12.4 Gene Regulation and Mutation
advertisement

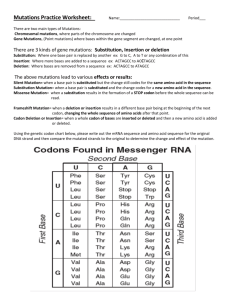
25.4 Gene Mutation Gene Mutations Mutation: a permanent genetic change Gene Mutation: a change in the sequence of bases within a gene Ex.: THE CAT ATE THE RAT Frameshift Mutations: changes the length of the codon sequence through nucleotide addition or deletion • Occur most frequently • can result in a non-functional protein Addition: THE ECA TAT ETH ERA T Deletion: THC ATA ET HER AT Point Mutations: a change in a single nucleotide, changing the codon Substitution: point mutations that occurs when one base is exchanged for another Silent Mutation: when the substitution has no noticeable effect (still codes for the same amino acid) Ex.: UAU become UAC Types of Mutations Nonsense Mutation: substitution changes amino acid codon to stop codon • Ends too early, may be unable to function • Ex.: UAC changes to UAG (from tyrosine to stop) Missense Mutation: substitution changes amino acids, resulting in wrong sequence • May or may not affect protein function/shape • Ex.:: if UAC canges to CAC, histidine incorporated into protein instead of tyrosine Rearrangements can also occur – genes can be moved to different locations Ex.: ATC GCC ACT GCC Tandem Repeats: copies of repeated codons Ex.: ATC GCC ATC ATC GCC Protein Folding and Stability Sickle Cell Disease • Codon for glutamic acid (GAA) changed to valine (GUA) • Changes hemoglobin’s structure ▫ Glutamic acid is polar, valine is nonpolar Causes of Mutations 1) Spontaneity – especially with point mutations 2) Mutagens: substances that cause mutations (ex. radiation such xrays/UV light and organic chemicals like pesticides) ▫ Can cause bases to mispair, change chemical structure of bases, substitute for nucleotides ▫ Xrays and gamma rays: electrons absorb energy, becoming free radicals Body-Cell VS. Sex-Cell Mutation • Somatic cell mutations aren’t passed to next generation ▫ Occur in body cells • Neutral Mutations: doesn’t affect organism (ie. codes for same a.a., occurred in exon, etc.) • Mutations in sex-cells (germ-line cells) are passed onto offspring ▫ May not affect parent, but could impact offspring ▫ When mutation results in abnormal protein in sex cell, organism is impacted ▫ Organism not impacted when abnormal protein in an isolated body cell