Heat
advertisement

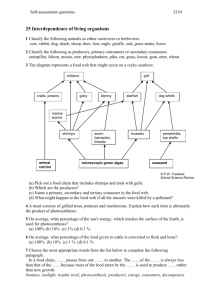
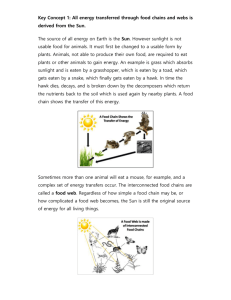
Topic: Ecology Aim: Describe the flow of energy in an ecosystem. Do Now: Evolution Review #4 HW: Evolution CL due tomorrow! 1. Which species have become extinct? Why? They had an unfavorable adaptation. There was no variation in the species and they could not adapt to a major environmental change. 2. Which two species are most closely related? 1. D and E 2. B and C 3. H and I 4. A and I • Where an organism Habitat lives • Organism’s “address” Niche • The role of a species in the environment • Ex: how, when, or way they obtain nutrients, its reproductive behavior Niches of a sunflower growing in the backyard - Absorb light, water and minerals - Provide shelter and food for other organisms (e.g. bees, ants, etc.) - Release oxygen into the atmosphere 2 organisms • Competition occupying the same niche Identify the type of organism described. 1. Feed on producers. 2. Feed on organisms that have already been killed. 3. Feed on both plants and animals. 4. Break down the remains of dead organisms and return some nutrients back to the soil. 5. Autotrophs 6. Meat eaters 7. Hunt and kill prey. 1. Identify the main source of energy in an ecosystem SUNLIGHT 2. What occurs to the energy in an ecosystem? - Energy is not recycled. - Energy is converted into different forms. 3. Describe • How matter and energy what a food chain shows. passes from one organism to another 4. Identify • Producers the organisms that make up the first step of a food chain. 5. Identify • Herbivores the • Primary Consumers organisms that make up the 2nd step of a food chain. 6. Identify • the organisms • that make up the 3rd step of a food chain. Carnivores and omnivores Secondary or tertiary consumer 7. Explain • Amount of available what energy is reduced as you happens to move though each level. the amount of energy as it is passed through a food chain. . Herbivore Carnivore Carnivore Grass Grasshopper Sparrows Hawks producers Primary consumer Secondary consumer Teritiary consumer Decrease in energy (lost in the form of heat) 8. Observe Figure 15 on p.727. . 8. Observe Figure 15 on p.727. Heat Grass Heat Marmots Soil Soil Heat Grizzly bear Soil Heat Grass Marmots Soil Heat Heat Grizzly bear Soil Soil a. Identify the producers. Grass b. Identify the herbivore. Marmots (primary consumer) Heat Grass Marmots Soil Heat Heat Grizzly bear Soil c. Identify the carnivore. Grizzly bear (secondary consumer) Soil Heat Grass Marmots Soil Heat Heat Soil Grizzly bear d. Infer what might happen if grizzly bears disappear from the food chain. The marmot population would increase. The grass population would decrease. Soil Heat Grass Heat Marmots Soil Soil Heat Grizzly bear Soil e. What do the red arrows represent? Heat (energy) released f. What do the blue arrows represent? Matter that makes up molecules of energy 9. Describe • Shows all possible a food feeding relationships in a web. community 10. Observe Figure 16 on page 728. a. Identify the producers. Berries and flowers, grasses, seeds b. Identify 2 herbivores. (Primary consumers) Deer, grouse, insects, chipmunk, marmot c. Identify 2 carnivores. Bear (Secondary consumer) (Also primary consumer) Decomposers 11. • Shows amount of energy Describe available at each feeding what an level in an ecosystem energy Pyramid shows. 12. Where • On the bottom is the 1st feeding level in an energy pyramid found 13. Explain • It contains the most why the energy and the largest # 1st level of organisms. is the largest level. 14. Explain • The transfer of energy is what less efficient occurs (Each level becomes to the transfer smaller) of energy as you move up the pyramid. Topic: Ecology Aim: Describe the flow of energy in an ecosystem. Do Now: Food Chain Reading Notes #’s 19-24 HW:3rd Marking Period Quarterly due Monday April 13th. Evolution Exam Tuesday, April 14th Food Chain Lab due Wednesday, April 15th 15. Identify the producers. Grass 16. Identify the 3 primary consumers. Mice Grasshoppers Rabbits 17. Identify 2 secondary consumers. Foxes Grasshoppers Sparrows Frogs Hawks Snakes 18. Identify a tertiary consumer. Hawks, Snakes 19. Identify the producers. Grasses 20. Identify primary consumers. Insects 21. Identify secondary consumers. Chipmunks 22. Identify a tertiary consumer. Grizzly bears Pyramid of energy Tertiary consumers Secondary consumers Energy decreases Primary consumers Producers Carnivores Herbivores Producers Let’s summarize… 1.Identify the main source of energy in an ecosystem. 2.Who is the first organism found in every food chain? Give an example. 3.Identify the sequence of organisms in a food chain. 4.Describe what happens to the energy that is passed through a food chain or up an energy pyramid. Explain why this happens. Which statement best describes one of the levels of this pyramid? (1.) The organisms in level B obtain food directly from level A. (2.) Level D contains the greatest number of heterotrophs in the pyramid. (3.) level C contains the largest group of consumers in the pyramid. (4.) Level A contains the largest producers in the pyramid. Which statement is best supported by the information shown in the pyramid? (1.) Chipmunks and insects can occupy the same niche. (2.) As the number of bears in this community increases, the number of chipmunks will increase. (3.) Insects are classified as omnivores in alpine meadow communities. (4.) Biomass decreases as energy is transferred from one level to another. Which organisms would most likely have a predator-prey relationship? (1.) tapeworm and dog (2.) barnacle and whale (3.) hawk and mouse (4.) rabbit and grass