The Spanish and the Native Americans
advertisement

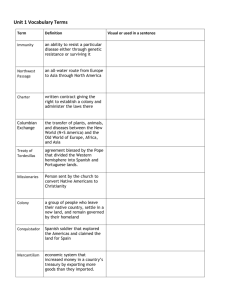
The Spanish and the Native Americans US History Spanish and the Native Americans • Main Idea: • Spanish rule in the Americas had terrible consequences for Native Americans. • Why It Matters Now: • The destruction of Native American cultures created social problems that continue today. Key Terms and Names • • • • Viceroyalty Encomienda Hacienda mission • • • • Popé Plantation Bartolomé de Las Casas Columbian Exchange Spanish Colonies in the Americas By 1700, Spain controlled much of the Americas. Two major steps to Govern the colonies: 1. Divided into two provinces: • New Spain • Peru Each province was called a viceroyalty, the top official was called the viceroy 2. Built new roads to transport goods and people • Moved soldiers quickly • Improved the economy, materials could be moved to the coast and sent more efficiently to Spain. Life in Spanish America Encomienda- was a grant of Native American Labor. Cortes received a grant of over 100,000 Native Americans to work on his estate. Hacienda- Large estates created to provide food for the colony. Usually became large farms where Native Americans worked to grow cash crops, like sugar cane, coffee, and cotton. Life in Spanish America Spanish Creoles Mestizos Native Americans & Enslaved Africans The Role of the Church Missions- settlements that included a church, a town, and farmlands. • The goal: to convert Native Americans to Christianity. The presence of the missions also increased Spanish control over the land. Sugar Plantations Develop The Spanish forced the Natives to work on plantations. Plantations- Large farms that produced cash crops. Sugar cane- Brought to the Caribbean from Europe. Tobacco Coffee The Abuse of Native Americans Many Spanish treated the Native Americans as nothing more than beasts of burden. “[The Spanish] do nothing but command. They are drones who suck the honey which is made by the poor bees, the Indians.” -Fray Toribio de Benavente, Catholic missionary Bartolomé de Las CasasReceived an encomienda, but faced a dilemma: How could a person serve God and Enslaved Natives at the same time? Gave up his encomienda, fought against the abuse of Native Americans, and earned the title “protector of the Indians” The Columbian Exchange The Columbian Exchange- The movement of plants, animals, and diseases between eastern and western hemispheres. Diseases: • Smallpox • Measles • Influenza • Malaria Estimates that 20 million Natives were killed by European disease in the first century after contact. Positive Benefits: • European livestock was brought to the Americas, and thrived: Cattle, pigs, horses • Crops from the Americas were brought to Europe: Potatoes, corn, tomatoes, peanuts, tobacco