What is Economics? Ch. 1
advertisement

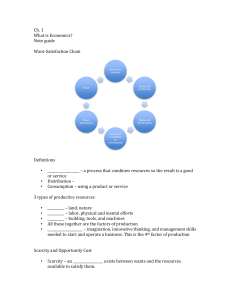
What is Economics? Ch. 1 MASON EDUCATION Table of Contents 1. Bell Journal 2. Lecture Notes 3. Factors of Production: 4. HW: Sect 1-3 5. Decision Making Grids 6. Opportunity Cost Handout Bell Journal Ch. 1 What is Economics Sec.1 Scarcity and the Factors of Production Pg. 3 Sect 1 Objectives: SWBAT 1. Explain why scarcity and choice are basic problems of economics 2. Identify land, labor and capital as the three factors of production, and identify the two types of capital 3. Explain the role of entrepreneurs 4. Explain why economist say all resources are scarce 1:Scarcity and the Factors of Production: Hook https://www.youtube.com/watch? v=6o6Hh6tQj2w 1:Scarcity and the Factors of Production Why scarcity? The world has billions of greedy humans with unlimited needs and wants Why Economics? People, cities, governments and the world must chose how to satisfy their needs and wants 1:Scarcity and the Factors of Production Their will always be scarcity. Goods and services are scarce because they are made from resources that are scarce. Scarcity v. shortage Scarcity is nature Shortage is usually based on choice over money. Shortage can be long term or short term. Ex. Strikes, wars, droughts 1:Scarcity and the Factors of Production The factors of production are used to create goods and services. Factors of Production: Land Labor Capital Physical Human 1:Scarcity and the Factors of Production Entrepreneurs bring together the factors of production to create a good or service. You can be a entrepreneur! Scarce Resources example My Fries: Pg. 6 Identify the factors of production in creating French fries Bell Journal What sacrifices have you made for your future success? 2:Opportunity Cost Sect 2 Objectives: SWBAT Describe why every decision involves trade-offs. Explain the concept of opportunity cost. Explain how people make decisions by thinking @ the margin 2:Opportunity Cost Choice you make has a trade off or alternatives. You give up those trade offs when you make a decision over another. Individuals, businesses and countries all have trade offs they give up over another when making economic decisions Guns or Butter? 2:Opportunity Cost Opportunity Cost is the most attractive alternative you chose to give up for your chosen option Decision making grids can help provide a visual element to lay out your options to make the best economic choice. Pg. 10 Karen’s Grid 2:Opportunity Cost Thinking at the margin is a great way to get a deeper understanding on your next move. Making decisions based on time or money can require adding one unit or subtracting one unit, this is thinking @ the margin 2:Opportunity Cost Comparing opportunity cost and benefits at the margin help people, business and governments make important economic decisions. Also called Cost/benefit analysis Sacrifice Once v. Gain opportunity cost outweighs benefit no more units should be added Gary Becker Social Connection: Love, Marriage and Economics Answer questions below in 2-3 sentences 1. Do you know anyone that makes relationship decisions based on economics 2. How do you think you might use economics to find your future husband/wife? 2:Opportunity Cost Create a “Decision Making Grid” & “Decision Making at the Margin” Chose a decision you have to make or have already made. Follow the examples on pg. 10-11 Bell Journal 1.List the trade offs and opportunity cost for taking a date to the prom? Hook https://www.youtube.com/watch? v=tW4G5IPpzFY What information does a PPC provide? INTRO 3:Production Possibilities Curves Interpret a production possibilities curve Demonstrate how production possibilities curves show efficiency, growth, and cost Understand that a country’s production possibilities depend on its available resources and technology 3:Production Possibilities Curves Economist often use graphs to analyze the choices and tradeoffs that people make. Graphs help us see how one value relates to another value A production possibilities curve shows alternative ways to use an economy’s productive resources. 3:Production Possibilities Curves Drawing a Production Possibilities Curve Chose two goods or services to examine Place one good or service on the vertical axis & one good or service on the horizontal axis. 3:Production Possibilities Curves Points are plotted along the graph to show the comparison amount of goods or services chosen to produce. The line that connects the plotted points represents the Production Possibilities Frontier showing combination production trade-off 3:Production Possibilities Curves Production Possibilities Curves provide information on: Efficiency Maximum production Underutilization Growth Cost 3:Production Possibilities Curves Resources and technology Economist must assess each country’s level of technological know-how, A country’s production possibilities depend on both technological level and the resources it has available. Outline your Graph Create a graph outline Identify and label the different parts of a production possibilities curve 1. Vertical and horizontal Axis 2. Good or services 3. PP Frontier 4. 3 Plotted point