What is a Cell? - Cloudfront.net

Wednesday 10/23
-Get notebooks
SMART START – on page 24
Draw and fill in diagrams using word bank
Word Bank:
Cells
Organs
Organ Systems
Organism
Tissues
Let’s define those words! (pg. 22)
1. Molecule
2. Organelles
3. Cells
4. Tissues
5. Organs
6. Organ Systems
7. Organisms
A particle made up of atoms.
Structures that carry out life functions in cells
Basic unit of life
Groups of cells with the same function
A collection of different tissues that carry out life functions
Several organs working together.
A living thing.
Building Bodies Unit
Cells – Cell Types
Today’s Objectives
Compare and contrast eukaryotic and prokaryotic cells.
How we are going to do this?
Get into pairs
One person reads about prokaryotic cells the other person reads about eukaryotic cells.
As you read fill in the appropriate column on your t-chart
Get back together with your partner and teach her/him what you learned.
Listen to your partner’s lesson and fill out the other side of your t-chart.
Article & t-chart directions:
Read and discuss the short article with your small group.
Please don’t write on it!
As you read record the following information in the t-chart
Definition
Nucleus?
Size of the cell
Location of the DNA
Examples
Thursday 10/24
Get your notebook.
Take out the T-Chart from yesterday
Glue it to page 25
Fold it in half first
If you owe me anything and MANY of you do you need to stay for enrichment today, tomorrow, and/or Monday!
Comparing & Contrasting
Eukaryotic Prokaryotic
Tuesday 11/5
Take out your interim so we can finish going over it.
Thank you.
Wednesday 11/6
Get your notebook.
Please update your table of contents
◦ 11. Cell Types: Eukaryotic v. Prokaryotic
◦ 12. Cell Theory & Cell Parts
◦ 13. Animal Cells v. Plants Cells
On page 26 Record today’s objectives:
State the Cell Theory
Explain how organelles function to maintain homeostasis
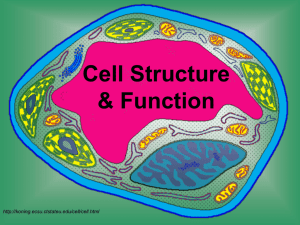
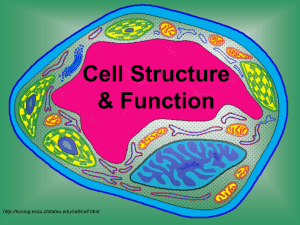
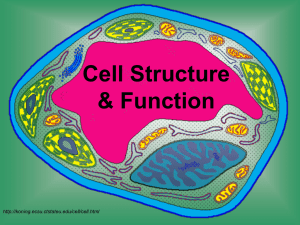
Cell Structure
& Function
http://koning.ecsu.ctstateu.edu/cell/cell.html
Cell Theory
All living things are made up of cells.
Cells are the smallest working units of all living things.
All cells come from preexisting cells through cell division.
What is a Cell?
A cell is the smallest unit that is capable of performing life functions.
What are the two types of cells?
Plant Cells
◦ Rectangular in shape
◦ Contain chloroplasts, cell wall, large vacuole
◦ Found only in plants
◦ Carry out photosynthesis
Animal Cells
◦ Rounded in shape
◦ Do not contain chloroplasts, cell wall, large vacuole
◦ Found only in animals
Examples of Cells
Amoeba proteus
Plant
Bacteria
Nerve Cell
Red Blood Cell
Cell Parts
Organelles
Surrounding the Cell…
(2 Parts)
Cell Membrane
Outer membrane of cell that controls movement in and out of the cell
Double layer- made of lipids (and protein) http://library.thinkquest.org/12413/structures.html
Cell Wall
Most commonly found in plant cells & bacteria
Supports & protects cells http://library.thinkquest.org/12413/structures.html
Inside the Cell…
(6 parts)
Nucleus
Directs cell activities
◦ Regulation!
Holds DNA
Separated from cytoplasm by nuclear membrane
Cytoplasm
Gel-like mixture
Surrounded by cell membrane
Contains dissolved food and oxygen
Ribosomes
Make proteins (Synthesis!)
Found on Rough ER & floating throughout the cell
◦ Cells contain thousands
Mitochondria
The “Powerhouse”
Produces energy through chemical reactions – breaking down carbohydrates
◦ This is Respiration! http://library.thinkquest.org/12413/structures.html
Vacuoles
Sacs for the storage of food water, and waste removal
Contains water solution
◦ Help plants maintain shape http://library.thinkquest.org/12413/structures.html
Chloroplast
Usually found in plant cells
Contains green chlorophyll
Where photosynthesis takes place http://library.thinkquest.org/12413/structures.html
Endoplasmic Reticulum
Network of membranes found throughout the cell
Assists with the packing and manufacturing of proteins
Golgi Apparatus
Gathers simple molecules and combines them together to make more complex molecules.
Helps the
Endoplasmic
Reticulum manufacture and package proteins.
Fundamentals Do Now 1/4/16