Cell Theory Resources
advertisement

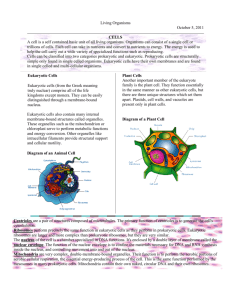
Cell Theory Resources The following brief write up on the cell and cell theory is from: http://sln.fi.edu/qa97/biology/biopoint3.html The Cell The cell is life's most basic unit of structure and function. Like a computer, it is responsible for storing an enormous amount of information in a tiny space. It is the center of life and is responsible for protecting, organizing, and coordinating an array of chemical reactions necessary for life. In 1838, Matthias Schleiden and Theodor Schwann proposed the first two beliefs of the cell theory. 1. All organisms are composed of one or more cells. 2. The smallest living unit of structure and function of all organisms is the cell. More than ten years later, Rudolf Virchow, proposed the third idea or belief of the cell theory. 3. All cells arise from preexisting cells. All cells are either prokaryotic or eukaryotic. Prokaryotic cells are bacteria and eukaryotic cells make up all other organisms. They are distinguishable by the types of organelles or internal structures they contain. Eukaryotic cells are larger and more complex. The nucleus stores the genetic material (DNA). Prokaryotes are smaller and do not have a true nucleus. The genetic material floats freely in the cytoplasm of the cell. A plasma membrane surrounds both eukaryotic and prokaryotic cells. Prokaryotes are thought to be the most primitive type of cell. Cells come in a variety of shapes and sizes, ranging from a tiny bacterial cell to a large nerve cell extending between two body parts. Some organisms, such as bacteria and protists, consist of only a single cell. In multicellular organisms, some cells are "generalists" and others are "specialists". The "specialists" work together to perform a job and make up a particular type of tissue. Tissues work together and form organs. Finally, organs work together performing a job and make up an organ system. An example of an organ system is your digestive system.Single-celled organisms are "generalists" and must perform all the functions performed by many "specialists". A cell is like a miniature body containing tiny organs, called organelles. The nucleus is an organelle that acts as the command center for the cell. The mitochondria is like a power plant providing the cell with energy. Still other organelles manufacture proteins necessary for the cell to perform certain chemical reactions in a timely fashion or replace old or damaged tissue. Cell biologists continue to study the workings of cells. Studies of cell organelles have led to the causes of some diseases. For example, Tay-Sachs disease which damages the nervous system is due to defective lysosomes. Basic research on the function of cells has led to a variety of improvements in health care. For example, an understanding of hormone release, binding, and action has enabled pharmacologists to design a medication for high blood pressure. New therapies for the treatment of cancer and other illnesses are often discovered through cell testing. As cell studies continue, a deeper understanding of the cell's activities and how to apply the knowledge will also evolve. This abbreviated definition of cell theory is from: http://scienceeducation.wikia.com/wiki/Mitosis_and_Cell_Theory_Lesson All organisms are made up of one or more cells. Cells are the fundamental functional and structural unit of life. All cells come from pre-existing cells. www.worldofteaching.com/powerpoints/.../The%20Cell%20Theory.ppt The last 4 slides obtain to cell theory. There is lots of color, but few details and no worksheet/activity.