Volume is the amount of space an object takes up. The basic unit of

MATTER – Anything that has MASS and VOLUME .
MASS – The amount of matter in an object.
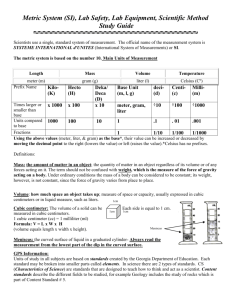
Basic Unit (SI unit) – kilogram , kg.
Measuring Tool - Balance, Triple-Beam or Electronic
Gizmo
Mass is commonly measured in grams or milligrams
WEIGHT – The gravitational force (pull) on an object.
The weight of an object can change , but the mass remains the same.
(Ex: On the moon your weight is 1/6 th of what it is on Earth)
Basic Unit (SI Unit) – Newtons, N
Measuring Tool – Spring Scale
VOLUME
– The amount of space an object takes up.
Basic Unit (SI Unit) for Liquids – Liter, l.
Measurement Tool - Graduated Cylinder
The curved surface of a liquid is called the meniscus.
Read at the BOTTOM of “the smile”.
Volume can be measured in milliliters (ml) or cubic centimeters (cc)
VOLUME – The amount of space an object takes up.
Basic Unit (SI Unit) for Solids – Cubic Meter, m 3 .
--To determine volume of a rectangular object:
Length x Width x Heighth (LxWxH)
(Can also be expressed in cubic centimeters, cm 3 )
--To determine volume of an irregular shaped object:
Displacement Method (the volume of water an object displaces)
The object displaces 3 ml of water .
Since 1 ml = 1 cm 3 , the object has a volume of 3 cm 3
LENGTH/DISTANCE – The measurement between two points.
Basic Unit (SI Unit) – Meter, m
Measurement Tool - Meter Stick, Metric Ruler, Metric Tape Measure
Length can be measured in centimeters and millimeters
TEMPERATURE – The average kinetic energy of an object.
Basic Unit (SI Unit) – Celsius, o C.
Measurement Tool Thermometer
Freshwater at sea level: Freezes @ 0 o C
Boils @ 100 o
C
.
0 K (zero Kelvin) is called absolute zero. Used primarily in research
No degree symbol is used. Absolute zero is when there is no kinetic energy (atoms stop moving) and has never been achieved in a lab.
Dimensional Analysis
– Converting from English to Metrics, and vice versa.
-P. 708 in Glencoe Introduction To Physical Science textbook
Example: 1) 6 miles equals how many kilometers?
6 miles x 1 km = 9.68 km
0.62 mi
2) 1 kg equals how many ounces?
or
1 kg x 1 # = 1 kg
2.2 # 16 oz 35.2 oz
16 oz x 2.2 # = 35.2 oz
1 # 1 kg 1 kg
SCIENTIFIC NOTATION
--Because many numbers used by scientists are so large, they use scientific notation to make working with these numbers easier.
-- P. 709 in Glencoe Introduction to Physical Science textbook
Example:
1,000,000 = 1.0 x 10 6
0.000055 = 5.5 x 10 -5