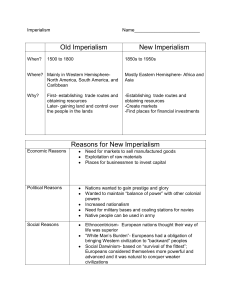
Imperialism
advertisement

The Height of Imperialism 1. Colonial Rule in Southeast Asia -fueled by a need for new markets and natural resources, large nations adopted the views of Social Darwinism in order to justify their behavior Imperialism: the expansion of a nation’s power over other lands (imposed economy and religion) -Colonization (direct and indirect control) -racism and religion were major conflicts during imperialism in the 19th century (A) Colonial Takeover -Southeast Asia during the period of 1800-1900 had been claimed by European Nations looking for opportunities and natural resources (1) Great Britain (India) -Singapore (Raffles) -Burma (2) France -Missionaries and Vietnam (Influence of France and its impact on Vietnam) -French Protectorate and formation of French Indochina (3) The United States -William McKinley and the concept of moral obligation (Little Brown Friends) -Takeover of the Philippines (George Dewey and moral idealism) -Emilio Aguinaldo (4) Colonial Regimes -Direct and Indirect colonial control -positive and negative effects of colonization -resistance to colonial rule 2. Empire Building in Africa -Europeans tried to take all of the natural resources in Africa; by 1900 they found resistance due to strong Nationalism (A) West Africa (peanuts, timber, hides, palm oil) -slave trade is now dead, West Africa had a strong resentment towards European presence (B) Gold Coast (C) North Africa (Egypt Independent) (1) Muhammad Ali (2) Suez Canal (Struggles in ownership) (3) British in the Sudan (a) Muhammad Ahmad (“Mahdi”) (b) Khartoum (Death of Gordon) (D)Central Africa (1) David Livingstone and Henry Stanley (a) Colonization of the Congo River Basin (b) Role of King Leopold of Belgium (E) South Africa (1) Boers (Calvinist) -S. Africa taken by the British during the Napoleonic Wars (a) Issue of slavery (b) Great Trek (1) Zulus and establishment of Natal (2) Orange Free State and Transvaal (2) Boer War (a) Cecil Rhodes (b) Jameson Raid (c) Armistice (d) Apartheid 3. British Rule in India (A) Sepoy Mutiny (1) British East India Trade Company (a) Sepoy (2) Sepoy Rebellion (a) Mistreatment and animal fat (b) Kanpur © Viceroy (B) British Colonial Rule -English education and language were pushed upon the Indian elite (1) Zamindars (2) Indian Nationalists (a) Indian National Congress (b) Mohandas Gandhi 4. Nation Building in Latin America (A) Nationalist Revolts (1) Creoles and Peninsulares (2) Miguel Hidalgo in Mexico (a)Pushed NA and Mestizos towards freedom from Spain (3) Agustin de Iturbide -Mexican independence in 1821 (4) Simon Bolivar (a) Gran Colombia (b) Jose San Martin (Battle of Chacabuco) (c) Unification in Lima (5) Introduction of Monroe Doctrine (B) Nation Building -as Nations became independent in S. America, countries went to war over borders, a lack of natural resources and tough conditions led to new dependence on imported goods (1) Antonio Lopez Santa Anna (2) Benito Juarez (3) Role of Americans (Dollar Diplomacy) (a) Manipulation of countries in order to extract cash crops (bananas, sugar) (b) Spanish American War (1) Roosevelt and the “Big Bully” approach