Adolescent and Emerging Adult Developmental Domains
advertisement
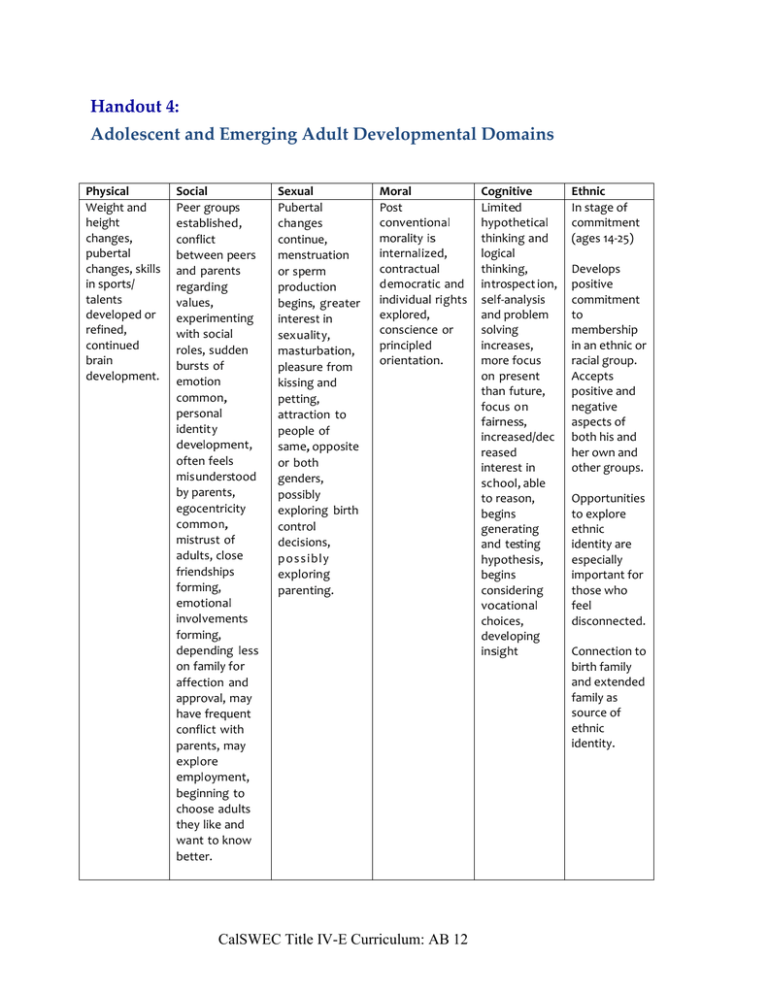
Handout 4: Adolescent and Emerging Adult Developmental Domains Physical Weight and height changes, pubertal changes, skills in sports/ talents developed or refined, continued brain development. Social Peer groups established, conflict between peers and parents regarding values, experimenting with social roles, sudden bursts of emotion common, personal identity development, often feels misunderstood by parents, egocentricity common, mistrust of adults, close friendships forming, emotional involvements forming, depending less on family for affection and approval, may have frequent conflict with parents, may explore employment, beginning to choose adults they like and want to know better. Sexual Pubertal changes continue, menstruation or sperm production begins, greater interest in sexuality, masturbation, pleasure from kissing and petting, attraction to people of same, opposite or both genders, possibly exploring birth control decisions, possibly exploring parenting. Moral Post conventional morality is internalized, contractual democratic and individual rights explored, conscience or principled orientation. CalSWEC Title IV-E Curriculum: AB 12 Cognitive Limited hypothetical thinking and logical thinking, introspect ion, self-analysis and problem solving increases, more focus on present than future, focus on fairness, increased/dec reased interest in school, able to reason, begins generating and testing hypothesis, begins considering vocational choices, developing insight Ethnic In stage of commitment (ages 14-25) Develops positive commitment to membership in an ethnic or racial group. Accepts positive and negative aspects of both his and her own and other groups. Opportunities to explore ethnic identity are especially important for those who feel disconnected. Connection to birth family and extended family as source of ethnic identity.





















