Developing Innovative Regional Clusters
advertisement

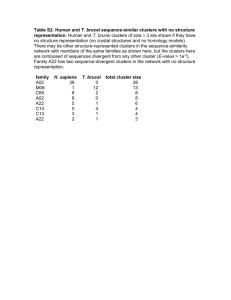
Developing Innovative Regional Clusters: State of the Art Philip Cooke Centre for Advanced Studies Cardiff University Knowledge Economy World Trade – High Tech 22% - KIBS 50% Key Cities 60-70% Knowledge Exports in UK, Italy & US Innovations/000 pop – US (SF, Boston, NYC) Explanation -‘Spillovers’ from Metro Agglomeration Cities & the Knowledge Economy 4 top US cities 400% more K intensive In UK M4 200% more K intensive Even east London (poorest part) above UK average E.g. Biosciences: Boston $1.1 billion NIH; Munich 12,000 Life Scientists; Heidelberg 13 spinouts per year Clusters Two basic types Porter ‘market’ led: Dalton (carpets) Cooke ‘science’-based: Cambridge (bio) Three variants in each ‘organic’ growth: Dalton/Cambridge ‘facilitated’ growth:Karlskrona/Oxford ‘induced’ growth: RTC/German Bioregio What Do policy Makers Want? Carpets (organic/market) vulnerable to competition from Developing Countries Science-driven ‘organic’ good but small and (in bio) scarcely profit generating but good at ‘rent seeking’ Facilitated can be good, but slow – RTC started in 1950s. BioRegios don’t have much in the ‘pipeline’ (next slide) European Biotechs, 2000 Source: Cap Drugs in Gemini Ernst & Pipeline Young, 2000 Number of firms Number of IPO Firms UK 128 223 48 Denmark 28 61 5 Ireland 23 29 2 Switzerl’nd 20 116 2 France 19 173 8 Sweden 18 158 9 Italy 7 50 2 Germany 6 317 15 Finland 5 81 1 Neths 5 77 4 Some Success Stories 1. Galician Fashion Industry Market-driven, ‘Organic’: La Coruna 3W Competition Drives Upmarket Regional (international) clustering Producers Become Design Intensive Integrate Design, Prod, Mktg – ‘Zara’ Outcompete Benetton, which VI’s Zara 1991, K19 jobs, 2001, K33 jobs 2. Karlskrona, Sweden Naval Shipyards Close > ‘Facilitated’ Leadership: (Firm, College, City) ‘Triple Helix’ Vision: TelecomCity Cluster Drivers: Ericsson, Vodafone, Sun, HP. 4,000 new jobs in the 1990s Networking: TC Association Social Environment: TC Youth Clubbing 3. Oxford Biotech (facilitated) Oxford BioTechNet (network: lawyers, patent agents, accountants, consultants, bankers, VCs etc). Fifty Core Biopharma firms. Terms – Free or Low Cost Advice & Work Mentoring – (1) Planning (BP, Fundraising, In-licensing, Incorporation etc) (2) Implementation (Systems, Interim Management, Outsourcing, Regulatory etc.) (3) Growth Phase ( Fundraising, Out-licensing, Marketing, supplyChain Management, etc. Northern Ireland (Induced) ‘IT Challenge’ accepted, ‘innovation system’ linkage Nortel & Fujitsu R&D facilities create 1,000 jobs (public-funded FDI) High Grade Human Capital Recruited from the 2 NI universities QUBIS and UU incubators Specialise in Software & Biotech 2 local VCs Subsidised - create Belfast cluster 200 telecom/internet software spinouts 4. Taiwan (ITRI) (Induced) Industrial Technology Research Institute Diffuses knowledge to SME clusters (Taipei) Mobile PCs lead, 1991 PPP consortium Data Switches dominating for PC networks to Ethernet standard 1992/3 IBM PowerPC emulated; Int. Proc. in 24 hrs. R&D Alliances in Digital Communications & Multimedia New moves into 1.2 litre 4-valve auto engine for China market. Knowledge Economies & Cities Why So Few Cities? Entrepreneurship-Growth-Investors (VCs) Key Cities Concentrate Knowledge Managers (‘symbolic analysts’) ‘Creative Class’ likes ‘Knowledge Cities’ (Richard Florida’s ‘Gay Index’ v ‘Easy Rider’ ‘Hazard County’ & ‘Boss Hogg’) Underperforming cities non-systemic in knowledge management. ‘System failure’ Concluding Questions & Answers Can knowledge-based cities be created? Yes, with Leadership, Vision & Cluster Drivers What are the Best Clusters? In a Knowledge Economy- Science-based (or Knowledgeintensive) What’s the Secret of Clusters? They Work in Cities Due to Knowledge Spillovers What are Knowledge Spillovers? Tips, Contacts, Specialised Services, ‘Intelligence, Insurance & Investment’ (The ‘3 I’s’)