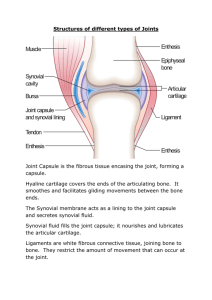
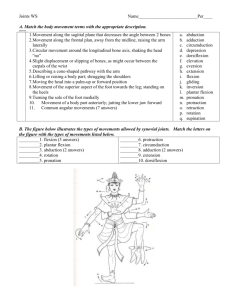
Joints
advertisement

Biology 322 Human Anatomy I Joints of the Skeletal System Previously: Defined bones as organs of skeletal system Also organs: joints (one or more types of tissues, all serving a common function) Joints: 1. 2. Classified two ways: Fibrous Joints: Bones connected by Depending on length of collagen fibers, Fibrous Joints: Three subtypes: 1. Fibrous Joints: Three subtypes: 2. Fibrous Joints: Three subtypes: 3. Cartilagenous Joints: Bones connected by Depending on length of collagen fibers, Cartilagenous Joints: Two subtypes: 1. Cartilagenous Joints: Two subtypes: 2. Synovial Joints: Bones separated by Synovial Joints: Components: Proximal bone with articular cartilage Distal bone with articular cartilage Articular capsule with: Fibrous capsule Synovial membrane surrounding Synovial cavity Ligaments of dense irregular C.T. Intrinsic = thickenings of fibrous capsule Extracapsular = outside of fibrous capsule Intracapsular = inside synovial cavity Synovial Joints: In knee, sternoclavicular, and temporomandibular joints: Also meniscus of fibrous cartilage Synovial Joints: Six types based on structure and type of motion: Synovial Joints: Six types 1. Synovial Joints: Six types 2. Synovial Joints: Six types 3. Synovial Joints: Six types 4. Synovial Joints: Six types 5. Synovial Joints: Six types 6. Synovial joints stabilized by a) b) Synovial joints stabilized by c) Synovial joints stabilized by d) Synovial joints stabilized by Synovial joints often cushioned by The following six specific synovial joints are described in your textbook: Jaw (Temporomandibular) Shoulder (Humeroscapular) Elbow (Humeroulnar, Humeroradial, Radioulnar) Hip (Femorocoxal or Coxal) Knee (Tibiofemoral) Ankle (Talotibial, Talofibular) On exams, you should be able to briefly but accurately describe the structure of each of these joints, including all major ligaments; and you should be able to describe the actions for each Movements of synovial diarthrotic joints: Flexion and Extension Movements of synovial diarthrotic joints: Abduction and Adduction Movements of synovial diarthrotic joints: Rotation and Circumduction Movements of synovial diarthrotic joints: Protraction and Retraction Movements of synovial diarthrotic joints: Elevation and Depression Movements of synovial diarthrotic joints: Inversion and Eversion Movements of synovial diarthrotic joints: Opposition (and Reposition)