Hcap & Hap - Clinical Departments
advertisement

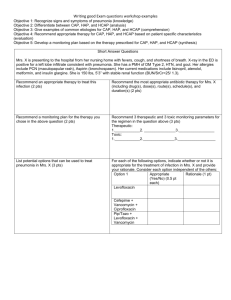
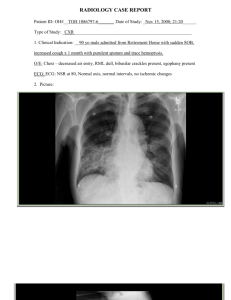
HCAP & HAP Pamela Charity, MD Cathryn Caton, MD, MS OBJECTIVES Define pneumonia Define HAP and review the characteristics Define HCAP Diagnosing HCAP and HAP Treatment of HCAP and HAP Review treatment algorithm KEY MESSAGES Be familiar with the following: Definition of both terms Start antibiotics within 4 hours of making the diagnosis Know which antibiotics to start empirically Know where to access the antibiogram Know how and when to de-escalate antibiotic therapy PNEUMONIA Fever Leukocytosis Infiltrate on CXR HOSPITAL ACQUIRED PNEUMONIA Category of pneumonia that occurs 48 hours or more after admission Encompasses healthcare associated pneumonia and ventilator associated pneumonia HOSPITAL ACQUIRED PNEUMONIA Time of onset Is an epidemiologic variable and Risk factor for specific pathogens and Affects outcomes HOSPITAL ACQUIRED PNEUMONIA Early onset Within first 4 days Better prognosis More likely to be caused by antibiotic-sensitive bacteria Above is true unless patient Received prior antibiotics Have had prior hospitalization within 90 days Greater risk for colonization and infection with MDR pathogens HOSPITAL ACQUIRED PNEUMONIA Late onset 5 days or more More likely to be caused by MDR pathogens risk factors for MDR Antimicrobial therapy in preceding 90 days Presence of risk factors for HCAP Immunosuppresive disease/therapy Increased morbidity and mortality HEALTHCARE ASSOCIATED PNEUMONIA Category of pneumonia in patients with recent close contact with the health care system Hospitalized for 2 or more days within last 90 days Resides in nursing home or long-term care facility Received recent IV antibiotic therapy, chemotherapy, or wound care within past 30 days Hemodialysis MAKING THE DIAGNOSIS History – this will determine the classification of pneumonia Physical exam findings Laboratory data Radiographic findings Antibiotics should be initiated within 4 hours of making the diagnosis. CHOOSING EMPIRIC ANTIBIOTICS HCAP and HAP are treated similarly Think about multi-drug resistant pathogens Gram Neg Pseudomona Aeruginosa – some are only sensitive to polymyxin B Serratia Marcescens Klebsiella Enterobacter Acinetobacter Gram Positive MRSA VRE CHOOSING EMPIRIC ANTIBIOTICS DE-ESCALATION OF ANTIBIOTIC THERAPY This may be appropriate if Clinical improvement at 48-72 hours Cultures are positive Treat for 7-8 days and reassess patient Single agent such as moxifloxacin may be appropriate May stop antibiotics if clinical improvement at 48-72 hours and cultures are negative TREATMENT ALGORITHM REFERENCES ATS/IDSA Guidelines Am J Respir Crit Care Med Vol 171. pp 388-416, 2005