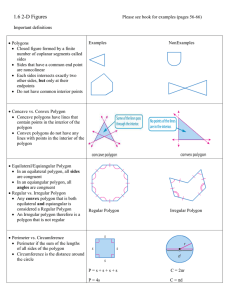
Polygons and Area Section 10-1 A polygon that is both equilateral and equiangular If all of the diagonals lie in the interior of the figure, then the polygon is convex. If any point of a diagonal lies outside of the figure, then the polygon is concave. Section 10-2 If a convex polygon has n sides, then the sum of the measures of its interior angles is (n-2)180 In any convex polygon, the sum of the measures of the exterior angles, one at each vertex, is 360. Section 10-3 For any polygon and a given unit of measure, there is a unique number A called the measure of the area of the polygon Congruent polygons have equal areas The area of a given polygon equals the sum of the areas of the nonoverlapping polygons that form the given polygon. Section 10-4 If a triangle has an area of A square units, a base of b units, and a corresponding altitude of h units, then A = ½ bh If a trapezoid has an area of A square units, bases of b1 and b2 units, and an altitude of h units, then A = ½ h(b1 +b2) Section 10-5 A point in the interior of a regular polygon that is equidistant from all vertices A segment that is drawn from the center that is perpendicular to a side of the regular polygon If a regular polygon has an area of A square units, and apothem of a units, and a perimeter of P units, then A = ½ aP All digits that are not zeros and any zero that is between two significant digits Significant digits represent the precision of a measurement Section 10-6 If you can draw a line down the middle of a figure and each half is a mirror image of the other, it has symmetry If you can draw this line, the figure is said to have line symmetry The line itself is called the line of symmetry If a figure can be turned or rotated less than 360° about a fixed point so that the figure looks exactly as it does in its original position, it has rotational or turn symmetry Section 10-7 A tiled pattern formed by repeating figures to fill a plane without gaps or overlaps When one type of regular polygon is used to form a pattern If two or more regular polygons are used in the same order at every vertex