organic
advertisement
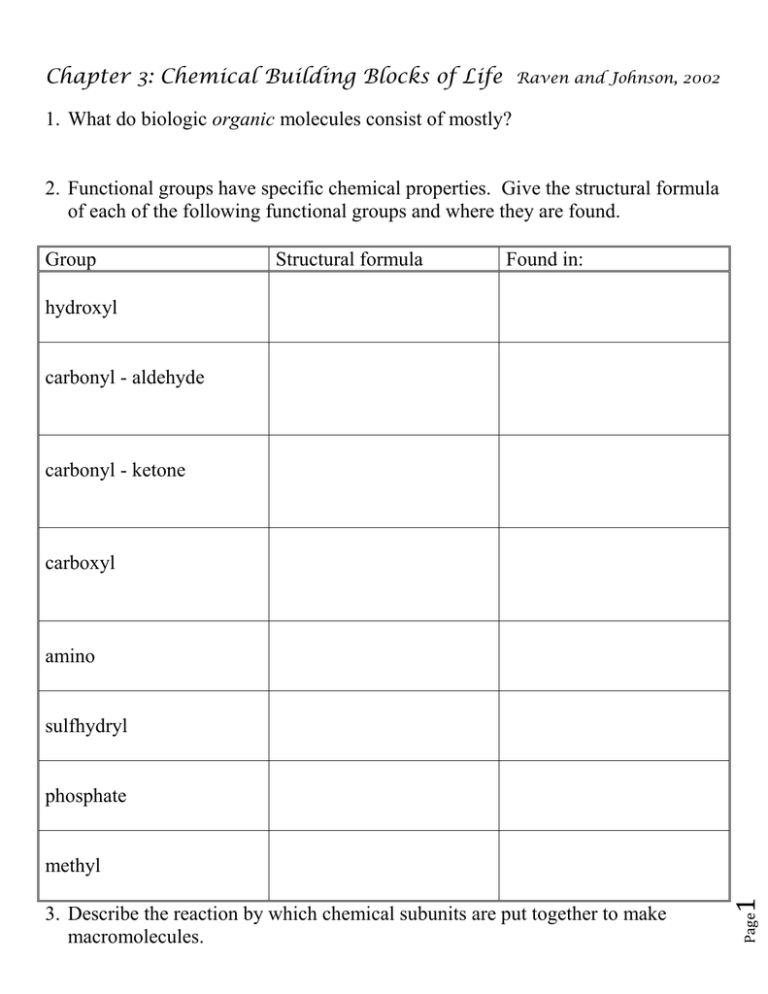
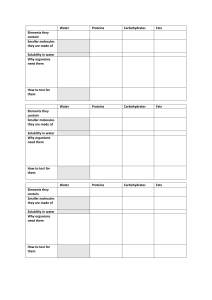
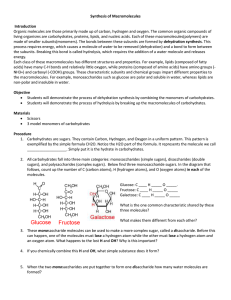
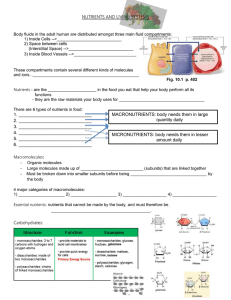
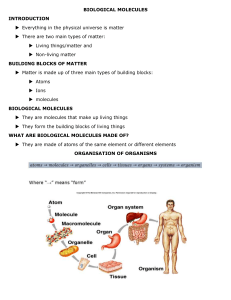
Chapter 3: Chemical Building Blocks of Life Raven and Johnson, 2002 1. What do biologic organic molecules consist of mostly? 2. Functional groups have specific chemical properties. Give the structural formula of each of the following functional groups and where they are found. Group Structural formula Found in: hydroxyl carbonyl - aldehyde carbonyl - ketone carboxyl amino sulfhydryl phosphate Page 3. Describe the reaction by which chemical subunits are put together to make macromolecules. 1 methyl Name ___________________________ Block ________________ 4. Describe the reaction by which macromolecules are disassembled into subunits. 5. What are the functions of proteins? Give an example for each. 6. Draw the structure of an amino acid. 7. What does the ‘R’ stand for? 8. What are the 5 side group categories? These are important in how proteins fold. Page 10. The way proteins fold is very important to how they function. What are the 4 levels of protein structure? Indicate what bonds are used to maintain these structures. 2 9. What is the bond called that connects amino acids into peptides? 11. What are motifs and domains? 12. What is the function of chaperonins? 13. What diseases can result from incorrectly folded proteins? 14. How does denaturation differ from disassociation? 15. What 2 molecules are important for information storage? 16. Draw a nucleic acid including all 3 components. 18. What are the basic structures of (a) DNA, (b) RNA, (c) ATP? Page 3 17. What is the difference between purines and pyrimidines? Draw them. 19. Phospholipids are the main molecules of biological membranes. Draw a diagram of the basic structure of a phospholipid. Include glycerol, fatty acids, and a phosphate group. Indicate the hydrophilic (water-soluble) and hydrophobic (water-insoluble) ends. 20. Describe and give examples of these other types of lipids: a. triacylglycerol b. steroids c. terpenes d. prostaglnadin 21. Why are saturated and unsaturated fats different structurally? 23. What are the two 5-carbon sugars? the three 6-carbon sugars? Page 4 22. What is the basic ratio of carbon, hydrogen , and oxygen in a carbohydrates? 24. What is an isomer? 25. What are the components of the disaccharides maltose, sucrose, and lactose? 26. Complex carbohydrates are energy-storage molecules. What are starch and glycogen, and where are they found? Page 5 27. Complex carbohydrates can also be used for structure. What are two important structural carbohydrates, and where are they found?