Digestive System part II Chemistry and Cells
advertisement

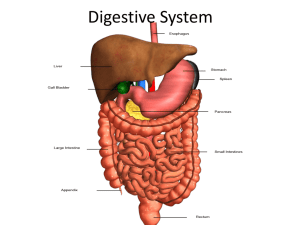
Digestive System part II Chemistry and Cells Atoms • Three major parts. – Protons: Positive Charge. Inside Nucleus – Neutrons: Neutral Charge. Inside Nucleus: – Electrons: Negative Charge. Outside Nucleus • 2 electrons in first shell • 8 electrons in the second shell • Eight is Great! Will not React with other atoms. • If the outer shell is not full it will react. Combining Chemicals Periodic Table Bonding • Compound: When two or more different elements combine. • Hydrogen Bond: H2O - H2O – When hydrogen bonds with another atom or molecule. Bonds are like Velcro. Make and break easily. • Covalent bond: CO2 – When atoms on the same side of the chart (same size) bond. Share electrons. • Both Hydrogen and Covalent bonds form molecules, ionic bonds do not. Ionic/ Covalent Bonds Combining Chemicals continued • Ionic Bonds: When atoms on different sides of the chart (different size) bond. Steal electrons. Create Ions. Make teeth and bones. – Ion: Charged particle either negative or positive. NaCl = table salt – Electrolytes: Ionic compounds that break into cations and anions when dissolved. (Salt) • Free Radical: Electrically charged ion with an unpaired electron in its outer shell. Antioxidants, What are they? • Substances that inactivate oxygen derived free-radicals • Slows damage from free-radicals • Examples: Selenium, Zinc Beta-carotene, Vitamins C & E Free Radicals Acai Berry Ph Scale • Measured on grams of Hydrogen (H+) – pH of 0= 1g of H+, pH of 1= .1g of H+ • Acid: form hydronium ions (H+) – pH of less than 7 ( 1 to 6.9) • Base: form hydroxide ions (OH-) – pH of more than 7 (7.1 to 14) • Acid + Base: salt & water, the solution is neutral with a pH of 7. – NaOH + HCL = H2O + NaCl with a pH of 7 What is a Buffer? • Chemical substances that neutralizes small amounts of an acid or base added to a solution. • Why are these important to your body? • three main buffers in the body: – bicarbonate buffer system: in the blood and stomach to neutralize acids – protein buffer system: inter and extra cellular buffering used with hemoglobin and blood – phosphate buffer system: used in the urinary system to remove H+ ions and make urine acidic Metabolism: All chemical reactions necessary to maintain life • Catabolism - substances broken down, energy released and captured to make ATP • Anabolism - larger molecules built from smaller ones • Question: Why are they called anabolic steroids? Chapter 19 Overview Of Digestion The Digestive System and Body Metabolism Takes in food, breaks it down into nutrient molecules and absorbs them into the bloodstream, then rids the body of indigestible remains https://www.supertracker.usda.gov/ The cartoon Pill Cam Metabolism & What We Eat • Carbohydrates (glucose) - broken down to make ATP, stored as glycogen. 1g= 4KCal • Lipids- build cell membranes, myelin sheaths, insulate, ATP. 1g= 9 KCal • Proteins - structural materials hoarded by body cells, ATP. 1g= 4KCal • What is a calorie? Energy value measured in kilocalories (Kcal) : amount of energy needed to raise the temp. of 1 kg of H2O 1 deg C. Anatomy of Digestive System • Alimentary canal – – or GI Tract - continuous hollow tube: mouth, pharynx, esophagus, stomach, small and large intestine • Accessory digestive organs - assist: teeth, tongue, glands Mouth (Oral Cavity) • Food enters – Mucus membrane-lined cavity – lips, cheeks, hard palate soft palate – uvula - fingerlike projection of soft palate Mouth • Tongue - attached to hyoid bone and styloid processes of skull – papillae containing taste buds on surface • Frenulum - secures tongue and limits its posterior movements Taste Salivary Glands - 3 pair • Parotid glands - anterior to ears – mumps is inflammation of parotid glands • Submandibular and sublingual glands empty secretions into mouth through ducts Saliva Polls Everywhere • Product of salivary glands, mixture of mucus and serous fluids –Creates a Bolus: mucus bound mass of food –Enzymes of saliva: • Amylase : for starch digestion • Lysozyme: kills bacteria Teeth • Masticate (chew) • Deciduous (baby or milk) teeth - first set (20); formed from 6 months to 2 years • Permanent teeth - cause baby teeth to fall out b/t 6 and 12 • 32 permanent teeth • 3rd molars (wisdom teeth) form b/t 17 and 25; sometimes absent or impacted in jawbone and must be surgically removed Enamel: Dentin: Hardest substance of the body! (Calcium phosphate and calcium carbonate) Calcified connective tissue. Cavities Teeth by shape/function: omnivores • • • • Incisors - chisel-shaped, cutting Canines - fanglike, tearing/piercing Premolars (bicuspids) Molars - broad crowns w/ rounded tips, grinding Organic Compounds: contain C-H bonds Carbohydrates • Carbohydrate: fast energy – made of Carbon, Hydrogen, and Oxygen. 1:2:1 proportion. Sacchar = sugar • Monosaccharides:C6H12O6, glucose,fructose (plants) glactose (milk) • Disaccharides: 2 sacchar’s: Sucrose: table sugar, Lactose: milk • Polysaccharides: Many sacchar’s: starch: Grains, Legumes (beans) Carbohydrate Metabolism • Carbs - preferred fuel to produce ATP from glucose (blood sugar): energy from bonds broken binds phosphate to ADP to make ATP – Carbon atoms leave as CO2 and hydrogen combines w/ oxygen to make water • Question: Why do we breathe out CO2? Carbohydrate Metabolism Homeostasis of blood glucose • Hyperglycemia - high levels; excess stored as glycogen and converted to fats • Hypoglycemia - low levels; liver breaks down stored glycogen and releases glucose to blood Pharynx – Nasopharynx (respiratory) – oropharynx (potesterior to oral cavity) – laryngopharynx (continuous w/ esophagus) • Peristalsis: Alternating contraction of muscles propel food into esophagus Peristalsis Esophagus • Conducts food from pharynx through diaphragm to stomach • 25 cm long Walls of Alimentary Canal • Mucosa - innermost layer; moist membrane • Submucosa - blood vessels, nerve endings, lymph • Muscularis externa - inner circular, outer longitudinal smooth muscle • Serosa - outermost layer Peristalsis Stomach • C-shaped, left side, nearly hidden by liver and diaphragm – cardioesophageal sphincter - food enters from esophagus – Pyloric sphincter - goes to small intestine • 25 cm long • when full, holds 4 L of food • empty - collapses into folds (rugae) • 3rd oblique layer in muscularis externa to move, churn, mix, and pummel food – chemically breakdown proteins Food entering the stomach Stomach: Physiology • Mucosa has gastric pits which lead into gastric glands that secrete gastric juice – chief cells - produce protein-digesting enzymes (pepsionogen) – parietal cells - produce HCl • Chyme is produced • contractions squirt 3 ml of chyme into small intestine • takes 4 hrs for stomach to empty How stomach acid is Made! Organic Compounds: All organic compounds contain Carbon. • Protein: the working molecule – 50 or more Amino Acids make a protein – Food: Beans, meat, nuts Protein – Types of Proteins • Muscle • Enzymes: Control chemical reactions and can be re-used like a key in a lock • Hair • When used for food: amine groups are removed as ammonia which is toxic so it combines w/ CO2 to form urea General Metabolic Function • Albumin - most abundant protein; holds fluids in bloodstream – insufficient albumin causes fluid to go from blood to tissues (edema) – Synthesize amino acids and detoxify ammonia Small Intestine • Major digestive organ • Muscular tube extending from pyloric sphincter to ileocecal valve • average length: 2 m (6 feet) • Hangs from coils suspended by mesentery encircled by and frames it Small Intestine - 3 structures that increase absorption • Microvilli - tiny projections that give fuzzy look (brush border) • Villi - fingerlike projections that give velvety appearance • Circular folds - deep folds of both mucosa and submucosa Small Intestine - 3 subdivisions DJI • Duodenum - curves around head of pancreas • Jejunum - extends from duodenum to ileum • ileum - terminal part that joins large intestine at ileocecal valve Small Intestine: Food Breakdown and Absorption • Takes 3-6 hours • By end, digestion is complete and most absorption has occurred • Microvilli have brush border enzymes to break down sugars and complete protein digestion • Pancreatic enzymes from pancreatic duct and bile from bile duct enter duodenum Food Breakdown and Absorption • Pancreatic juice digests starch, proteins, fats, and nucleic acids; contains bicarbonate to neutralize chyme • When chyme enters, it stimulates hormones secretin and cholecystokinin to release bile Food Breakdown and Absorption • Bile is necessary for absorption of fats and fatsoluble vitamins K,D,A • At end, all that remains is water, indigestible food and bacteria which enters large intestine • Food propulsion - peristalsis Organic Compounds: C-H bonds • Lipids: long term energy, very few oxygen atoms – Cholesterol: LDL & HDL • (HDL is heart healthy) – Saturated fats: All C bonded to H. Lard, and butter. Don’t eat Transfats (they have been hydrogenated) – Unsaturated fats: C is double bonded to itself. Oil. Currently considered healthier. Trans fats Lipids Lipids • Neutral fats: saturated in animal products, unsaturated in seeds, nuts, vegetable oils • Cholesterol - egg yolk, meats, and milk • Phospholipids: the plasma membrane • PS What organelle in the cell makes lipids? • Answer: Smooth ER Lipid Metabolism • Liver - make ATP, synthesize lipoproteins, clotting protein and cholesterol for membranes or steroid hormones • Form myelin sheaths and fatty cushions around organs • Liver makes Bile ships it to the Gallbladder. Bile emulsifies fats. The bilirubin in bile turns feces brown. Lipid Metabolism • To be used for ATP synthesis, it must be broken down into acetic acid; when not enough glucose, acetone accumulates in blood making it acidic (acidosis/ketosis) – no carb diets, diabetes, and starvation – People smell of keytones when they get diabetes, why? Central Role of Liver • Manufactures bile, detoxifies drugs and alcohol, degrades hormones, makes substances vital to body, metabolism – This process uses many enzymes: Speed up chemical reactions and reduce activation energy. – Most enzymes are Proteins some are RNA • We have more liver tissue than needed, so if damaged, it regenerates rapidly and easily General Metabolic Functions • Liver maintains blood glucose levels • After high carb meal, glucose is removed from blood and converted to glycogen (glycogenesis) and stored in liver General Metabolic Functions • As body cells remove glucose from blood, liver breaks down stored glycogen (glycogenolysis) • gluconeogenesis - make glucose from fat and protein Organic Compounds: All organic compounds contain Carbon. • Nucleic Acids: pg. 37 DNA and RNA –Made of nucleotides: Sugar, Phosphate, and X • ATP: energy cells run on. DNA What is a calorie? • Energy value measured in kilocalories (kcal) or Calories (C Vitamins: the last of the Organics • Organic nutrients, small amounts • No one food contains all required vitamins, need balanced diet • Most function as coenzymes: act w/ enzymes for task Vitamins: the last of the Organics • Organic nutrients, small amounts • No one food contains all required vitamins, need balanced diet • Most function as coenzymes: act w/ enzymes for task Minerals • Requires adequate supplies of 7: Ca, P, K, S, Na, Cl, and Mg; trace amounts of others • Fats/sugars have none, cereals and grains poor sources • In veggies, legumes, milk, meats Basal Metabolic Rate • Carbs & proteins yield 4 kcal/g, fats yield 9 kcal/g • Basal metabolic rate (BMR) - amount of heat produced by body per unit time at rest; energy supply for breathing, heartbeat, and kidney function Basal Metabolic Rate • Avg. adult has BMR of 60-72 kcal/hr; influenced by surface area, gender, age, and thyroxin production (more thyroxin produced by thyroid gland, higher O2 consumption and ATP use and metabolic rate) Basal Metabolic Rate • Hyperthyroidism - excessive rate, lose weight despite increased hunger and food intake, bones and muscles weaken • Hypothyroidism - slow rate, obesity, diminished thought process Total Metabolic Rate • When active, more glucose must be oxidized to provide more energy for activities • Total Metabolic Rate (TMR) - total amount of kcal body must consume to fuel all activities Total Metabolic Rate • When total calories = TMR, weight is constant • If eat more, excess calories appear as fat deposits • If active w/o enough food, break down fat reserves and even tissues to satisfy TMR Large Intestine • Larger in diameter, shorter in length (1.5 m) • Extends from ileocecal valve to anus • Dries out indigestible food by absorbing water, eliminates residue as feces Large Intestine Subdivisions • Cecum - saclike, first part • Appendix - wormlike structure hanging from cecum; ideal bacteria location - appendicitis • Colon - ascending, transverse, descending, and sigmoid • Rectum • Anal canal - ends in anus which opens to exterior; has external voluntary sphincter and internal involuntary sphincter Large Intestine • Lots of goblet cells to produce mucus to act as lubricant to ease passage of feces Large Intestine: Food Breakdown and Absorption • Residue is there 12-24 hours • Bacteria metabolize nutrients and release gases (methane, hydrogen sulfide) • 500 ml of gas produced each day Gallbladder • Small, thin-walled green sac in the inferior surface of liver • When digestion is not occurring, bile is stored and concentrated by removal of water – bile stored too long, it crystallizes forming gallstones – Yellow-green, watery solution of bile salts, bile pigments (bilirubin), cholesterol, phospholipids, and electrolytes – bile salts emulsify fats to provide more surface area Digestive System Review Disease: Jaundice • Bile pigments enter bloodstream • Can result from hepatitis (inflammation of liver from viral infection of contaminated water or blood transfusion) or cirrhosis (severe damage from drinking excess alcoholic beverages) Nutrition and Metabolism • Most foods used as metabolic fuels (transformed into ATP); some nutrients build cellular molecules • Energy value measured in kilocalories (kcal) or Calories (C) Nutrition • Nutrient - substance in food used to promote normal growth, maintenance and repair • Carbohydrates, lipids, proteins - bulk of food; vitamins, and minerals in minute amounts . • Water - 60% of volume of food • Most foods are combination of nutrients from 5 food groups (grains, fruits, vegetables, meats, and milk products) Obesity Rates in the US. Dietary Sources of Major Nutrients Carbohydrates • From plants except lactose and glycogen in meats • sugar - fruit, sugar cane, milk • starch - grains, legumes, root vegetables • cellulose - most vegetables Food Breakdown and Absorption • Absorption limited to vitamins, some ions, and most of remaining water • Feces - solid product delivered to rectum; undigested food residue, mucus, bacteria, and some water Large Intestine: Propulsion and Defecation • Peristalsis and mass movements (long, slowmoving, powerful contractile waves that move over colon 3-4 times daily to push contents toward rectum) – occur after eating; fiber increases strength of contraction Propulsion and Defecation • When feces in rectum, defecation reflex causes rectum to contract and anal sphincters to relax • Diarrhea - food rushes through before water is absorbed, can result in dehydration and electrolyte imbalance Propulsion and Defecation • Constipation - food residue remains too long and too much water is absorbed; due to lack of fiber, poor bowel habits, or laxative abuse Poll Everywhere Poll Everywhere Poll Everywhere A constipated body Other Accessory Digestive Organs – Pancreas • Soft, pink, triangular gland extending from spleen to duodenum • produces enzymes that break down food and neutralize acidic chyme from stomach, produces hormones insulin, glucagon Liver • Liver - largest gland in body; under diaphragm on right – 4 lobes – produces bile which leaves liver through common hepatic duct Developmental Aspects • 5th week - alimentary canal forms • cleft palate/lip - child unable to suck properly • tracheoesophageal fistula - connection b/t esophagus and trachea - causes drool, cyanosis during feedings Development Aspect • Cystic fibrosis - blockage of pancreatic ducts so that fats and fat-soluble vitamins are not digested or absorbed • PKU - inability of tissue cells to use phenylalanine (amino acid) causes brain damage Developmental Aspects • Newborn: rooting & sucking reflex • Appetite decreases in elementary age and increases in adolescence • Gastroenteritis - inflammation of GI tract due to contaminated food • Appendicitis - common in teens Developmental Aspects • Middle age - metabolic rate decreases 5-8% every 10 yrs – ulcers & gallbladder problems • Old age - activity of GI tract declines, taste and smell decrease – cancer of stomach and colon